Intro
Discover the importance of A1c range in diabetes management, including normal, prediabetes, and diabetic levels, to maintain a healthy blood sugar balance and prevent complications with optimal A1c test results and glucose control strategies.
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. One of the most effective ways to monitor and manage blood sugar levels is by tracking the A1c range. The A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a vital tool for assessing how well diabetes is being managed and for making informed decisions about treatment plans. In this article, we'll delve into the significance of the A1c range and explore five key aspects related to it.
The A1c range is a critical indicator of blood sugar control, and understanding its implications can significantly impact health outcomes. For individuals with diabetes, the goal is often to achieve an A1c level as close to the normal range as possible, which is typically below 5.7%. However, for those with diabetes, the target A1c range may vary depending on factors such as age, other health conditions, and the risk of hypoglycemia. Managing blood sugar levels effectively can prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Effective management of the A1c range involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, including diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication. Lifestyle changes can significantly impact A1c levels, and even small reductions can lead to substantial health benefits. For instance, losing weight, increasing physical activity, and making dietary changes can all contribute to lowering A1c levels. Furthermore, understanding the factors that influence A1c levels, such as the timing and content of meals, the type and intensity of physical activity, and the proper use of medications, is essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy A1c range.
A1c Range and Diabetes Management
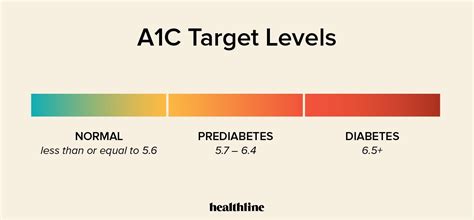
Understanding A1c Levels
Understanding what A1c levels mean is crucial for effective diabetes management. An A1c level below 5.7% is considered normal, while a level between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes. An A1c level of 6.5% or higher suggests diabetes. However, these thresholds are general guidelines, and the target A1c range can vary from person to person. Factors such as age, duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system, as well as the presence of other health conditions like cardiovascular disease, can influence the target A1c range.Lifestyle Modifications for A1c Management

Dietary Changes for A1c Control
Dietary changes are among the most effective lifestyle modifications for controlling the A1c range. Focus on consuming a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It's also important to limit or avoid foods that can negatively impact blood sugar levels, such as sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats. Meal planning and portion control can help manage carbohydrate intake and prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.Medications and A1c Management
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment Plans
Regular monitoring of the A1c range is essential for adjusting treatment plans and ensuring that blood sugar levels are under control. Healthcare providers may recommend A1c tests at regular intervals, typically every 3 to 6 months, to assess how well the current treatment plan is working. Based on the results, adjustments may be made to medications, lifestyle recommendations, or both. It's also important for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, using a glucometer to track levels throughout the day. This information can provide valuable insights into how different factors, such as meals, exercise, and stress, affect blood sugar levels.A1c Range Targets for Different Populations
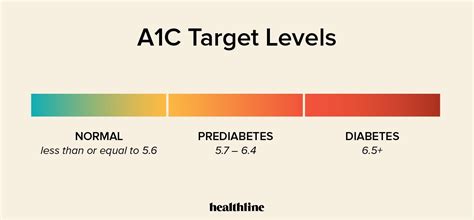
Individualizing A1c Targets
Individualizing A1c targets involves considering a person's unique health needs, preferences, and circumstances. Factors such as the presence of other health conditions, the risk of hypoglycemia, and the individual's ability to manage their diabetes all play a role in determining the appropriate A1c target. Healthcare providers work closely with patients to set realistic and achievable A1c goals, taking into account the potential benefits and risks of different treatment strategies.Technological Advances in A1c Monitoring

Future Directions in A1c Management
The future of A1c management holds much promise, with ongoing research into new technologies, medications, and therapeutic approaches. Advances in fields such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, and personalized medicine are expected to further enhance the management of diabetes, enabling more precise and effective control of the A1c range. Additionally, efforts to improve access to diabetes care and education, particularly in underserved communities, are critical for reducing health disparities and improving outcomes for individuals with diabetes.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about managing the A1c range in the comments below. Your insights can help others in their journey to better diabetes management. Additionally, consider sharing this article with friends, family, or healthcare professionals who may benefit from the information provided. Together, we can work towards improving diabetes care and promoting healthier lives for all.
What is the normal range for A1c levels?
+An A1c level below 5.7% is considered normal. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while levels of 6.5% or higher suggest diabetes.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The frequency of A1c tests depends on your diabetes type and how well your diabetes is controlled. Generally, tests are recommended every 3 to 6 months.
Can lifestyle changes alone lower my A1c levels?
+Yes, lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and weight loss can significantly lower A1c levels. For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes alone may be enough to achieve target A1c levels.
