Intro
Discover the Rhesus blood group system, including Rh factor, blood typing, and compatibility, to understand its impact on pregnancy, transfusions, and health, with insights into Rh positive and negative differences.
The Rhesus blood group system is one of the most important blood group systems in human medicine, playing a critical role in transfusion medicine and obstetrics. It is named after the Rhesus monkey, in which it was first identified. The Rhesus system is complex, with several different antigens and antibodies that can be present or absent, leading to various blood types within this system. Understanding the Rhesus blood group is essential for ensuring safe blood transfusions and for managing pregnancies where there may be incompatibility between the mother's and the fetus's blood types.
The importance of blood group systems, including the Rhesus system, cannot be overstated. Blood transfusions are a common medical procedure, and compatibility between the donor's and the recipient's blood is crucial to prevent adverse reactions. Moreover, in obstetrics, the Rhesus system is significant because of the potential for incompatibility between a pregnant woman and her fetus, which can lead to complications during pregnancy. Thus, understanding the basics of the Rhesus blood group system is vital for both medical professionals and the general public.
The Rhesus system involves several antigens, but the most significant ones are the RhD and RhCE antigens. Individuals who have the RhD antigen on their red blood cells are considered RhD positive, while those without it are RhD negative. Similarly, the presence or absence of the RhCE antigen determines whether someone is RhCE positive or negative. The combination of these antigens determines an individual's Rhesus blood type. The presence or absence of these antigens can lead to the production of antibodies against them if an individual is exposed to a different type, which is a critical consideration in transfusion medicine and pregnancy management.
Rhesus Blood Group System Basics
The Rhesus blood group system is characterized by its complexity, with multiple antigens that can be present on the surface of red blood cells. The main antigens in this system are RhD and RhCE, but there are others, such as RhE, RhC, Rhc, and RhG. The presence or absence of these antigens determines an individual's Rhesus blood type. For example, someone who is RhD positive and has the RhCE antigen could be classified as having a specific Rhesus blood type based on the combination of these antigens.
Understanding Rhesus Blood Types
The classification of Rhesus blood types is based on the presence or absence of the RhD and RhCE antigens. The most common classification is based on the RhD antigen, where individuals are either RhD positive or RhD negative. The presence of the RhD antigen makes an individual's blood type "positive" (e.g., A+, B+, AB+, O+), while the absence of the RhD antigen makes it "negative" (e.g., A-, B-, AB-, O-). The RhCE antigen further refines the blood type, but the RhD status is the primary concern in transfusion medicine and obstetrics.Rhesus Factor and Pregnancy
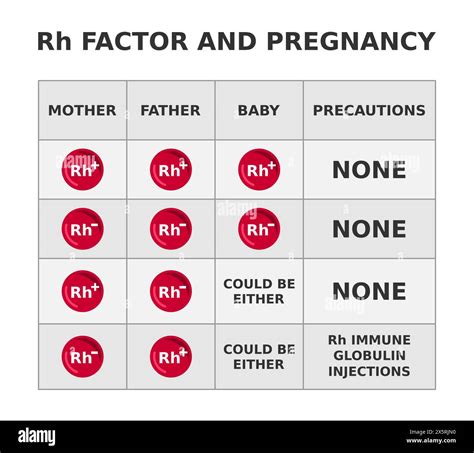
The Rhesus factor plays a significant role in pregnancy, particularly if the mother is RhD negative and the fetus is RhD positive. This situation can occur if the father is RhD positive, as he can pass this trait to the fetus. During pregnancy, if the mother's immune system is exposed to the RhD positive blood of the fetus (which can happen during delivery, miscarriage, or certain prenatal tests), she may develop antibodies against the RhD antigen. These antibodies can then cross the placenta in future pregnancies, attacking the red blood cells of an RhD positive fetus, leading to a condition known as hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
Prevention of Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
To prevent HDN in RhD negative mothers carrying RhD positive fetuses, a procedure known as RhoGAM or Rh immune globulin administration is used. RhoGAM is given to the mother at around 28 weeks of gestation and within 72 hours of delivery if the baby is RhD positive. This injection helps to prevent the mother's immune system from reacting to the RhD positive blood of the fetus, thus preventing the production of antibodies that could harm future RhD positive pregnancies.Importance of Blood Typing
Blood typing is crucial for ensuring safe blood transfusions. Transfusing blood that is incompatible with the recipient's blood type can lead to severe reactions, including hemolysis (the destruction of red blood cells), which can be fatal. The ABO blood group system and the Rhesus system are the two most important blood group systems in transfusion medicine. Knowing an individual's blood type allows healthcare providers to select compatible blood for transfusions, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Steps in Blood Typing
Blood typing involves several steps: - **Sample Collection**: A blood sample is collected from the individual. - **ABO Typing**: The sample is tested to determine the ABO blood type (A, B, AB, or O). - **Rhesus Typing**: The sample is then tested for the presence or absence of the RhD antigen to determine if the individual is RhD positive or negative. - **Cross-Matching**: Before a transfusion, the donor's blood is cross-matched with the recipient's blood to ensure compatibility.Rhesus Blood Group System and Transfusion Medicine
In transfusion medicine, the Rhesus blood group system is critical for preventing adverse reactions. The primary concern is ensuring that the blood transfused is compatible with the recipient's blood type, particularly concerning the RhD antigen. If an RhD negative individual receives RhD positive blood, they may develop antibodies against the RhD antigen, which can cause problems in future transfusions or pregnancies.
Complications of Incompatible Transfusions
Incompatible blood transfusions can lead to severe complications, including: - **Hemolysis**: The destruction of red blood cells, which can lead to jaundice, kidney failure, and even death. - **Allergic Reactions**: Ranging from mild (such as itching or hives) to severe (anaphylaxis). - **Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD)**: A rare but potentially fatal complication where the transfused immune cells attack the recipient's body.Future Developments and Research

Research into the Rhesus blood group system and its implications for transfusion medicine and obstetrics is ongoing. Advances in molecular biology have improved our understanding of the genetics behind the Rhesus system, allowing for better prediction and management of potential complications. Additionally, developments in transfusion medicine, such as the use of Rh immune globulin, have significantly reduced the risk of HDN and improved outcomes for mothers and babies.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, including gene editing and advanced diagnostic techniques, hold promise for further improving our ability to manage and prevent complications related to the Rhesus blood group system. For example, gene editing technologies like CRISPR/Cas9 could potentially be used to modify the genes responsible for the Rhesus antigens, offering new avenues for the prevention and treatment of related conditions.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, the Rhesus blood group system plays a vital role in transfusion medicine and obstetrics. Understanding this system is crucial for ensuring safe blood transfusions and managing pregnancies where there may be incompatibility between the mother's and the fetus's blood types. As research and technology continue to advance, our ability to predict, prevent, and treat complications related to the Rhesus system will improve, leading to better outcomes for patients and further emphasizing the importance of blood typing and compatibility in medical practice.
What is the Rhesus blood group system?
+The Rhesus blood group system is one of the most important blood group systems in human medicine, named after the Rhesus monkey in which it was first identified. It plays a critical role in transfusion medicine and obstetrics.
Why is the Rhesus factor important in pregnancy?
+The Rhesus factor is important in pregnancy because if an RhD negative mother is carrying an RhD positive fetus, there is a risk of the mother's immune system reacting to the fetus's blood, leading to complications. This can be managed with the administration of Rh immune globulin.
How is blood typing done?
+Blood typing involves testing a blood sample to determine the individual's ABO blood type and their Rhesus status (RhD positive or negative). This information is crucial for selecting compatible blood for transfusions.
As we continue to explore and understand the complexities of the human body, the importance of the Rhesus blood group system will only continue to grow. Whether you are a medical professional, an expectant mother, or simply someone interested in learning more about the intricacies of human biology, the Rhesus system is a fascinating and critical aspect of our health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, and explore further the many facets of this vital topic. Together, we can deepen our understanding and appreciation of the Rhesus blood group system and its role in modern medicine.
