Intro
Discover a healthy Low Cholesterol Diet Plan, featuring cholesterol-lowering foods, heart-healthy recipes, and lifestyle tips to reduce LDL and increase HDL levels, promoting overall cardiovascular wellness.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for overall well-being, and one of the key aspects of this is managing cholesterol levels. High cholesterol can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease and stroke. Fortunately, adopting a low cholesterol diet plan can significantly reduce the risk of these conditions. A well-structured diet plan focuses on consuming foods that are low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol, while emphasizing nutrient-dense foods. This approach not only helps in lowering cholesterol levels but also promotes weight management and improves overall health.
The importance of a low cholesterol diet plan cannot be overstated. It is a proactive step towards preventing cardiovascular diseases, which are among the leading causes of death globally. By making informed dietary choices, individuals can effectively manage their cholesterol levels, reducing their reliance on medications and minimizing the risk of complications. Moreover, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants, contributing to better health outcomes.
Adopting a low cholesterol diet plan requires a comprehensive understanding of nutritional principles and the ability to make sustainable lifestyle changes. It involves identifying and avoiding foods that are high in unhealthy fats and cholesterol, while incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into daily meals. This dietary approach is not only beneficial for individuals with high cholesterol but also serves as a preventative measure for those at risk. By understanding the benefits and implementing the strategies outlined in a low cholesterol diet plan, individuals can take significant steps towards protecting their heart health and overall well-being.
Understanding Cholesterol

Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
LDL cholesterol is considered "bad" because high levels can lead to the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Foods high in saturated and trans fats can raise LDL levels. Therefore, limiting the intake of these foods is a critical component of a low cholesterol diet plan.High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, is beneficial because it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from the bloodstream. Higher levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a lower risk of heart disease. Foods and nutrients that help boost HDL levels include omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, avocados, and nuts.Key Components of a Low Cholesterol Diet Plan

- Soluble Fiber: Foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, barley, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Soluble fiber works by binding to bile acids and removing them from the body, which in turn reduces the amount of cholesterol produced in the liver.
- Lean Proteins: Choosing lean proteins like poultry, fish, and legumes can help reduce saturated fat and cholesterol intake. It's also important to select lean cuts of meat and remove the skin from poultry to minimize fat consumption.
- Healthy Fats: Foods high in healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. These fats are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health.
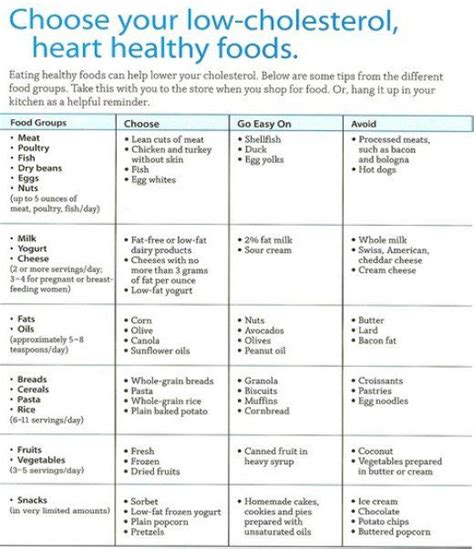
Foods to Emphasize
Foods that should be emphasized in a low cholesterol diet plan include: - Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids - Avocados, nuts, and seeds, which are high in healthy fats and fiber - Fruits and vegetables, which are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals - Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread, which provide fiber and nutrients - Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and peas, which are excellent sources of protein, fiber, and mineralsFoods to Limit
On the other hand, foods that should be limited or avoided in a low cholesterol diet plan include: - Foods high in saturated fats, such as red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed meats - Foods containing trans fats, such as processed snacks, fried foods, and baked goods - Foods high in dietary cholesterol, such as egg yolks and organ meats - Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, sugary snacks, and sweetened beveragesImplementing a Low Cholesterol Diet Plan

- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before making any significant dietary changes, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider, especially for individuals with existing health conditions or those taking medications.
- Keep a Food Diary: Recording food intake and cholesterol levels can help identify patterns and areas for improvement.
- Gradual Changes: Introduce dietary changes gradually to ensure they are sustainable. Start by replacing one or two high-cholesterol foods with healthier alternatives each week.
- Meal Planning: Plan meals in advance to ensure a balanced intake of nutrients and to avoid last-minute, high-cholesterol food choices.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help with digestion and overall health.
Practical Tips for a Low Cholesterol Diet
- **Read Food Labels:** Pay attention to the nutrition facts and ingredient lists on food labels to make informed choices. - **Cook at Home:** Preparing meals at home allows for better control over ingredients and cooking methods. - **Healthy Snacking:** Choose nuts, fruits, and vegetables as snacks instead of processed or high-cholesterol foods. - **Limit Portion Sizes:** Even healthy foods can contribute to high cholesterol if consumed in excess. Paying attention to portion sizes is crucial.Benefits of a Low Cholesterol Diet Plan
Statistical Evidence
Studies have consistently shown that dietary changes can significantly impact cholesterol levels. For example, a diet rich in soluble fiber can lower LDL cholesterol by up to 10%. Additionally, replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats can reduce the risk of heart disease by up to 20%.Challenges and Solutions

Solutions to these challenges include:
- Meal Prep: Preparing meals in advance can save time and ensure healthy eating.
- Finding Healthy Alternatives: Identifying healthy alternatives to high-cholesterol foods can help manage cravings.
- Support Systems: Sharing dietary goals with friends and family can provide encouragement and support.
Seeking Professional Help
For individuals struggling to make dietary changes or requiring personalized advice, consulting a registered dietitian or a healthcare provider can be incredibly beneficial. These professionals can offer tailored guidance, support, and resources to help individuals achieve their health goals.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your experiences, tips, or questions about managing cholesterol levels through dietary changes. Your feedback and insights can help others on their journey to better health. Please comment below, and let's start a conversation about the importance of a low cholesterol diet plan for a healthier tomorrow.
What are the primary foods to avoid in a low cholesterol diet?
+Foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and dietary cholesterol should be limited or avoided. These include red meat, full-fat dairy products, processed meats, foods containing trans fats, and foods high in dietary cholesterol like egg yolks and organ meats.
How can I lower my LDL cholesterol through diet?
+Eating foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, barley, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, can help lower LDL cholesterol. Additionally, choosing lean proteins, healthy fats, and limiting foods high in saturated and trans fats can also be beneficial.
What are some healthy snacks for a low cholesterol diet?
+Healthy snack options include nuts, fruits, vegetables, and whole grain crackers. These foods are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and can help manage hunger and support overall health.
