Intro
Discover the miraculous 4 week fetus development stage, where embryonic formation, neural tube growth, and vital organ formation begin, marking crucial milestones in prenatal growth and fetal health.
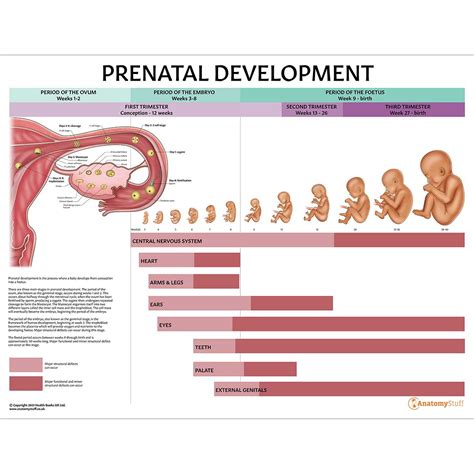
At four weeks of gestation, the fetus is undergoing significant transformations, laying the groundwork for the complex structures and systems that will eventually support its life outside the womb. This period is crucial, as it sets the stage for the rapid growth and development that will occur in the coming weeks. Understanding the milestones achieved during this time can provide valuable insights into the miraculous process of fetal development.
As the fetus enters its fourth week, it measures approximately 5-6 millimeters in length, roughly the size of a poppy seed. Despite its small size, the fetus is already beginning to take on a more defined shape, with the formation of the neural tube, which will eventually give rise to the brain and spinal cord. The heart is also starting to develop, with the emergence of a primitive cardiac structure that will eventually pump blood through the fetus's body.
The fourth week of gestation is a time of rapid cell division and differentiation, as the fetus's major organs and systems begin to take shape. The embryo's three primary germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm – are forming, and will eventually give rise to all of the fetus's tissues and organs. The ectoderm will develop into the nervous system, skin, and hair, while the mesoderm will form the muscles, bones, and circulatory system. The endoderm, meanwhile, will give rise to the lining of the digestive tract, liver, and pancreas.
Embryonic Development
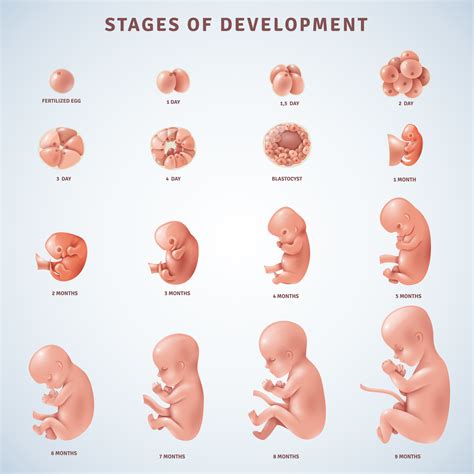
During this period, the fetus's embryonic development is characterized by the formation of the embryoblast and trophoblast. The embryoblast will eventually give rise to the fetus itself, while the trophoblast will develop into the placenta and other supporting tissues. The embryoblast is composed of two layers: the epiblast and the hypoblast. The epiblast will eventually form the three primary germ layers, while the hypoblast will give rise to the yolk sac.
Formation of the Neural Tube
The neural tube is a critical structure that will eventually give rise to the brain and spinal cord. During the fourth week, the neural tube begins to form, as the ectoderm folds in on itself to create a hollow tube. This tube will eventually close, and the neural cells will begin to differentiate and migrate to their final positions. The formation of the neural tube is a complex process, involving the coordinated action of multiple cell signaling pathways and morphogenetic movements.Fetal Heart Development
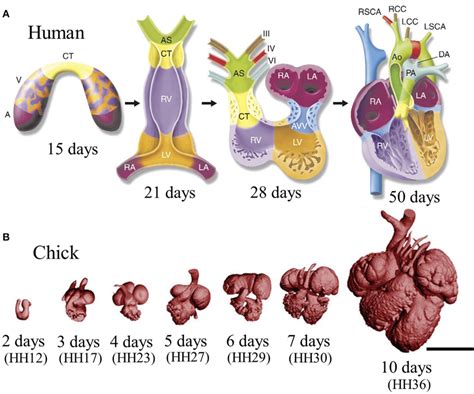
The fetal heart is also beginning to develop during this period. The heart starts as a primitive tube-like structure, which will eventually give rise to the four-chambered heart. The heart begins to beat around the fourth week, pumping blood through the fetus's body. This is a critical milestone, as it marks the beginning of the circulatory system's development. The heart will continue to develop and mature over the coming weeks, eventually forming a complex network of blood vessels and chambers that will support the fetus's growth and development.
Formation of the Limbs
The limbs are also beginning to form during this period. The upper and lower limb buds emerge as small protrusions from the body, and will eventually give rise to the arms and legs. The limb buds are composed of mesenchymal cells, which will eventually differentiate into the various tissues that make up the limbs, including bone, muscle, and connective tissue. The formation of the limbs is a complex process, involving the coordinated action of multiple cell signaling pathways and morphogenetic movements.Placenta and Umbilical Cord Development
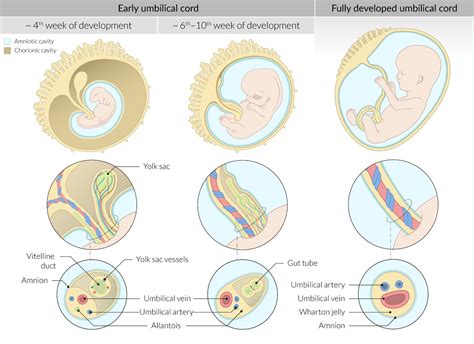
The placenta and umbilical cord are also developing during this period. The placenta is a critical organ that will provide the fetus with oxygen and nutrients, while removing waste products. The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta, and will eventually become the lifeline that sustains the fetus throughout its development. The placenta begins to form as a network of blood vessels and trophoblastic cells, which will eventually give rise to the mature placenta.
Maternal Health and Fetal Development
Maternal health plays a critical role in fetal development, particularly during the fourth week. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest can all support the fetus's growth and development. Meanwhile, exposure to toxins, stress, and other environmental factors can potentially harm the fetus. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should take steps to optimize their health, including quitting smoking, limiting caffeine intake, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.Fetal Development Milestones
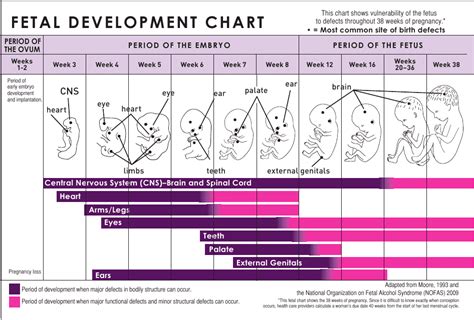
The fourth week of gestation is a critical period in fetal development, marked by the formation of the neural tube, heart, and limbs. The fetus is also beginning to develop its major organs and systems, including the digestive tract, liver, and pancreas. As the fetus continues to grow and develop, it will eventually become a complex, fully formed human being, capable of surviving outside the womb.
Supporting Fetal Development
There are several ways to support fetal development during the fourth week, including: * Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains * Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water * Getting regular exercise, such as walking or swimming * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing * Avoiding exposure to toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals * Getting enough rest and sleepPrenatal Care and Fetal Development
Prenatal care is critical for supporting fetal development, particularly during the fourth week. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify any potential issues or complications, and provide an opportunity for women to ask questions and seek guidance. Prenatal care may include:
- Routine blood tests and urine screenings
- Fetal ultrasound examinations
- Measurement of fetal heart rate and blood pressure
- Discussion of nutrition, exercise, and stress management
Fetal Development and Pregnancy Complications
While the fourth week of gestation is a critical period in fetal development, it is also a time when pregnancy complications can arise. Women who are experiencing symptoms such as bleeding, cramping, or severe nausea should seek medical attention immediately. Other potential complications that may arise during this period include: * Miscarriage * Ectopic pregnancy * Gestational diabetes * HypertensionFetal Development and Future Health
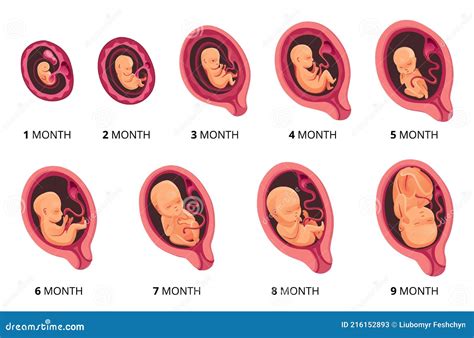
The fourth week of gestation is a critical period in fetal development, laying the groundwork for the complex structures and systems that will eventually support the fetus's life outside the womb. As the fetus continues to grow and develop, it will eventually become a complex, fully formed human being, capable of surviving outside the womb. The health and development of the fetus during this period can have a lasting impact on its future health, making it essential for women to prioritize their health and well-being during pregnancy.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the fourth week of gestation is a critical period in fetal development, marked by the formation of the neural tube, heart, and limbs. As the fetus continues to grow and develop, it will eventually become a complex, fully formed human being, capable of surviving outside the womb. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should take steps to optimize their health, including eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and getting regular exercise. By prioritizing their health and well-being, women can help support the healthy development of their fetus, and set the stage for a lifetime of good health.What is the importance of the fourth week of gestation in fetal development?
+The fourth week of gestation is a critical period in fetal development, marked by the formation of the neural tube, heart, and limbs. This period sets the stage for the rapid growth and development that will occur in the coming weeks, and lays the groundwork for the complex structures and systems that will eventually support the fetus's life outside the womb.
How can women support fetal development during the fourth week of gestation?
+Women can support fetal development during the fourth week of gestation by eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting regular exercise, and practicing stress-reducing techniques. They should also avoid exposure to toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals, and get enough rest and sleep.
What are some common pregnancy complications that may arise during the fourth week of gestation?
+Some common pregnancy complications that may arise during the fourth week of gestation include miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, gestational diabetes, and hypertension. Women who are experiencing symptoms such as bleeding, cramping, or severe nausea should seek medical attention immediately.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the fourth week of gestation in fetal development. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of prenatal care and fetal development. Together, we can support the health and well-being of mothers and babies around the world.
