Intro
Unlock the secrets of Alk Phos test results, understanding alkaline phosphatase levels, liver function, and bone health implications, with expert insights on enzyme elevations, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options.
The alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the level of ALP enzyme in the blood. This enzyme is found in various tissues throughout the body, including the liver, bones, kidneys, and digestive system. Elevated or decreased levels of ALP can indicate a range of health issues, making it essential to understand the test results. In this article, we will delve into the world of ALP test results, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and what factors can influence them.
The ALP test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as liver disease, bone disorders, and certain types of cancer. It is also used to assess the overall health of the liver and bones. When the ALP level is elevated, it can indicate liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. On the other hand, low ALP levels can be a sign of a bone disorder, such as osteomalacia or rickets. Understanding the test results is crucial for healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans.
The ALP test is a relatively simple and non-invasive procedure, involving a blood sample drawn from a vein in the arm. The blood is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the level of ALP enzyme is measured. The test results are typically reported in units per liter (U/L) or international units per liter (IU/L). The normal range for ALP levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. Generally, a normal ALP level is between 30 and 120 U/L. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the specific normal range for your test results.
Understanding ALP Test Results
To interpret ALP test results, healthcare providers consider various factors, including the individual's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory test results. Elevated ALP levels can be caused by a range of conditions, including liver disease, bone disorders, and certain types of cancer. On the other hand, low ALP levels can be a sign of a bone disorder, such as osteomalacia or rickets. In some cases, ALP levels may be elevated due to non-pathological conditions, such as pregnancy or certain medications.
Factors Influencing ALP Levels
Several factors can influence ALP levels, including age, sex, and certain medical conditions. For example, ALP levels tend to be higher in children and adolescents due to bone growth and development. Additionally, ALP levels may be elevated in individuals with liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. Certain medications, such as antacids and anti-seizure medications, can also affect ALP levels.Interpreting ALP Test Results
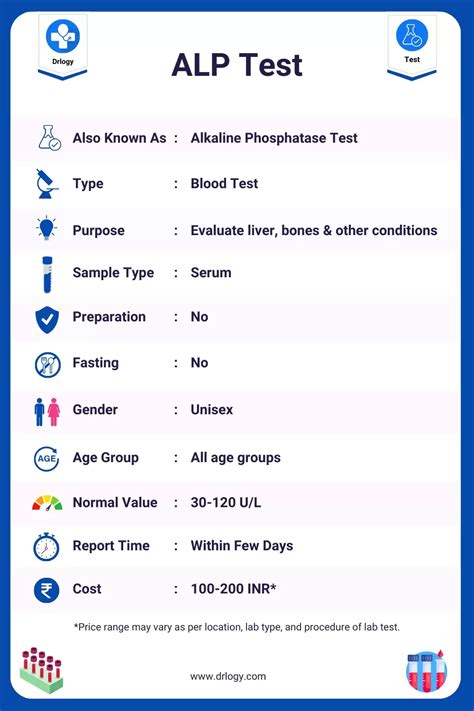
When interpreting ALP test results, healthcare providers consider the individual's overall health and medical history. Elevated ALP levels can indicate a range of health issues, including liver disease, bone disorders, and certain types of cancer. On the other hand, low ALP levels can be a sign of a bone disorder, such as osteomalacia or rickets. In some cases, ALP levels may be elevated due to non-pathological conditions, such as pregnancy or certain medications.
What Do Elevated ALP Levels Mean?
Elevated ALP levels can indicate a range of health issues, including liver disease, bone disorders, and certain types of cancer. For example, elevated ALP levels can be a sign of liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. Additionally, elevated ALP levels can indicate bone disorders, such as osteomalacia or rickets. In some cases, elevated ALP levels can be a sign of certain types of cancer, such as liver or bone cancer.ALP Test Results and Liver Disease
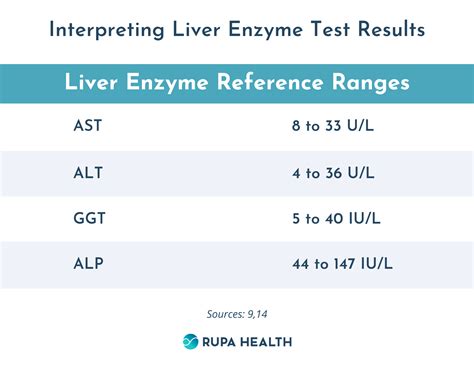
The ALP test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor liver disease. Elevated ALP levels can indicate liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. Additionally, ALP levels can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for liver disease. For example, if ALP levels decrease after treatment, it may indicate that the treatment is effective.
ALP Test Results and Bone Disorders
The ALP test is also used to diagnose and monitor bone disorders, such as osteomalacia or rickets. Low ALP levels can be a sign of a bone disorder, while elevated ALP levels can indicate bone growth or development. For example, ALP levels tend to be higher in children and adolescents due to bone growth and development.ALP Test Results and Cancer
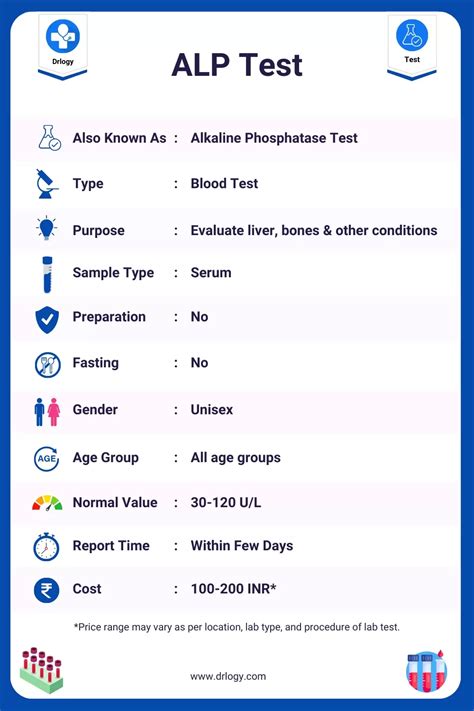
In some cases, elevated ALP levels can be a sign of certain types of cancer, such as liver or bone cancer. For example, elevated ALP levels can be a sign of liver cancer, while low ALP levels can be a sign of bone cancer. However, it is essential to note that ALP levels are not a definitive diagnostic tool for cancer, and other tests and examinations are necessary to confirm a diagnosis.
What to Do If You Have Abnormal ALP Test Results
If you have abnormal ALP test results, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the cause and develop an effective treatment plan. In some cases, abnormal ALP levels may be a sign of an underlying health issue, such as liver disease or bone disorders. In other cases, abnormal ALP levels may be due to non-pathological conditions, such as pregnancy or certain medications.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding ALP test results is crucial for healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans. Elevated or decreased ALP levels can indicate a range of health issues, including liver disease, bone disorders, and certain types of cancer. If you have abnormal ALP test results, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the cause and develop an effective treatment plan.
Final Thoughts
The ALP test is a valuable diagnostic tool used to measure the level of ALP enzyme in the blood. By understanding ALP test results, healthcare providers can diagnose and monitor a range of health issues, including liver disease, bone disorders, and certain types of cancer. If you have any questions or concerns about ALP test results, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider.What is the normal range for ALP levels?
+The normal range for ALP levels varies depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. Generally, a normal ALP level is between 30 and 120 U/L.
What can cause elevated ALP levels?
+Elevated ALP levels can be caused by a range of conditions, including liver disease, bone disorders, and certain types of cancer. Additionally, ALP levels may be elevated due to non-pathological conditions, such as pregnancy or certain medications.
What do low ALP levels indicate?
+Low ALP levels can be a sign of a bone disorder, such as osteomalacia or rickets. Additionally, low ALP levels can be a sign of certain types of cancer, such as bone cancer.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of ALP test results and their significance in diagnosing and monitoring various health issues. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Remember, understanding your test results is the first step towards taking control of your health and well-being.
