Intro
Discover key facts about Alendronate, a bisphosphonate medication, including its uses, benefits, and side effects for osteoporosis treatment and bone health management.
Alendronate is a medication that has been widely used for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men. It belongs to a class of drugs known as bisphosphonates, which work by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone tissue. This leads to an overall increase in bone mass and mineral density, reducing the risk of fractures. The importance of understanding alendronate and its effects cannot be overstated, given the significant impact of osteoporosis on the quality of life and the risk of fractures in the elderly population.
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by a decrease in bone mass and density, leading to an increased risk of fractures. It is a major public health concern, particularly in older adults, as it can significantly impair mobility and independence. The economic burden of osteoporosis is also substantial, with costs associated with the treatment of fractures and the management of the condition. Therefore, medications like alendronate play a crucial role in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. By reducing the risk of fractures, alendronate can help maintain the quality of life and reduce the economic burden associated with osteoporosis.
The mechanism of action of alendronate, like other bisphosphonates, involves its binding to hydroxyapatite found in bone, which leads to the inhibition of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. This results in an overall increase in bone mineral density, which is crucial for reducing the risk of fractures. Alendronate is administered orally, usually once a week, and its efficacy has been demonstrated in numerous clinical trials. These trials have shown that alendronate can significantly reduce the risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in patients with osteoporosis.
Introduction to Alendronate
How Alendronate Works
The working mechanism of alendronate is based on its ability to inhibit bone resorption. This process is crucial for maintaining bone health, as excessive bone resorption can lead to a decrease in bone mass and density, characteristic of osteoporosis. Alendronate acts by binding to bone hydroxyapatite, which leads to the inhibition of osteoclast activity. Osteoclasts are the bone cells responsible for the breakdown and resorption of bone tissue. By inhibiting these cells, alendronate reduces bone resorption, leading to an increase in bone mass and mineral density.Benefits of Alendronate

Side Effects and Precautions
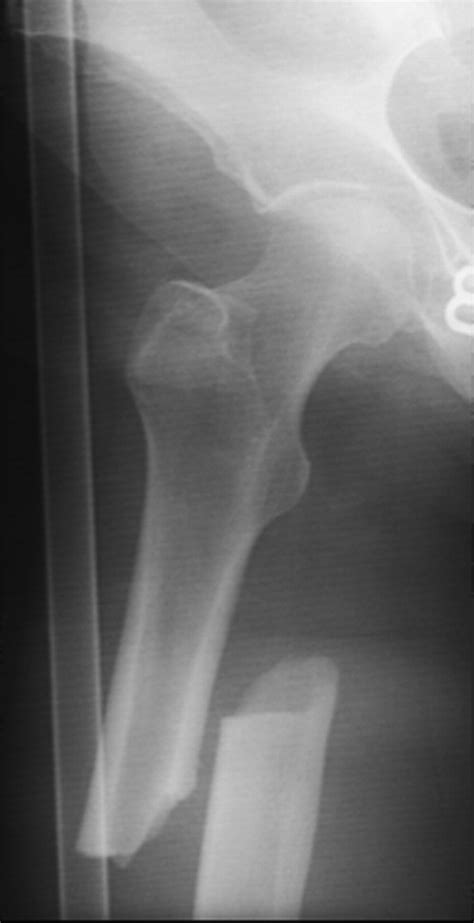
While alendronate is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, some of which can be serious. Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and esophageal irritation. More severe side effects, although rare, can include esophageal ulcers, osteonecrosis of the jaw, and atypical femoral fractures. It is essential for patients to follow the instructions for taking alendronate carefully to minimize the risk of these side effects. This includes taking the medication with a full glass of water and remaining upright for at least 30 minutes after administration.Administration and Dosage
Contraindications and Interactions
Alendronate is contraindicated in patients with certain conditions, including hypocalcemia, esophageal abnormalities, and hypersensitivity to the drug. It can also interact with other medications, such as antacids and calcium supplements, which can reduce its absorption. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking before starting alendronate therapy.Long-Term Use and Efficacy
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients on alendronate therapy should be monitored regularly to assess the efficacy of the treatment and potential side effects. This includes regular measurements of bone mineral density and assessment of fracture risk. Follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to adjust the treatment plan as needed and to ensure that the patient is receiving the maximum benefit from alendronate therapy.Alternatives and Future Directions
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, alendronate is a valuable medication in the management of osteoporosis, offering significant benefits in terms of reducing fracture risk and improving bone health. However, its use requires careful consideration of potential side effects and interactions. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the best treatment plan for their individual needs. By understanding the benefits and risks of alendronate and adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen, patients can maximize the benefits of this medication and reduce their risk of osteoporotic fractures.What is the primary mechanism of action of alendronate?
+Alendronate works by inhibiting osteoclast-mediated bone resorption, leading to an increase in bone mass and mineral density.
What are the common side effects of alendronate?
+Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and esophageal irritation. More severe side effects can include esophageal ulcers and osteonecrosis of the jaw.
How is alendronate administered, and what is the typical dosage?
+Alendronate is administered orally, once a week, with a typical dosage of 70 mg. The medication should be taken with a full glass of water, and the patient should remain upright for at least 30 minutes after administration.
Can alendronate be used in patients with kidney disease?
+Alendronate should be used with caution in patients with kidney disease, as it can exacerbate renal impairment. The dosage may need to be adjusted based on the patient's creatinine clearance.
What are the alternatives to alendronate for the treatment of osteoporosis?
+Alternatives to alendronate include other bisphosphonates, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), and parathyroid hormone analogs. The choice of therapy depends on the patient's specific needs, risk factors, and response to previous treatments.
To further engage with the topic of alendronate and its role in managing osteoporosis, we invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions in the comments section below. Sharing this article with others who may benefit from the information can also help spread awareness about the importance of bone health and the available treatment options. By working together, we can promote better understanding and management of osteoporosis, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
