Intro
Treat gum abscesses with effective methods, including drainage, antibiotics, and home remedies, to alleviate pain and swelling, promoting oral health and preventing infection complications.
Gum abscesses are painful and potentially serious conditions that can affect anyone, regardless of their oral health habits. A gum abscess is a pocket of pus that forms in the tissues of the gum, often as a result of a bacterial infection. If left untreated, a gum abscess can lead to more severe complications, such as the spread of infection to other parts of the body or the formation of a more serious abscess. Fortunately, there are several effective ways to treat gum abscesses, and understanding these options can help individuals seek the right treatment and prevent future occurrences.
Gum abscesses can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor oral hygiene, gum disease, and trauma to the gums. When bacteria accumulate in the mouth and are not properly removed through brushing and flossing, they can infect the gums and lead to the formation of an abscess. Additionally, individuals with gum disease or those who have experienced trauma to the gums may be more susceptible to developing a gum abscess. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a gum abscess, such as pain, swelling, and discharge, is crucial for seeking prompt treatment and preventing further complications.
The importance of treating gum abscesses cannot be overstated. If left untreated, a gum abscess can lead to serious health consequences, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body, such as the brain or heart. Furthermore, untreated gum abscesses can also lead to the formation of more severe abscesses, such as a periodontal abscess, which can cause significant damage to the teeth and surrounding tissues. By understanding the available treatment options and seeking prompt medical attention, individuals can effectively manage gum abscesses and prevent future occurrences.
Treatment Options for Gum Abscesses

There are several treatment options available for gum abscesses, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most effective treatment option will depend on the severity of the abscess and the individual's overall health. Some of the most common treatment options for gum abscesses include:
Incision and Drainage
Incision and drainage is a common treatment option for gum abscesses. This procedure involves making a small incision in the abscess to allow the pus to drain out. The area is then cleaned and disinfected to prevent further infection. In some cases, a drain may be inserted to allow the pus to continue draining over the next few days.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed to help treat the underlying bacterial infection that is causing the gum abscess. The type and duration of antibiotic treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotic treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Root Canal Therapy
In some cases, a gum abscess may be caused by an infected tooth. If this is the case, root canal therapy may be necessary to treat the infection and prevent further complications. During a root canal, the infected pulp is removed from the tooth, and the canal is cleaned and disinfected.
Surgical Debridement
Surgical debridement is a procedure that involves removing dead tissue and bacteria from the affected area. This procedure can help promote healing and prevent further infection. Surgical debridement may be performed in conjunction with other treatment options, such as incision and drainage or antibiotic therapy.
Home Remedies
There are also several home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms of a gum abscess. These include applying a warm compress to the affected area, rinsing with salt water, and using over-the-counter pain medication. However, it is essential to note that home remedies should not be used as a replacement for professional medical treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gum Abscesses
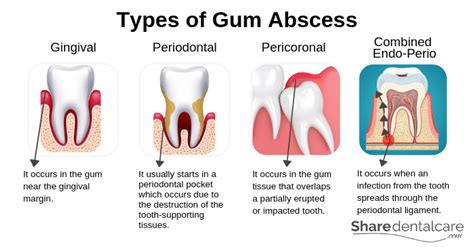
Understanding the causes and risk factors of gum abscesses can help individuals take steps to prevent future occurrences. Some of the most common causes and risk factors of gum abscesses include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Gum disease
- Trauma to the gums
- Infected teeth
- Weakened immune system
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease
Preventing Gum Abscesses
Preventing gum abscesses requires a combination of good oral hygiene habits and regular dental check-ups. Some of the most effective ways to prevent gum abscesses include:
- Brushing and flossing regularly
- Using an antibacterial mouthwash
- Avoiding sugary and acidic foods and drinks
- Quitting smoking
- Visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings
Complications of Untreated Gum Abscesses
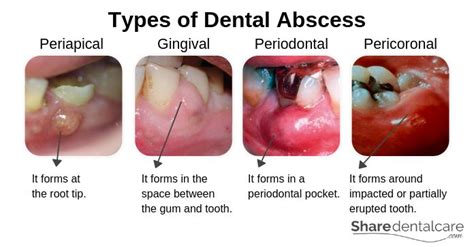
If left untreated, gum abscesses can lead to serious health consequences. Some of the most common complications of untreated gum abscesses include:
- Spread of infection to other parts of the body
- Formation of more severe abscesses, such as a periodontal abscess
- Damage to the teeth and surrounding tissues
- Increased risk of heart disease and other systemic conditions
- Weakened immune system
Seeking Medical Attention
If you suspect that you have a gum abscess, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. A dentist or healthcare provider can diagnose the condition and provide effective treatment to prevent further complications.
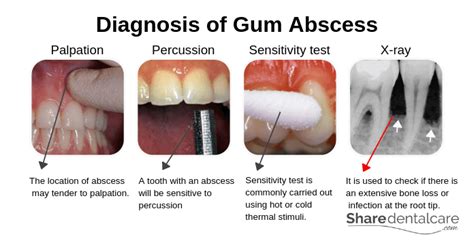
Diagnosing Gum Abscesses
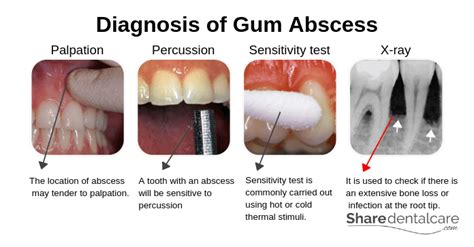
Diagnosing gum abscesses typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Some of the most common methods used to diagnose gum abscesses include:
- Visual examination of the affected area
- Review of medical history
- X-rays or other imaging tests
- Blood tests to check for signs of infection
- Physical examination to check for tenderness and swelling
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing further complications and promoting effective healing. If you suspect that you have a gum abscess, do not hesitate to seek medical attention.
Treatment Outcomes and Prognosis
The prognosis for gum abscesses is generally good, especially if treatment is sought promptly. With effective treatment, most individuals can expect to make a full recovery and prevent future occurrences. However, in some cases, complications can arise, and the prognosis may be less favorable.
Factors Affecting Treatment Outcomes
Several factors can affect treatment outcomes, including:
- Severity of the abscess
- Overall health of the individual
- Effectiveness of treatment
- Presence of underlying medical conditions
- Adherence to treatment plan
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, gum abscesses are serious conditions that require prompt medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to prevent future occurrences and promote effective healing. Further research is needed to fully understand the causes and complications of gum abscesses and to develop more effective treatment options.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with gum abscesses in the comments below. Have you or someone you know been affected by a gum abscess? What treatment options were used, and what were the outcomes? Your input can help others understand the importance of seeking prompt medical attention and the available treatment options.
What are the symptoms of a gum abscess?
+The symptoms of a gum abscess can include pain, swelling, and discharge. In some cases, individuals may also experience fever, chills, and a general feeling of illness.
How can I prevent gum abscesses?
+Gum abscesses can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing regularly, and visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
What are the complications of untreated gum abscesses?
+Untreated gum abscesses can lead to serious health consequences, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body, formation of more severe abscesses, and damage to the teeth and surrounding tissues.
