Intro
Understand what an antibody screen negative result means. Learn about false negatives, test accuracy, and implications for blood donations, transfusions, and medical treatments, including antibody testing and screening processes.
The importance of understanding medical test results cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to something as critical as an antibody screen. An antibody screen is a test used to detect the presence of antibodies in the blood, which are proteins produced by the immune system in response to foreign substances. This test is commonly used in blood banks to ensure the safety of the blood supply and in medical settings to diagnose and monitor various conditions. A negative result on an antibody screen can be a source of relief, but it's essential to understand what this result means and its implications.
Understanding the concept of antibodies and their role in the body is crucial for grasping the significance of an antibody screen negative result. Antibodies are a key part of the immune system, helping to fight off infections and diseases. When the body detects a foreign substance, such as a virus or bacteria, it produces antibodies specifically designed to target and neutralize that substance. The presence of certain antibodies can indicate current or past infections, exposure to certain substances, or the presence of autoimmune diseases. Therefore, detecting these antibodies through a screen can provide valuable information about an individual's health status.
The process of interpreting an antibody screen involves understanding the test's sensitivity and specificity. A negative result indicates that the test did not detect any significant levels of antibodies against the substances it was designed to identify. This can be reassuring, especially in the context of blood transfusions, where the risk of transmitting infectious diseases is a concern. However, it's also important to recognize that no test is 100% accurate, and there are scenarios where a negative result might not entirely rule out the presence of antibodies or the risk of disease transmission. Therefore, healthcare professionals must consider the results of an antibody screen in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and clinical evaluations.
What is an Antibody Screen?
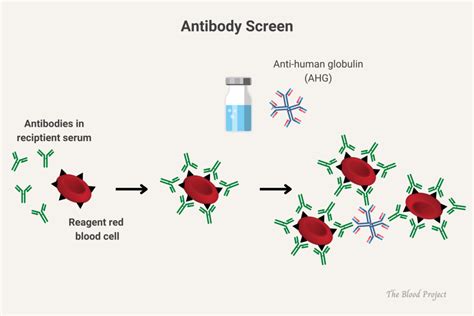
How Does an Antibody Screen Work?
The process of conducting an antibody screen involves several steps. First, a blood sample is collected from the individual being tested. This sample is then sent to a laboratory where it is mixed with various antigens (substances that can trigger an immune response) to see if any antibodies react with these antigens. If antibodies are present, they will bind to the antigens, and this reaction can be detected using specialized techniques. The results of the test are then interpreted to determine if any significant antibody reactions were observed.Interpreting Antibody Screen Results
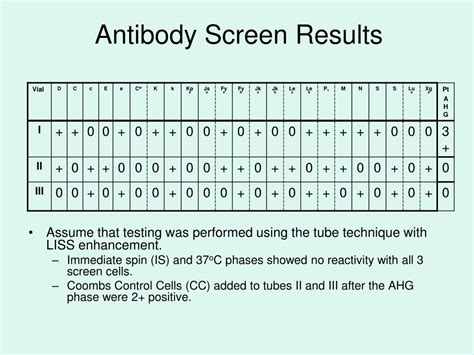
Implications of a Negative Result
The implications of a negative antibody screen result can vary depending on the context in which the test was performed. For individuals being screened for blood donation, a negative result is reassuring and indicates that the blood is safe for transfusion. In clinical settings, a negative result can help rule out certain diagnoses or reduce the suspicion of specific infections. However, healthcare providers must also consider the limitations of the test and the possibility of false-negative results. This might involve repeating the test at a later time or using additional diagnostic tools to confirm or rule out a diagnosis.Limitations of Antibody Screens

False-Negative and False-Positive Results
False-negative and false-positive results are significant concerns in the interpretation of antibody screen results. A false-negative result occurs when the test fails to detect antibodies that are actually present, potentially leading to missed diagnoses or incorrect assumptions about safety. On the other hand, a false-positive result indicates the presence of antibodies when none are actually there, which can lead to unnecessary anxiety, additional testing, and even inappropriate treatment. Understanding the potential for these errors is crucial for healthcare providers and individuals undergoing testing, as it underscores the importance of considering test results in the context of overall clinical evaluation.Applications of Antibody Screens
Future Directions
The future of antibody screening holds much promise, with advancements in technology and methodology continually improving the accuracy, speed, and scope of these tests. Next-generation sequencing and other molecular techniques are being explored for their potential to detect antibodies with higher sensitivity and specificity. Additionally, there is a growing interest in using antibody screens for predictive medicine, where the presence of certain antibodies might indicate an individual's risk of developing specific diseases or their likelihood of responding to certain treatments.Conclusion and Next Steps

Encouraging Engagement
If you or someone you know has recently undergone an antibody screen, we encourage you to share your experiences and ask questions in the comments below. Understanding and discussing the implications of medical test results can help foster a community of informed individuals who are better equipped to navigate the healthcare system and make informed decisions about their health. Additionally, consider sharing this article with others who might benefit from a deeper understanding of antibody screens and their role in modern medicine.What does a negative antibody screen result mean?
+A negative result generally indicates that no significant levels of antibodies were detected, suggesting that the individual has not been exposed to the substances tested for or has not developed an immune response to them.
Can a negative antibody screen result be wrong?
+Yes, there is a possibility of false-negative results, which can occur due to the window period of the disease, the sensitivity and specificity of the test, or other factors.
What are the applications of antibody screens in medicine?
+Antibody screens are used in blood banking to ensure the safety of the blood supply, in clinical practice to diagnose and monitor infectious diseases and autoimmune conditions, and in research to study the immune response and develop new diagnostic tests and treatments.
