Intro
Discover what Ana Positive means, a sign of autoimmune disorders like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and sclerosis, indicating immune system dysfunction and potential chronic inflammation, requiring medical attention and diagnosis for effective treatment and management.
The presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in an individual's blood can be an indicator of an underlying autoimmune disorder. Autoimmune disorders occur when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, tissues, and organs. In the case of ANA positivity, the immune system produces antibodies that target the cell nucleus, leading to inflammation and damage.
Autoimmune disorders can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, muscles, and internal organs. Some common autoimmune disorders associated with ANA positivity include systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), scleroderma, and Sjögren's syndrome. These conditions can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can significantly impact an individual's quality of life.
Understanding the implications of ANA positivity is crucial for individuals who have tested positive for these antibodies. It is essential to recognize that a positive ANA test result does not necessarily mean that an individual has an autoimmune disorder. However, it can indicate an increased risk of developing one of these conditions. A comprehensive medical evaluation, including a thorough physical examination, medical history, and additional diagnostic tests, is necessary to determine the underlying cause of ANA positivity.
What is ANA Positivity?
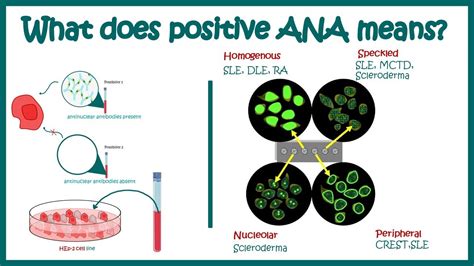
The presence of ANA can be detected through a blood test, which measures the level of these antibodies in the blood. A positive ANA test result indicates that the individual has a higher-than-normal level of these antibodies. However, it is essential to note that a positive ANA test result does not necessarily mean that an individual has an autoimmune disorder. Many people with positive ANA test results do not have any symptoms or signs of an autoimmune disorder.
Types of ANA
There are several types of ANA, each targeting different components of the cell nucleus. The most common types of ANA include: * Anti-dsDNA antibodies: These antibodies target the double-stranded DNA in the cell nucleus. * Anti-histone antibodies: These antibodies target the histone proteins that surround the DNA in the cell nucleus. * Anti-centromere antibodies: These antibodies target the centromere region of the chromosome. * Anti-Scl-70 antibodies: These antibodies target the Scl-70 protein, which is involved in the regulation of gene expression.Each type of ANA is associated with specific autoimmune disorders. For example, anti-dsDNA antibodies are commonly found in individuals with SLE, while anti-histone antibodies are often associated with drug-induced lupus.
Autoimmune Disorders Associated with ANA Positivity
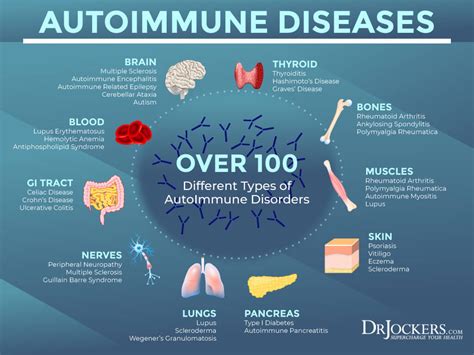
These conditions can cause a range of symptoms, including fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and organ damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage these conditions and prevent long-term damage.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Disorders
The symptoms of autoimmune disorders can vary depending on the specific condition and the organs affected. Common symptoms include: * Fatigue: Feeling tired or exhausted, even after resting. * Joint pain: Pain, stiffness, or swelling in the joints, such as the hands, feet, or knees. * Skin rashes: Red, itchy, or scaly skin lesions, such as those found in lupus or scleroderma. * Organ damage: Damage to internal organs, such as the kidneys, liver, or lungs, which can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or abdominal pain.It is essential to recognize that these symptoms can be nonspecific and may be similar to those of other conditions. A comprehensive medical evaluation, including a thorough physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, is necessary to determine the underlying cause of these symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune Disorders

The diagnostic tests used to diagnose autoimmune disorders include:
- Blood tests: To detect the presence of ANA and other autoantibodies.
- Imaging tests: Such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans, to evaluate the extent of organ damage.
- Biopsy: To examine a sample of tissue from the affected organ.
Treatment for autoimmune disorders depends on the specific condition and the severity of the symptoms. Common treatments include:
- Medications: Such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologics, to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
- Lifestyle modifications: Such as avoiding triggers, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine.
- Alternative therapies: Such as acupuncture, massage, or yoga, to manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage autoimmune disorders and prevent long-term damage. It is crucial to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan and to monitor the condition regularly to adjust the treatment as needed.
Managing Autoimmune Disorders
Managing autoimmune disorders requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies. Some tips for managing autoimmune disorders include: * Staying informed: Learning about the condition, its symptoms, and its treatment options. * Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep. * Managing stress: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises. * Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that can exacerbate the condition.By working with a healthcare provider and following a personalized treatment plan, individuals with autoimmune disorders can manage their symptoms, prevent long-term damage, and improve their overall quality of life.
Prevention and Screening
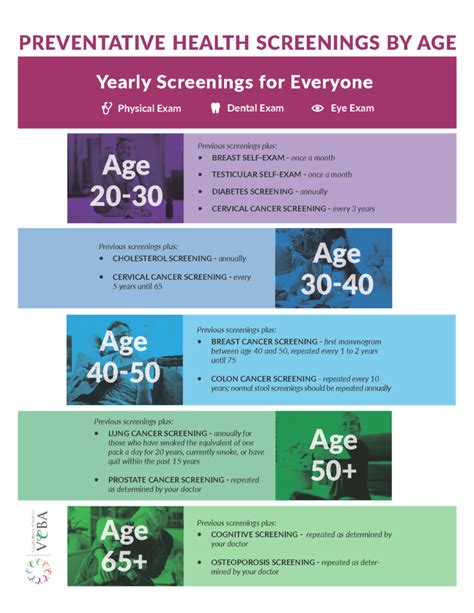
Screening for autoimmune disorders is essential to detect these conditions early, when they are more treatable. The American College of Rheumatology recommends that individuals with a family history of autoimmune disorders or those who are experiencing symptoms of an autoimmune disorder undergo screening.
Screening Tests
The screening tests used to detect autoimmune disorders include: * Blood tests: To detect the presence of ANA and other autoantibodies. * Imaging tests: Such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans, to evaluate the extent of organ damage. * Biopsy: To examine a sample of tissue from the affected organ.Early detection and treatment are essential to manage autoimmune disorders and prevent long-term damage. It is crucial to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized screening plan and to monitor the condition regularly to adjust the treatment as needed.
What is ANA positivity?
+ANA positivity refers to the presence of antinuclear antibodies in an individual's blood. These antibodies are a type of autoantibody that targets the cell nucleus, which contains the genetic material.
What are the symptoms of autoimmune disorders?
+The symptoms of autoimmune disorders can vary depending on the specific condition and the organs affected. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and organ damage.
How are autoimmune disorders diagnosed?
+Diagnosing autoimmune disorders can be challenging, as the symptoms can be nonspecific and similar to those of other conditions. A comprehensive medical evaluation, including a thorough physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, is necessary to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms.
In conclusion, ANA positivity can be an indicator of an underlying autoimmune disorder. Understanding the implications of ANA positivity and the associated autoimmune disorders is crucial for individuals who have tested positive for these antibodies. By working with a healthcare provider and following a personalized treatment plan, individuals with autoimmune disorders can manage their symptoms, prevent long-term damage, and improve their overall quality of life. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with autoimmune disorders in the comments below and to share this article with others who may be affected by these conditions.
