Intro
Discover how normal respiration works through 5 essential processes, including breathing, gas exchange, and oxygenation, revealing the intricacies of respiratory function and overall health.
Normal respiration is a vital process that occurs in the human body, allowing us to breathe in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. It's a complex mechanism that involves multiple organs and systems working together in harmony. Understanding how normal respiration works is essential for appreciating the importance of maintaining good respiratory health. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of normal respiration, exploring its various aspects and shedding light on the fascinating processes that occur within our bodies.
The process of respiration is often taken for granted, yet it's a remarkable feat of biology that sustains life. From the moment we're born, our bodies begin to breathe, and this continuous process continues until we die. Respiration is not just about inhaling and exhaling air; it's a sophisticated mechanism that involves the coordination of multiple organs, including the lungs, diaphragm, and brain. As we explore the world of normal respiration, we'll discover the intricate relationships between these organs and how they work together to maintain optimal respiratory function.
Normal respiration is a multifaceted process that involves various stages, from inhalation to exhalation, and everything in between. It's a dynamic process that's influenced by factors such as physical activity, environmental conditions, and overall health. By examining the different aspects of normal respiration, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible complexity and beauty of the human body. Whether you're a healthcare professional, a fitness enthusiast, or simply someone interested in learning more about the human body, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of normal respiration and its many wonders.
Introduction to Normal Respiration
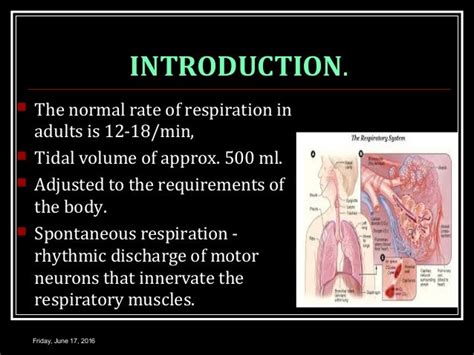
Key Players in Normal Respiration
The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity, plays a crucial role in normal respiration. As the diaphragm contracts, it descends, increasing the volume of the chest cavity and allowing air to enter the lungs. The intercostal muscles, which are located between the ribs, also contribute to respiration by helping to expand and contract the chest cavity. The brain, specifically the respiratory center, regulates breathing by sending signals to the diaphragm and other breathing muscles to control the rate and depth of respiration.The Process of Inhalation
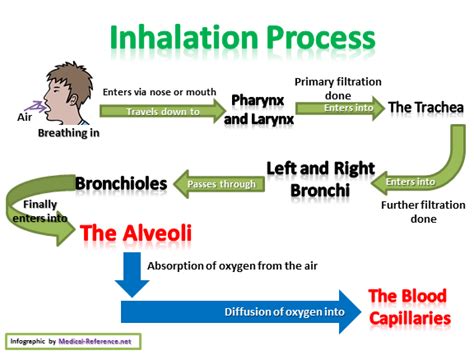
Gas Exchange in the Alveoli
The alveoli are tiny sacs located at the end of the bronchioles, and they're responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the bloodstream. The walls of the alveoli are extremely thin, allowing for efficient gas exchange to occur. As oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses into the bloodstream, it binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, which then transports it to the body's tissues. Simultaneously, carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular metabolism, diffuses out of the bloodstream and into the alveoli, where it's exhaled out of the body.The Process of Exhalation
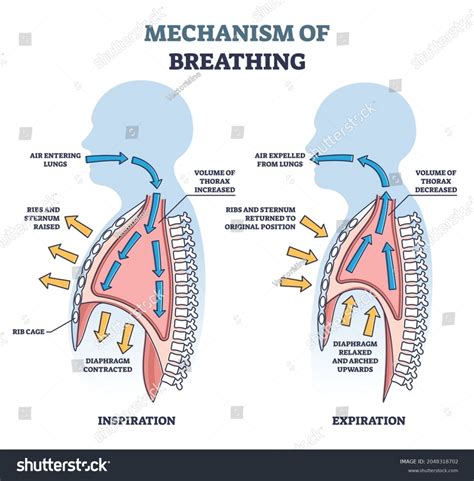
Regulation of Breathing
The regulation of breathing is a complex process that involves the coordination of multiple neural and chemical mechanisms. The respiratory center, located in the brainstem, receives input from various sensors that monitor the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in the blood. Based on this information, the respiratory center sends signals to the diaphragm and other breathing muscles to adjust the rate and depth of respiration. This ensures that the body maintains optimal oxygenation and removes waste products, such as carbon dioxide, efficiently.Factors that Influence Normal Respiration

Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
Respiratory diseases and disorders, such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia, can significantly impact normal respiration. These conditions can cause inflammation, obstruction, or damage to the airways and lungs, leading to breathing difficulties, wheezing, and coughing. Understanding the causes and symptoms of these conditions is essential for early diagnosis and treatment, which can help to manage symptoms and improve respiratory function.Maintenance of Good Respiratory Health
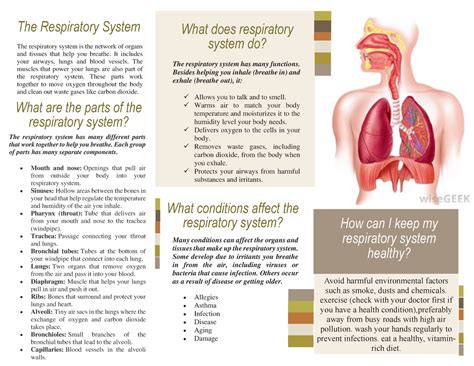
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, normal respiration is a complex and fascinating process that's essential for human life. By understanding the mechanisms and factors that influence normal respiration, we can appreciate the importance of maintaining good respiratory health. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of normal respiration, we can expect to see advances in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases and disorders. By taking a proactive approach to respiratory health, we can promote optimal breathing and overall well-being, ensuring a healthier and happier life.What is the primary function of the diaphragm in normal respiration?
+The primary function of the diaphragm is to contract and relax, allowing air to enter and leave the lungs. As the diaphragm contracts, it increases the volume of the chest cavity, creating a negative pressure that allows air to enter the lungs.
What is the role of the alveoli in gas exchange?
+The alveoli are responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the bloodstream. The walls of the alveoli are extremely thin, allowing for efficient gas exchange to occur.
What factors can influence normal respiration?
+Normal respiration can be influenced by various factors, including physical activity, environmental conditions, and overall health. During exercise, for example, the body requires more oxygen to meet the increased energy demands of the muscles.
