Intro
Learn about Af Catheter Ablation treatment for atrial fibrillation, a minimally invasive procedure using radiofrequency ablation to restore heart rhythm, reducing arrhythmia symptoms and improving cardiac health.
Atrial fibrillation, commonly referred to as Afib, is a type of irregular heartbeat that can increase the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications. One of the most effective treatments for Afib is catheter ablation, a minimally invasive procedure that uses energy to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause the arrhythmia. In this article, we will delve into the world of catheter ablation treatment for Afib, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and what patients can expect during and after the procedure.
Catheter ablation has revolutionized the treatment of Afib, offering a highly effective and relatively safe alternative to medication and surgery. By targeting and eliminating the sources of abnormal electrical activity in the heart, catheter ablation can restore a normal heart rhythm, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall quality of life. With advances in technology and technique, catheter ablation has become an increasingly popular treatment option for patients with Afib, and its popularity continues to grow as more people become aware of its benefits.
The importance of treating Afib cannot be overstated, as the condition affects millions of people worldwide and can have a significant impact on daily life. Afib can cause symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue, making it difficult for people to perform everyday activities. Furthermore, Afib increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions, making prompt and effective treatment essential. Catheter ablation offers a unique opportunity for patients to take control of their condition, reducing their reliance on medication and improving their overall health and wellbeing.
Af Catheter Ablation Treatment Overview
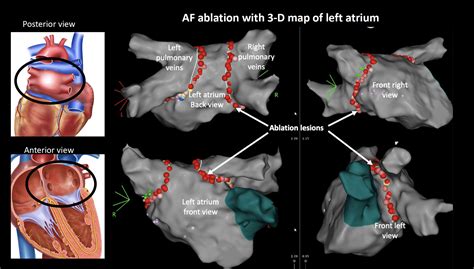
How Catheter Ablation Works
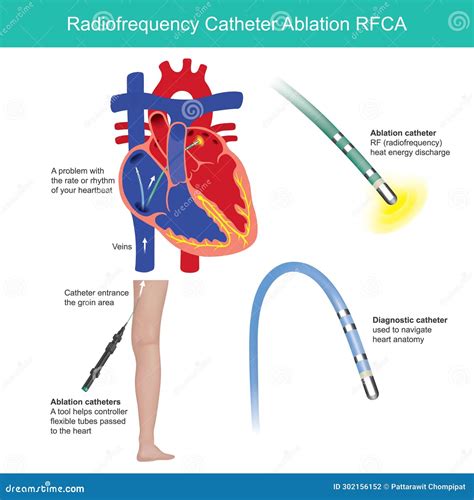
The catheter ablation procedure works by using energy to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause Afib. There are several types of energy that can be used, including radiofrequency energy, cryoenergy, and laser energy. The type of energy used will depend on the individual patient's needs and the specific procedure being performed. During the procedure, the catheter is used to deliver the energy to the targeted areas, which are typically located in the left atrium, the upper chamber of the heart. The energy is delivered in a controlled and precise manner, ensuring that only the abnormal tissue is destroyed, while healthy tissue is preserved.Benefits of Catheter Ablation
Who is a Candidate for Catheter Ablation?
Catheter ablation is typically recommended for patients with Afib who: * Have symptoms that are not well-controlled with medication * Have a high risk of stroke or heart failure * Are unable to tolerate medication due to side effects * Have a history of cardiovascular disease * Are seeking a more permanent solution to their conditionCatheter Ablation Procedure
Risks and Complications
While catheter ablation is generally a safe procedure, there are risks and complications that can occur, including: * Bleeding or bruising at the catheter site * Infection * Damage to the heart or surrounding tissues * Stroke or heart attack * DeathRecovery and Follow-Up

Long-Term Results
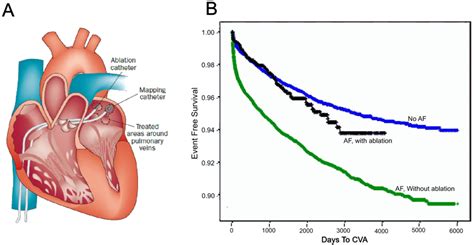
The long-term results of catheter ablation can vary depending on the individual patient and the specific procedure performed. However, studies have shown that catheter ablation can be highly effective in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life for patients with Afib. In some cases, catheter ablation can even eliminate the need for medication, allowing patients to take control of their condition and improve their overall health and wellbeing.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with catheter ablation treatment in the comments below. If you have any questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please don't hesitate to reach out. We are committed to providing you with the most up-to-date and accurate information available, and we look forward to hearing from you.
What is catheter ablation and how does it work?
+Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses energy to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause Afib. The procedure involves the use of a catheter, a thin, flexible tube, to deliver energy to the targeted areas, which are typically located in the left atrium, the upper chamber of the heart.
Who is a candidate for catheter ablation?
+Catheter ablation is typically recommended for patients with Afib who have symptoms that are not well-controlled with medication, have a high risk of stroke or heart failure, are unable to tolerate medication due to side effects, have a history of cardiovascular disease, or are seeking a more permanent solution to their condition.
What are the benefits of catheter ablation?
+The benefits of catheter ablation include reduced risk of stroke and heart failure, improved quality of life, reduced symptoms, decreased reliance on medication, improved exercise tolerance, and reduced risk of cardiovascular complications.
