Intro
Discover how antibiotics combat strep throat, exploring 5 effective ways they fight strep infections, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications, using antimicrobial properties to target bacterial causes.
The importance of antibiotics in fighting bacterial infections cannot be overstated. Among the many types of bacterial infections, strep throat is one of the most common and contagious. It is caused by the Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria and can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Fortunately, antibiotics have proven to be highly effective in treating strep throat and other strep infections. In this article, we will delve into the world of antibiotics and explore the ways in which they fight strep infections.
Antibiotics have been a cornerstone of modern medicine for decades, providing a powerful tool in the fight against bacterial infections. By understanding how antibiotics work and how they are used to treat strep infections, individuals can better appreciate the importance of these medications and take steps to use them responsibly. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, it is more important than ever to use antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary. In the following sections, we will examine the mechanisms by which antibiotics fight strep infections and discuss the different types of antibiotics that are commonly used to treat these infections.
The use of antibiotics to treat strep infections is a well-established practice that has been shown to be highly effective. By targeting the bacteria that cause these infections, antibiotics can help to alleviate symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and prevent the spread of infection to others. In addition to their use in treating strep throat, antibiotics are also used to treat a range of other strep infections, including skin infections, pneumonia, and septicemia. With their ability to target and eliminate bacteria, antibiotics have revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections and saved countless lives.
How Antibiotics Work
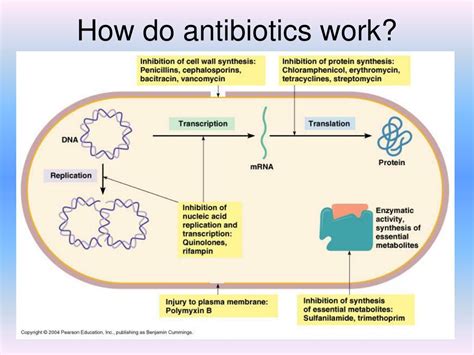
Types of Antibiotics
There are several types of antibiotics that are commonly used to treat strep infections, including penicillin, amoxicillin, and azithromycin. Each of these antibiotics has its own unique mechanism of action and is effective against a specific range of bacteria. By selecting the most appropriate antibiotic for the type of bacteria causing the infection, healthcare providers can ensure that patients receive the most effective treatment possible.Benefits of Antibiotics in Treating Strep Infections

Common Antibiotics Used to Treat Strep Infections
Some of the most common antibiotics used to treat strep infections include: * Penicillin: This is one of the most commonly used antibiotics to treat strep throat and other strep infections. * Amoxicillin: This antibiotic is often used to treat strep throat and other bacterial infections, particularly in children. * Azithromycin: This antibiotic is often used to treat strep throat and other bacterial infections, particularly in individuals who are allergic to penicillin.5 Ways Antibiotics Fight Strep
Importance of Completing the Full Course of Antibiotics
It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. This is because stopping the antibiotic too soon can allow the bacteria to develop resistance, making the infection more difficult to treat.Side Effects and Risks of Antibiotics

Preventing Antibiotic Resistance
To prevent antibiotic resistance, it is essential to use antibiotics responsibly and only when necessary. This includes: * Only using antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare provider * Completing the full course of antibiotics as prescribed * Not sharing antibiotics with others * Not using antibiotics to treat viral infections, such as the common cold or fluConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with antibiotics and strep infections in the comments below. Have you or a loved one been treated with antibiotics for a strep infection? What was your experience like? Do you have any questions or concerns about antibiotics or strep infections? Share your story and help others understand the importance of responsible antibiotic use.
What are the most common antibiotics used to treat strep infections?
+The most common antibiotics used to treat strep infections include penicillin, amoxicillin, and azithromycin.
How long does it take for antibiotics to start working?
+Antibiotics can start working within a few days of starting treatment, but it may take several days to a week or more to fully recover from a strep infection.
Can I stop taking antibiotics if I start to feel better?
+No, it is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
