Intro
Discover how Ace Inhibitors effectively manage hypertension, reducing blood pressure and cardiovascular risk with angiotensin-converting enzyme blockers, diuretics, and beta blockers for optimal heart health.
Managing blood pressure is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health, as hypertension can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. One of the most commonly prescribed classes of medications for blood pressure control is Ace inhibitors. These drugs have been widely used for decades due to their effectiveness in lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of associated health issues. Understanding how Ace inhibitors work, their benefits, potential side effects, and how they compare to other blood pressure medications is essential for individuals looking to manage their hypertension effectively.
The importance of blood pressure control cannot be overstated. High blood pressure, or hypertension, affects millions of people worldwide and is a leading cause of premature death. It can lead to the hardening and thickening of arteries, heart failure, and an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. The management of hypertension often involves lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, but for many individuals, medication is necessary to bring their blood pressure under control. Ace inhibitors are a cornerstone in the treatment of hypertension due to their ability to not only lower blood pressure but also to protect against organ damage.
The mechanism of action of Ace inhibitors is what sets them apart from other types of blood pressure medications. They work by blocking the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), a naturally occurring substance in the body that constricts blood vessels and increases blood pressure. By inhibiting this enzyme, Ace inhibitors cause blood vessels to relax and widen, which lowers blood pressure and increases the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart. This action also reduces the workload on the heart, which can help to slow the progression of heart failure and reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Ace Inhibitors Mechanism and Benefits
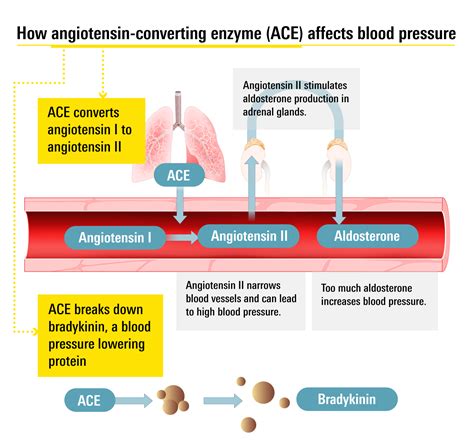
Types of Ace Inhibitors
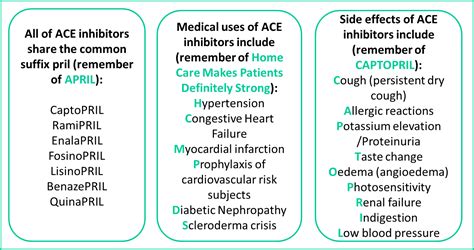
There are several types of Ace inhibitors available, each with its own unique characteristics and side effect profiles. Some of the most commonly prescribed Ace inhibitors include lisinopril, enalapril, captopril, and ramipril. The choice of which Ace inhibitor to use depends on various factors, including the patient's specific health conditions, other medications they are taking, and how well they tolerate the medication. For example, lisinopril is often prescribed for patients with heart failure because it has been shown to improve survival and reduce hospitalization.Side Effects and Precautions
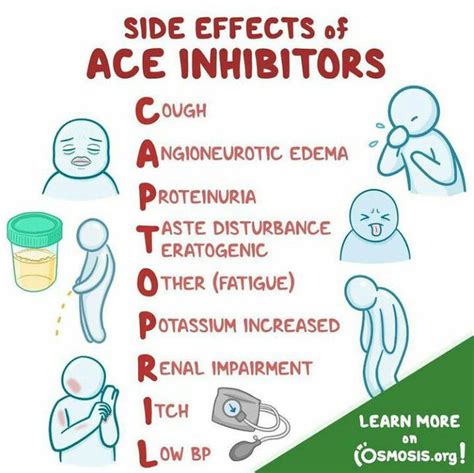
Comparing Ace Inhibitors to Other Blood Pressure Medications
Ace inhibitors are just one of many classes of medications used to treat hypertension. Other classes include diuretics, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). The choice of medication depends on the individual's specific health needs and how they respond to treatment. For example, diuretics are often used as a first-line treatment because they are effective and inexpensive, but they may not offer the same level of kidney protection as Ace inhibitors. ARBs work similarly to Ace inhibitors but are used when patients cannot tolerate the side effects of Ace inhibitors, such as the cough.Using Ace Inhibitors Effectively
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Ace Inhibitor Effectiveness
Lifestyle changes play a critical role in the management of hypertension. A diet low in salt and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower blood pressure. Regular physical activity, such as walking, can also reduce blood pressure and improve overall health. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are additional steps that can enhance the effectiveness of Ace inhibitors and improve overall cardiovascular health. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can also help to reduce blood pressure.Ace Inhibitors in Special Populations

Potential Future Developments
Research into the use of Ace inhibitors and other blood pressure medications is ongoing. Newer medications and combination therapies are being developed to improve blood pressure control and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, there is a growing interest in the use of Ace inhibitors for conditions beyond hypertension, such as heart failure and diabetic nephropathy. As our understanding of the mechanisms of hypertension and the actions of Ace inhibitors evolves, we can expect to see the development of more targeted and effective treatments.Conclusion and Next Steps

Final Thoughts
The management of hypertension is a complex and ongoing process. Ace inhibitors are just one part of this process, but they play a critical role. As research continues to uncover the complexities of hypertension and the mechanisms of Ace inhibitors, we can expect to see new and innovative treatments emerge. In the meantime, individuals with hypertension must remain vigilant, working with their healthcare providers to find the right treatment plan and making lifestyle changes to enhance the effectiveness of their medications.What are Ace inhibitors used for?
+Ace inhibitors are primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart failure. They work by relaxing blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure and increases the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart.
What are the common side effects of Ace inhibitors?
+Common side effects of Ace inhibitors include a dry cough, dizziness, and increased potassium levels. Less common but more serious side effects can include kidney problems and angioedema, a condition characterized by swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Can Ace inhibitors be used in pregnant women?
+Ace inhibitors are generally avoided in pregnant women, particularly in the second and third trimesters, due to the risk of fetal harm. However, in some cases, the benefits of using an Ace inhibitor may outweigh the risks, and the decision should be made under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
We hope this comprehensive guide to Ace inhibitors has provided you with valuable insights into the management of hypertension and related conditions. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with Ace inhibitors, please don't hesitate to comment below. Your input can help others understand the complexities of hypertension treatment and the role that Ace inhibitors play in maintaining good health.
