Intro
Understand 5 A1c levels, from normal to diabetic ranges, and learn how HbA1c tests diagnose and monitor blood sugar control, prediabetes, and diabetes management.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, particularly for individuals with diabetes. One of the key metrics used to assess blood sugar control is the HbA1c test, which measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. Understanding A1c levels is vital for managing diabetes effectively and preventing complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of A1c levels, exploring their significance, the factors that influence them, and the steps you can take to achieve optimal blood sugar control.
The importance of monitoring A1c levels cannot be overstated. By keeping track of these levels, individuals with diabetes can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication, allowing them to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Moreover, A1c levels serve as a valuable tool for healthcare providers, enabling them to assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make adjustments as needed.
For individuals without diabetes, understanding A1c levels can also be beneficial. By being aware of the factors that influence blood sugar control, they can take proactive steps to maintain healthy blood sugar levels, reducing their risk of developing insulin resistance, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, A1c levels can provide valuable insights into overall health, highlighting potential issues such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and hormonal imbalances.
Understanding A1c Levels

Factors That Influence A1c Levels
Several factors can influence A1c levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high amounts of carbohydrates, sugar, and saturated fats can raise A1c levels. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and lower A1c levels. * Medication: Certain medications, such as metformin, can help lower A1c levels. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar control and raise A1c levels. * Stress: Chronic stress can increase cortisol levels, leading to insulin resistance and higher A1c levels.Benefits of Maintaining Healthy A1c Levels

Strategies for Achieving Optimal A1c Levels
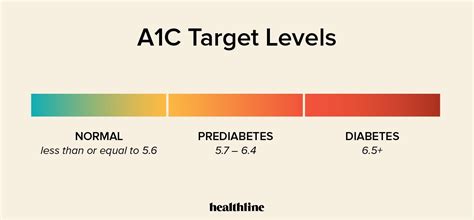
To achieve optimal A1c levels, consider the following strategies: * Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water and limit sugary drinks. * Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. * Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night. * Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.A1c Level Targets
A1c Level Monitoring
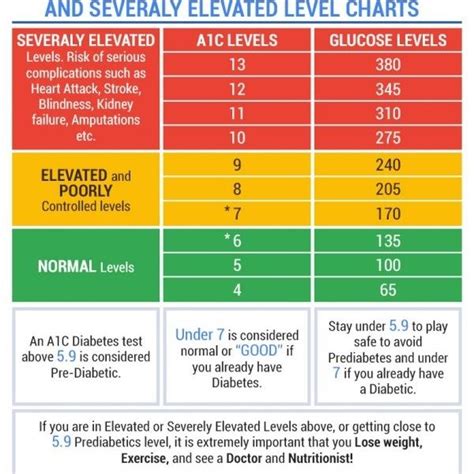
Regular A1c level monitoring is essential for individuals with diabetes. The frequency of monitoring depends on individual factors such as treatment goals, health status, and medication regimen. Generally, A1c levels should be checked: * Every 3-6 months for individuals with stable blood sugar control. * Every 1-3 months for individuals with unstable blood sugar control or those who have recently started or changed medication.Consequences of Poor A1c Level Control
Managing A1c Levels with Medication
Medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin can help lower A1c levels. However, medication should be used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, and stress management. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan and to monitor A1c levels regularly.A1c Levels and Lifestyle Modifications
A1c Levels and Mental Health
A1c levels can have a significant impact on mental health. Poor blood sugar control can lead to: * Mood disturbances: High A1c levels can cause irritability, anxiety, and depression. * Cognitive impairment: Poor blood sugar control can impair cognitive function and increase the risk of dementia. * Reduced quality of life: Poor A1c level control can lead to reduced physical function, social isolation, and decreased overall well-being.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with A1c levels in the comments section below. How do you manage your blood sugar control? What strategies have you found most effective? By sharing your knowledge and insights, you can help others better understand the importance of A1c levels and take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal blood sugar control.
What is the normal range for A1c levels?
+The normal range for A1c levels is less than 5.7% for individuals without diabetes.
How often should I check my A1c levels?
+The frequency of A1c level monitoring depends on individual factors such as treatment goals, health status, and medication regimen. Generally, A1c levels should be checked every 3-6 months for individuals with stable blood sugar control.
What are the consequences of poor A1c level control?
+Poor A1c level control can increase the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. It can also lead to reduced quality of life, fatigue, and mood disturbances.
