Intro
Discover key Amoxicillin facts, including its antibiotic uses, dosage, and side effects, to understand this popular medications benefits and risks, and learn about its interactions and allergic reactions.
Amoxicillin is one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics worldwide, used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. Despite its widespread use, many people are not aware of the key facts surrounding this medication. Understanding these facts is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare and to use amoxicillin safely and effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of amoxicillin, exploring its history, mechanism of action, benefits, and potential side effects, as well as providing practical advice for those prescribed this antibiotic.
The discovery of amoxicillin marked a significant milestone in the fight against bacterial infections. Developed in the 1960s, amoxicillin was designed to improve upon earlier penicillin-based antibiotics by offering a broader spectrum of activity and better absorption rates. This enhancement allowed amoxicillin to become a staple in the treatment of various infections, from respiratory tract infections to skin and soft tissue infections. Its impact on public health has been profound, saving countless lives and reducing the morbidity associated with bacterial diseases.
As we explore the realm of amoxicillin, it becomes clear that this antibiotic is not just a simple medication but a complex tool that requires careful consideration. Patients need to understand how amoxicillin works, its potential benefits and risks, and how to use it responsibly to avoid contributing to antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, the role of healthcare providers in educating patients about amoxicillin and monitoring its use is paramount. By working together, we can ensure that amoxicillin remains an effective treatment option for generations to come.
Introduction to Amoxicillin

History and Development
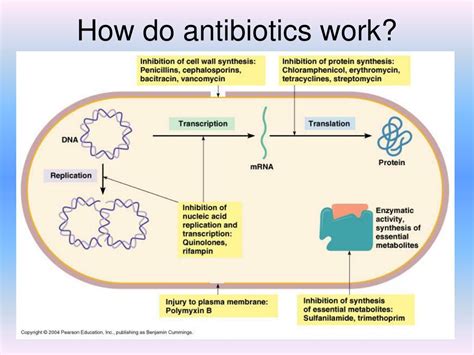
The development of amoxicillin was a response to the need for antibiotics that could overcome the limitations of earlier penicillins, such as narrow spectra of activity and susceptibility to beta-lactamase enzymes produced by certain bacteria. Amoxicillin was engineered to be more resistant to these enzymes, thereby expanding its range of effectiveness. Its introduction into clinical practice marked a significant advancement in the treatment of bacterial infections, offering healthcare providers a powerful tool against a broader range of pathogens.How Amoxicillin Works
Benefits of Amoxicillin
The benefits of amoxicillin are multifaceted. Its broad-spectrum activity makes it a valuable option for treating infections when the causative agent is not yet identified. Additionally, amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, with common side effects being mild and transient. It is also available in various formulations, including oral suspensions and tablets, making it accessible for patients of all ages. The cost-effectiveness of amoxicillin compared to newer antibiotics is another significant advantage, contributing to its widespread use in both developed and developing countries.Common Uses of Amoxicillin

Side Effects and Interactions
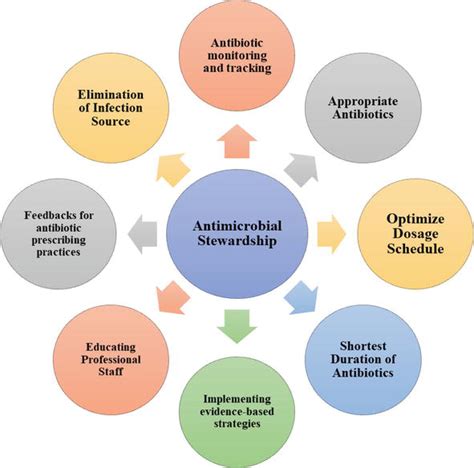
While amoxicillin is generally safe, it can cause side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances like diarrhea and nausea, and allergic reactions ranging from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis. Interactions with other medications, such as anticoagulants and methotrexate, can also occur, necessitating careful monitoring and adjustment of therapy. Patients with a history of allergy to penicillins should avoid amoxicillin, and those with renal impairment may require dose adjustments.Resistance and Stewardship
Future Perspectives
The future of amoxicillin and other antibiotics is closely tied to our ability to address the challenge of antibiotic resistance. Research into new antibiotics and alternative therapies, such as bacteriophage therapy, is underway. Additionally, efforts to improve prescribing practices, enhance infection prevention and control, and develop rapid diagnostic tests to guide antibiotic use will be crucial in extending the useful life of amoxicillin and other current antibiotics.Conclusion and Recommendations

As we reflect on the importance of amoxicillin, it becomes evident that our actions today will shape the future of antibiotic therapy. We invite readers to share their thoughts on how we can collectively work towards responsible antibiotic use and the development of new antimicrobial strategies. Your comments and insights are invaluable in this discussion, and we look forward to hearing your perspectives.
What is amoxicillin used for?
+Amoxicillin is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and certain sexually transmitted infections.
How does amoxicillin work?
+Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to the death of the bacterial cells. It is bactericidal, meaning it kills the bacteria rather than just inhibiting their growth.
What are the common side effects of amoxicillin?
+Common side effects of amoxicillin include gastrointestinal disturbances like diarrhea and nausea, and allergic reactions ranging from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis.
