Intro
Learn effective 2nd degree burn treatment methods, including wound care, pain management, and scar prevention, to promote healing and minimize damage from partial-thickness burns and blistering injuries.
Burns are a common type of injury that can occur due to various reasons such as scalds, flames, or contact with hot surfaces. They are classified into different degrees based on their severity, with 2nd-degree burns being more severe than 1st-degree burns but less severe than 3rd-degree burns. 2nd-degree burns, also known as partial-thickness burns, affect both the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and the underlying layer (dermis). They can be further divided into two categories: superficial and deep. Superficial 2nd-degree burns affect the upper part of the dermis, while deep 2nd-degree burns extend into the deeper part of the dermis.
The treatment of 2nd-degree burns is crucial to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. If left untreated, 2nd-degree burns can lead to serious complications such as infection, sepsis, and even death. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know has suffered a 2nd-degree burn. In this article, we will discuss the treatment options for 2nd-degree burns, including home remedies, medical treatments, and wound care.
2nd-degree burns can be identified by their characteristic signs and symptoms, which include redness, swelling, blisters, and pain. The burned area may appear white or splotchy, and the skin may be sensitive to touch. In some cases, 2nd-degree burns can also cause fever, chills, and nausea. If you suspect that you or someone you know has suffered a 2nd-degree burn, it is essential to act quickly to provide proper treatment and prevent further complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
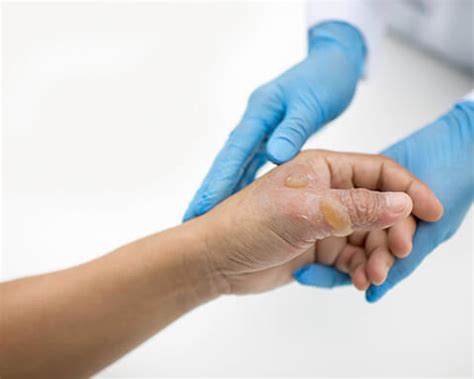
Prevention
Preventing 2nd-degree burns is crucial to avoid the pain, discomfort, and potential complications associated with these injuries. Some simple prevention measures include being cautious when handling hot objects, keeping children away from open flames, and wearing protective clothing when working with electrical appliances. Additionally, installing smoke alarms and keeping a fire extinguisher in the home can help prevent fires and reduce the risk of burns.Symptoms and Diagnosis
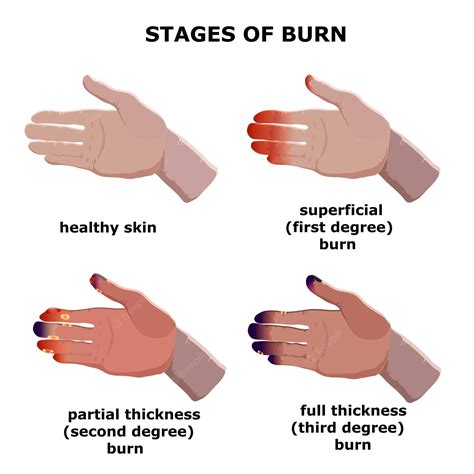
Treatment Options
The treatment of 2nd-degree burns depends on the severity of the injury. For minor 2nd-degree burns, home remedies such as cool compresses, topical creams, and over-the-counter pain medications may be sufficient. However, for more severe 2nd-degree burns, medical attention is necessary to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. Medical treatments for 2nd-degree burns may include antibiotics, pain medications, and wound dressings. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged skin and promote healing.Home Remedies
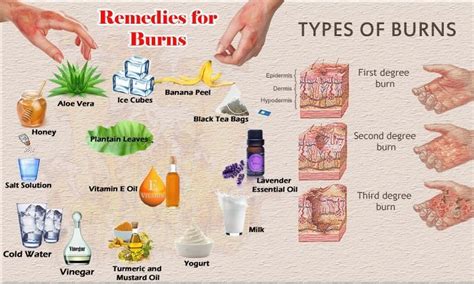
Medical Treatments
For more severe 2nd-degree burns, medical attention is necessary to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. Medical treatments for 2nd-degree burns may include: * Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection and promote healing. * Pain medications: Pain medications, such as morphine or codeine, may be prescribed to reduce pain and discomfort. * Wound dressings: Wound dressings, such as bandages or gauze, may be applied to protect the burned area and promote healing. * Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged skin and promote healing.Wound Care

Complications
If left untreated, 2nd-degree burns can lead to serious complications such as infection, sepsis, and even death. Some common complications of 2nd-degree burns include: * Infection: Bacteria can infect the burned area, leading to serious complications. * Sepsis: If left untreated, infection can spread to the bloodstream, leading to sepsis. * Scarring: 2nd-degree burns can cause permanent scarring, which can be disfiguring and affect self-esteem. * Contractures: 2nd-degree burns can cause contractures, which can limit mobility and affect daily activities.Recovery and Rehabilitation
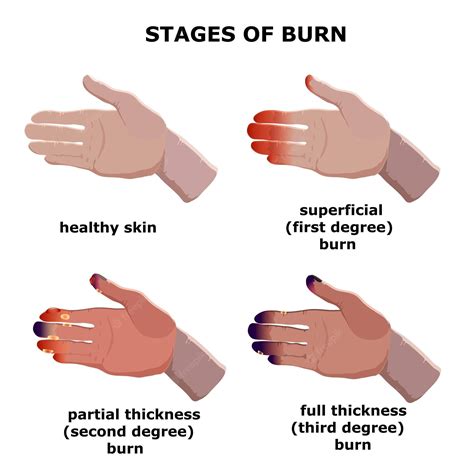
Preventing Future Burns
Preventing future burns is crucial to avoid the pain, discomfort, and potential complications associated with these injuries. Some simple prevention measures include: * Being cautious when handling hot objects * Keeping children away from open flames * Wearing protective clothing when working with electrical appliances * Installing smoke alarms and keeping a fire extinguisher in the homeWhat are the symptoms of a 2nd-degree burn?
+The symptoms of a 2nd-degree burn include redness, swelling, blisters, and pain. The burned area may appear white or splotchy, and the skin may be sensitive to touch.
How do I treat a 2nd-degree burn at home?
+For minor 2nd-degree burns, home remedies such as cool compresses, topical creams, and over-the-counter pain medications may be sufficient. However, for more severe 2nd-degree burns, medical attention is necessary to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring.
What are the complications of 2nd-degree burns?
+If left untreated, 2nd-degree burns can lead to serious complications such as infection, sepsis, and even death. Some common complications of 2nd-degree burns include infection, sepsis, scarring, and contractures.
In conclusion, 2nd-degree burns are a serious type of injury that requires prompt treatment to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for 2nd-degree burns, individuals can take steps to prevent these injuries and promote recovery and rehabilitation. If you or someone you know has suffered a 2nd-degree burn, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately to prevent complications and promote healing. We encourage you to share this article with others to raise awareness about the importance of burn prevention and treatment. Additionally, we invite you to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have about 2nd-degree burns, and we will do our best to provide you with helpful and informative responses.
