Intro
Detect albumin in urine with our guide, exploring causes, symptoms, and tests for proteinuria, kidney disease, and nephrotic syndrome diagnosis.
The presence of albumin in urine, also known as albuminuria, is a common indicator of kidney damage or disease. Albumin is a type of protein that is normally found in the blood, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining blood volume and preventing fluid from leaking out of blood vessels. However, when the kidneys are damaged, they may not be able to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood effectively, leading to the presence of albumin in the urine. In this article, we will discuss the importance of detecting albumin in urine, the causes of albuminuria, and the steps that can be taken to prevent or manage kidney damage.
The detection of albumin in urine is a critical step in diagnosing and managing kidney disease. Albuminuria can be detected using a simple urine test, and it is often the first sign of kidney damage. If left untreated, kidney damage can progress to more serious conditions, such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD). CKD is a condition in which the kidneys are damaged and cannot filter waste and excess fluids from the blood effectively, while ESRD is a condition in which the kidneys have failed and require dialysis or a kidney transplant to sustain life. Early detection and treatment of albuminuria can help to prevent or slow the progression of kidney disease, and it is essential for individuals who are at risk of developing kidney disease to undergo regular urine tests.
The causes of albuminuria are numerous and varied. Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease, and individuals with diabetes are at increased risk of developing albuminuria. High blood pressure is another common cause of kidney disease, and it can also lead to the presence of albumin in the urine. Other causes of albuminuria include kidney damage or disease, such as glomerulonephritis or nephrotic syndrome, as well as certain medications or toxins. Additionally, individuals who are overweight or obese, or who have a family history of kidney disease, may also be at increased risk of developing albuminuria.
Understanding Albuminuria
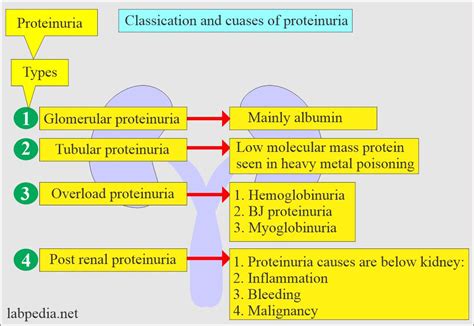
Types of Albuminuria
There are several types of albuminuria, including: * Microalbuminuria: This is a condition in which small amounts of albumin are present in the urine. Microalbuminuria is often the first sign of kidney damage, and it can be detected using a simple urine test. * Macroalbuminuria: This is a condition in which large amounts of albumin are present in the urine. Macroalbuminuria is a sign of more severe kidney damage, and it requires immediate medical attention. * Transient albuminuria: This is a condition in which albumin is present in the urine for a short period of time. Transient albuminuria can be caused by a variety of factors, including dehydration or intense exercise. * Orthostatic albuminuria: This is a condition in which albumin is present in the urine when an individual is standing, but not when they are lying down. Orthostatic albuminuria is often seen in adolescents and young adults.Causes of Albuminuria

Risk Factors for Albuminuria
There are several risk factors for albuminuria, including: * Age: Older adults are at increased risk of developing albuminuria. * Obesity: Individuals who are overweight or obese are at increased risk of developing albuminuria. * Family history: Individuals who have a family history of kidney disease are at increased risk of developing albuminuria. * Certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, can increase the risk of developing albuminuria.Diagnosis and Treatment of Albuminuria
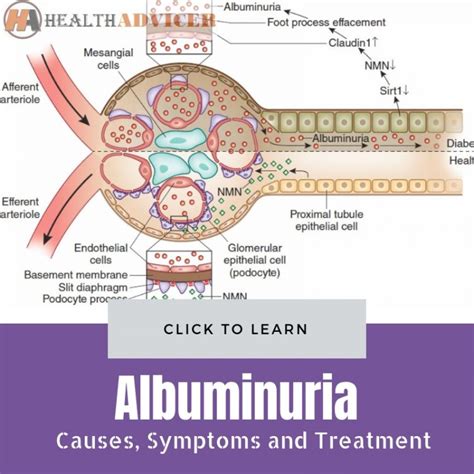
The treatment of albuminuria depends on the underlying cause of the condition. If the cause is diabetes or high blood pressure, treatment may involve managing these conditions through lifestyle changes or medication. If the cause is kidney damage or disease, treatment may involve medications or other therapies to slow the progression of the disease. In some cases, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be necessary to treat albuminuria.
Treatment Options for Albuminuria
There are several treatment options for albuminuria, including: * Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can help to manage conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure, which can contribute to albuminuria. * Medications: Medications, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), can help to slow the progression of kidney disease and reduce the amount of albumin in the urine. * Dialysis: Dialysis may be necessary to treat albuminuria in individuals with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). * Kidney transplant: A kidney transplant may be necessary to treat albuminuria in individuals with ESRD.Prevention of Albuminuria

Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of albuminuria is critical to preventing or slowing the progression of kidney disease. If albuminuria is detected early, treatment can be started to slow the progression of the disease and prevent complications. Additionally, early detection can help to identify individuals who are at risk of developing kidney disease, and steps can be taken to prevent or manage the condition.Complications of Albuminuria

Managing Complications
There are several steps that can be taken to manage complications of albuminuria, including: * Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can help to manage conditions like kidney disease or cardiovascular disease. * Medications: Medications, such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs, can help to slow the progression of kidney disease and reduce the amount of albumin in the urine. * Dialysis: Dialysis may be necessary to treat albuminuria in individuals with ESRD. * Kidney transplant: A kidney transplant may be necessary to treat albuminuria in individuals with ESRD.What is albuminuria?
+Albuminuria is a condition in which the kidneys are damaged, leading to the presence of albumin in the urine.
What are the causes of albuminuria?
+The causes of albuminuria include diabetes, high blood pressure, kidney damage or disease, certain medications or toxins, and family history.
How is albuminuria diagnosed?
+Albuminuria is typically diagnosed using a simple urine test that measures the amount of albumin in the urine.
What are the treatment options for albuminuria?
+Treatment options for albuminuria include lifestyle changes, medications, dialysis, and kidney transplant.
Can albuminuria be prevented?
+Yes, albuminuria can be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing medical conditions, avoiding certain medications or toxins, and getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider.
In summary, albuminuria is a condition in which the kidneys are damaged, leading to the presence of albumin in the urine. The causes of albuminuria include diabetes, high blood pressure, kidney damage or disease, certain medications or toxins, and family history. Early detection and treatment of albuminuria are critical to preventing or slowing the progression of kidney disease. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with albuminuria in the comments section below. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns about albuminuria, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support. By working together, we can raise awareness about the importance of kidney health and promote early detection and treatment of albuminuria.
