Intro
Discover 5 ways Alanine Aminotransferase Alt affects liver health, including enzyme regulation, amino acid transfer, and liver damage assessment, using ALT tests for diagnosis and monitoring.
The importance of amino acids in our bodies cannot be overstated. They are the building blocks of proteins, which are essential for various bodily functions, including muscle growth and maintenance, immune function, and the production of enzymes and hormones. Among the 20 amino acids that the human body uses, alanine is one of the most versatile and crucial. It plays a significant role in the metabolism of glucose and tryptophan and is also involved in the production of energy. The enzyme responsible for the interconversion of alanine and pyruvate is alanine aminotransferase (ALT), which is found primarily in the liver but also in smaller amounts in the kidneys, heart, and muscles.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is an enzyme that is critical for the proper functioning of the liver. It is involved in the transfer of an amino group from the amino acid alanine to a keto acid, resulting in the formation of pyruvate and glutamate. This process is essential for the synthesis of glucose and the production of energy in the body. The ALT enzyme is also a key indicator of liver health, with elevated levels of ALT in the blood often indicating liver damage or disease. The liver plays a vital role in detoxification, metabolism, and the production of proteins and bile, making the ALT enzyme a crucial component of liver function.
The functioning of ALT and its role in the body highlights the importance of maintaining liver health. The liver is susceptible to damage from various sources, including viruses, toxins, and excessive alcohol consumption. When the liver is damaged, ALT is released into the bloodstream, resulting in elevated levels. This makes ALT a valuable biomarker for assessing liver health and detecting potential liver problems early on. Understanding the mechanisms and significance of ALT can help in the prevention and management of liver diseases, underscoring the need for a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of harmful substances to maintain liver health.
Introduction to Alanine Aminotransferase
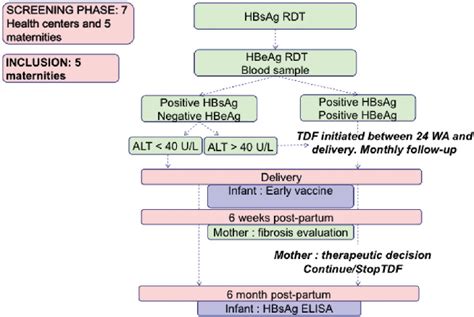
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is a transaminase enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from the amino acid alanine to a keto acid, resulting in the formation of pyruvate and glutamate. This reaction is reversible and is a critical step in the metabolism of amino acids and the production of energy in the body. ALT is primarily found in the liver, where it plays a central role in gluconeogenesis, the process by which the liver generates glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
Function of ALT in the Liver
The liver is the primary site of ALT activity, where it is involved in the interconversion of alanine and pyruvate. This process is essential for the synthesis of glucose and the production of energy in the body. The liver's unique role in metabolism, detoxification, and protein synthesis makes ALT a critical enzyme for maintaining proper liver function. Elevated levels of ALT in the blood are often indicative of liver damage or disease, highlighting the importance of ALT as a biomarker for liver health.Role of ALT in Energy Production
ALT plays a crucial role in the production of energy in the body. By catalyzing the conversion of alanine to pyruvate, ALT helps to generate energy through the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. This process is essential for the proper functioning of cells and tissues, particularly in the liver, where energy demand is high. The role of ALT in energy production underscores the importance of this enzyme in maintaining cellular homeostasis and overall health.
ALT and Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is the process by which the liver generates glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, such as amino acids, lactate, and glycerol. ALT is a key enzyme in this process, as it helps to convert alanine into pyruvate, which can then be used to synthesize glucose. This process is critical for maintaining blood glucose levels, particularly during fasting or when glucose is in short supply. The role of ALT in gluconeogenesis highlights the importance of this enzyme in maintaining glucose homeostasis and preventing hypoglycemia.ALT as a Biomarker for Liver Health

ALT is a valuable biomarker for assessing liver health and detecting potential liver problems. Elevated levels of ALT in the blood are often indicative of liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. The liver's unique role in metabolism, detoxification, and protein synthesis makes ALT a sensitive indicator of liver function. Monitoring ALT levels can help diagnose liver problems early on, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further liver damage.
Causes of Elevated ALT Levels
Elevated ALT levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including liver damage, viral infections, and exposure to toxins. The most common causes of elevated ALT levels include: * Hepatitis B and C * Alcoholic liver disease * Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) * Liver cancer * Medications, such as statins and antibiotics * Toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metalsImportance of Maintaining Liver Health
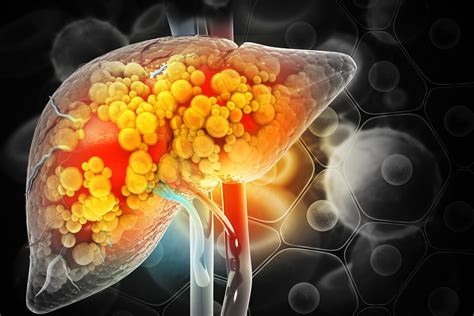
Maintaining liver health is essential for overall health and well-being. The liver plays a critical role in detoxification, metabolism, and protein synthesis, making it a vital organ for maintaining proper bodily functions. A healthy liver is essential for:
- Detoxifying harmful substances
- Metabolizing nutrients and medications
- Producing proteins and bile
- Maintaining blood sugar levels
- Supporting immune function
Ways to Maintain Liver Health
Maintaining liver health can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle modifications and dietary changes. Some ways to maintain liver health include: * Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains * Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption * Avoiding exposure to toxins and pollutants * Maintaining a healthy weight * Getting regular exercise * Avoiding medications that can harm the liverConclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is a critical enzyme that plays a central role in liver function and energy production. Maintaining liver health is essential for overall health and well-being, and ALT is a valuable biomarker for assessing liver health. By understanding the mechanisms and significance of ALT, we can better appreciate the importance of maintaining liver health and preventing liver disease. Future research directions should focus on developing new treatments and therapies for liver disease, as well as promoting public awareness and education about the importance of liver health.
What is alanine aminotransferase (ALT)?
+Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is a transaminase enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from the amino acid alanine to a keto acid, resulting in the formation of pyruvate and glutamate.
What is the role of ALT in the liver?
+ALT is primarily found in the liver, where it plays a central role in gluconeogenesis, the process by which the liver generates glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
What are the causes of elevated ALT levels?
+Elevated ALT levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including liver damage, viral infections, and exposure to toxins.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the importance of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and its role in maintaining liver health. By understanding the mechanisms and significance of ALT, we can better appreciate the importance of maintaining liver health and preventing liver disease. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. We also encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about liver health and ALT.
