Intro
Understand A1c blood sugar levels with our detailed chart, managing diabetes through HbA1c tests, glucose monitoring, and healthy lifestyle choices.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. The A1c blood sugar levels chart is a valuable tool for monitoring and managing blood glucose levels. In this article, we will delve into the importance of A1c testing, how it works, and provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the A1c blood sugar levels chart.
The A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. It is a vital indicator of how well diabetes is being managed and can help identify individuals who are at risk of developing complications related to diabetes. By understanding the A1c blood sugar levels chart, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
The significance of the A1c test lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive picture of blood glucose control over an extended period. Unlike daily blood glucose monitoring, which only provides a snapshot of current glucose levels, the A1c test offers a more detailed understanding of glucose control. This information can be used to adjust treatment plans, make lifestyle changes, and monitor the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies. By regularly monitoring A1c levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps to prevent complications related to diabetes.
A1c Blood Sugar Levels Chart Overview

The A1c blood sugar levels chart is a standardized tool used to interpret the results of the A1c test. The chart typically ranges from 4% to 14%, with lower values indicating better blood glucose control. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following A1c targets for individuals with diabetes: less than 7% for most adults, less than 7.5% for adults with a history of severe hypoglycemia or limited life expectancy, and less than 8% for adults with a history of cardiovascular disease or significant comorbidities.
Understanding A1c Levels
The A1c test measures the percentage of hemoglobin molecules that have attached to glucose in the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body's tissues. When glucose is present in the blood, it can bind to hemoglobin, forming a molecule called glycated hemoglobin. The A1c test measures the amount of glycated hemoglobin in the blood, which reflects the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.A1c Blood Sugar Levels Chart Interpretation

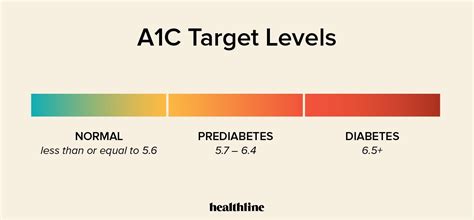
Interpreting the A1c blood sugar levels chart requires an understanding of the different ranges and their corresponding glucose control levels. The following ranges are commonly used to interpret A1c results:
- Less than 5.7%: Normal blood glucose levels
- 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher: Diabetes
- Less than 7%: Good glucose control
- 7% to 8%: Fair glucose control
- Greater than 8%: Poor glucose control
A1c Targets for Different Populations
A1c targets may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, comorbidities, and duration of diabetes. For example: * Pregnant women with diabetes: less than 6.5% * Children and adolescents with diabetes: less than 7.5% * Older adults with diabetes: less than 8%A1c Testing Frequency
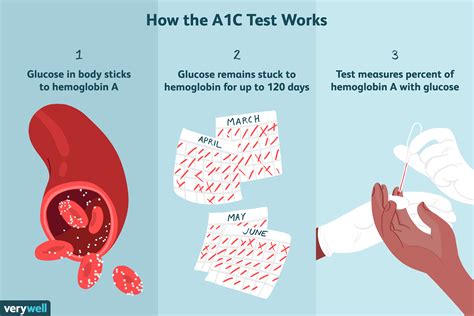
The frequency of A1c testing depends on individual circumstances, such as the presence of diabetes, the effectiveness of treatment, and the risk of complications. The ADA recommends the following A1c testing frequencies:
- Individuals with diabetes: at least twice a year, or more frequently if glucose control is poor or if treatment is changed
- Individuals with prediabetes: at least once a year
- Individuals without diabetes: as part of routine health screenings, typically every 3 years
Limitations of A1c Testing
While the A1c test is a valuable tool for monitoring glucose control, it has some limitations. For example: * A1c results can be affected by factors such as hemoglobin variants, anemia, and blood transfusions * A1c testing may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as sickle cell disease or thalassemia * A1c results may not reflect recent changes in glucose control, as they represent an average of glucose levels over the past 2-3 monthsA1c Blood Sugar Levels Chart and Lifestyle Changes

Maintaining healthy A1c levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, such as:
- Healthy eating: focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, and limiting sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates
- Regular physical activity: aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week
- Weight management: maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise
- Stress management: engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga
- Getting enough sleep: aiming for 7-8 hours of sleep per night
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
In addition to A1c testing, regular blood glucose monitoring is essential for managing diabetes. This can be done using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system. The following are some tips for monitoring blood glucose levels: * Test blood glucose levels at the same time each day * Use a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system to track glucose levels * Keep a log of glucose readings to track progress and identify patterns * Adjust treatment plans as needed based on glucose readingsA1c Blood Sugar Levels Chart and Medications
For individuals with diabetes, medications may be necessary to maintain healthy A1c levels. The following are some common medications used to manage diabetes:
- Metformin: a first-line medication for type 2 diabetes
- Sulfonylureas: a class of medications that stimulate insulin release
- Pioglitazone: a medication that improves insulin sensitivity
- SGLT2 inhibitors: a class of medications that reduce glucose reabsorption in the kidneys
- Insulin: a hormone that regulates glucose levels, often used in combination with other medications
Combination Therapy
In some cases, combination therapy may be necessary to achieve optimal glucose control. This can involve using multiple medications or combining medications with lifestyle changes. The following are some tips for combination therapy: * Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan * Monitor glucose levels regularly to adjust treatment plans as needed * Be aware of potential side effects and interactions between medicationsA1c Blood Sugar Levels Chart and Complications
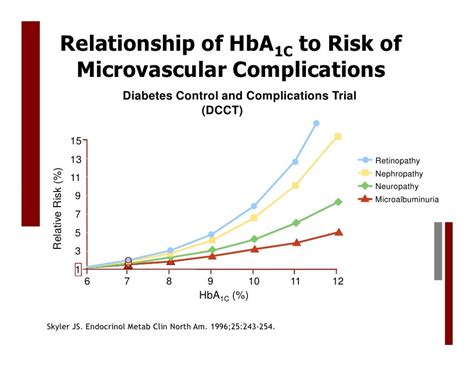
Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to a range of complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease: high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke
- Nerve damage: numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet
- Kidney damage: kidney failure and end-stage renal disease
- Eye damage: diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma
- Foot damage: ulcers, infections, and amputations
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and timely treatment. The following are some tips for preventing complications: * Maintain healthy A1c levels through lifestyle changes and medication * Monitor glucose levels regularly to adjust treatment plans as needed * Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan * Be aware of potential complications and seek medical attention if symptoms occurA1c Blood Sugar Levels Chart and Pregnancy
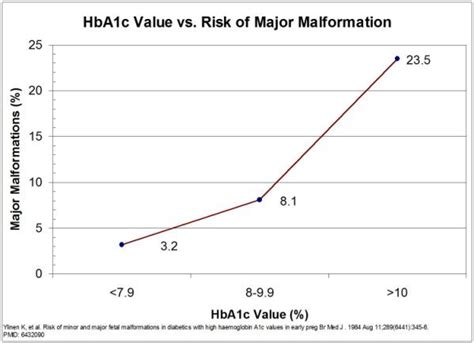
For women with diabetes, maintaining healthy A1c levels during pregnancy is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring a healthy pregnancy. The following are some tips for managing diabetes during pregnancy:
- Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan
- Monitor glucose levels regularly to adjust treatment plans as needed
- Maintain healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity
- Be aware of potential complications and seek medical attention if symptoms occur
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. The following are some tips for managing gestational diabetes: * Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan * Monitor glucose levels regularly to adjust treatment plans as needed * Maintain healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity * Be aware of potential complications and seek medical attention if symptoms occurA1c Blood Sugar Levels Chart and Children
For children with diabetes, maintaining healthy A1c levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and timely treatment. The following are some tips for managing diabetes in children:
- Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan
- Monitor glucose levels regularly to adjust treatment plans as needed
- Maintain healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity
- Be aware of potential complications and seek medical attention if symptoms occur
Type 1 Diabetes in Children
Type 1 diabetes is a type of diabetes that is often diagnosed in childhood. The following are some tips for managing type 1 diabetes in children: * Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan * Monitor glucose levels regularly to adjust treatment plans as needed * Maintain healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity * Be aware of potential complications and seek medical attention if symptoms occurWhat is the A1c test?
+The A1c test is a blood test that measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
What are the normal A1c levels?
+Normal A1c levels are less than 5.7%.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on individual circumstances, such as the presence of diabetes, the effectiveness of treatment, and the risk of complications.
What are the risks of high A1c levels?
+High A1c levels can increase the risk of complications, such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney damage.
How can I lower my A1c levels?
+Lowering A1c levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating, regular physical activity, and stress management, as well as medication and regular monitoring.
In conclusion, maintaining healthy A1c levels is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring a healthy life. By understanding the A1c blood sugar levels chart and incorporating lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and timely treatment, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their diabetes and reduce the risk of long-term complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments below, and to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing diabetes.
