Intro
The term Ashkenazi Jewish refers to a specific ethnic and cultural subgroup within the Jewish population. This group originated from Central and Eastern Europe, particularly from countries such as Germany, Poland, and Russia. The history and heritage of Ashkenazi Jews are rich and complex, with a unique blend of traditions, customs, and genetic characteristics. Understanding the Ashkenazi Jewish meaning is essential to appreciating the diversity within the Jewish community and the significant contributions this group has made to Jewish culture and the world at large.
Ashkenazi Jews have a distinct history that dates back to the Middle Ages, when Jewish communities began to form in the Rhineland region of Germany. Over time, these communities developed their own dialect, known as Yiddish, which is a fusion of Middle High German, Hebrew, and other languages. The Ashkenazi Jewish community expanded throughout Europe, with many settling in Poland, Lithuania, and other parts of Eastern Europe. This migration and the subsequent isolation of these communities led to the development of unique cultural and religious practices.
The Ashkenazi Jewish population has made significant contributions to various fields, including science, art, literature, and politics. Many notable figures, such as Albert Einstein, Sigmund Freud, and Golda Meir, are of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. The group's cultural heritage is also reflected in its rich tradition of music, dance, and cuisine, with popular dishes like bagels, knishes, and matzo ball soup originating from Ashkenazi Jewish communities.
Ashkenazi Jewish History and Origins
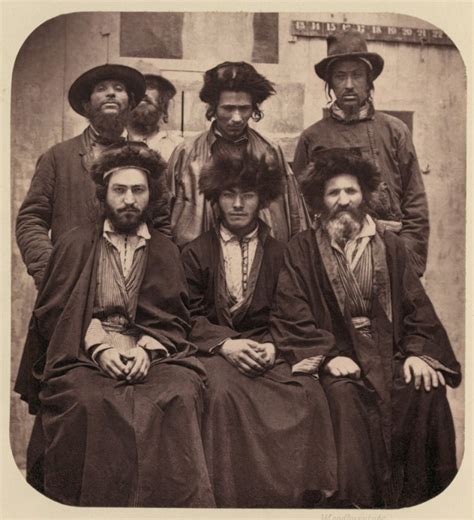

Early Migration and Settlement
The early migration of Jewish communities to Central Europe was driven by a combination of factors, including economic opportunities, religious persecution, and the search for intellectual and cultural exchange. Many Jewish scholars and traders were attracted to the region's thriving trade centers, such as Mainz and Worms, where they could engage in commerce, study, and cultural exchange. As the Ashkenazi Jewish community grew, it developed its own system of governance, education, and social welfare, which was based on the principles of Jewish law and tradition.Ashkenazi Jewish Culture and Traditions

Music and Dance
Ashkenazi Jewish music and dance are also an essential part of the group's cultural heritage. Traditional Ashkenazi Jewish music includes genres such as klezmer, which is characterized by its lively rhythms and soulful melodies. Klezmer music is often played at Jewish weddings and other celebrations, where it is accompanied by traditional dances such as the hora. The hora is a circular dance that is performed to the music of the klezmer band, with participants holding hands and moving in a counterclockwise direction.Ashkenazi Jewish Genetics and Health
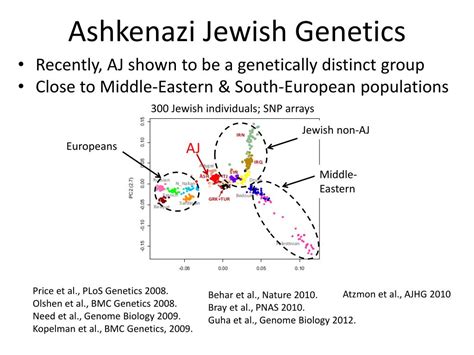
Genetic Screening and Testing
As a result of these genetic risks, many Ashkenazi Jews undergo genetic screening and testing to identify potential mutations and prevent the transmission of genetic disorders to their offspring. Genetic screening is often performed before marriage or during pregnancy, and it can help identify individuals who are carriers of genetic mutations. By identifying these carriers, couples can take steps to prevent the transmission of genetic disorders, such as through the use of in vitro fertilization or preimplantation genetic diagnosis.Ashkenazi Jewish Contributions to Society

Science and Technology
Ashkenazi Jews have been at the forefront of scientific and technological advancements, with many making groundbreaking discoveries in fields such as physics, chemistry, and biology. For example, Albert Einstein's theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of space and time, while Sigmund Freud's development of psychoanalysis transformed the field of psychology. Other notable Ashkenazi Jewish scientists include Jonas Salk, who developed the polio vaccine, and Rosalind Franklin, who contributed to the discovery of the structure of DNA.Ashkenazi Jewish Community and Identity

Preserving Ashkenazi Jewish Heritage
Efforts are being made to preserve Ashkenazi Jewish heritage, including the establishment of museums, cultural centers, and educational institutions. These organizations work to promote Ashkenazi Jewish culture, language, and traditions, as well as to provide a sense of community and belonging for Ashkenazi Jews around the world. Additionally, many Ashkenazi Jews are involved in initiatives to preserve the group's historical and cultural artifacts, such as the restoration of synagogues and the digitization of Yiddish literature and music.Ashkenazi Jewish Cuisine and Traditions

Food and Identity
Food plays a significant role in Ashkenazi Jewish identity, with many dishes serving as a connection to the group's heritage and traditions. For example, the bagel, which originated in Eastern Europe, is a staple of Ashkenazi Jewish cuisine, often served with lox, cream cheese, or other toppings. Similarly, the knish, a filled pastry that is typically filled with potatoes, meat, or cheese, is a popular snack in many Ashkenazi Jewish communities.Ashkenazi Jewish Education and Learning

Yeshivas and Talmudic Studies
Yeshivas, or Jewish seminaries, have played a central role in Ashkenazi Jewish education for centuries. These institutions provide a rigorous program of study in Jewish law, Talmudic studies, and other subjects, with many students going on to become rabbis, scholars, or community leaders. The study of Talmud, a central text of Jewish law and tradition, is a key component of Ashkenazi Jewish education, with many yeshivas placing a strong emphasis on Talmudic studies.Ashkenazi Jewish Challenges and Opportunities

Interfaith Dialogue and Cooperation
Another opportunity for the Ashkenazi Jewish community is interfaith dialogue and cooperation. By engaging in open and respectful dialogue with other faith communities, Ashkenazi Jews can build bridges of understanding, promote mutual respect, and work towards common goals. This can involve initiatives such as interfaith education, cultural exchange programs, and joint community service projects.What is the origin of the term "Ashkenazi"?
+The term "Ashkenazi" is derived from the Hebrew word "Ashkenaz," which refers to Germany. Over time, the term came to be used to describe Jewish communities from Central and Eastern Europe.
What are some common Ashkenazi Jewish genetic disorders?
+Some common Ashkenazi Jewish genetic disorders include Tay-Sachs disease, Gaucher's disease, and breast cancer. These disorders are often caused by genetic mutations that are more common in the Ashkenazi Jewish population.
What is the significance of Yiddish in Ashkenazi Jewish culture?
+Yiddish is a unique and important part of Ashkenazi Jewish culture, serving as a symbol of identity, community, and heritage. It is a fusion of Middle High German, Hebrew, and other languages, and has been spoken by Ashkenazi Jews for centuries.
How can I learn more about Ashkenazi Jewish history and culture?
+There are many ways to learn more about Ashkenazi Jewish history and culture, including reading books and articles, attending cultural events and festivals, and visiting museums and historical sites. You can also explore online resources, such as websites and documentaries, to gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating topic.
What are some traditional Ashkenazi Jewish dishes?
+Some traditional Ashkenazi Jewish dishes include bagels, knishes, matzo ball soup, kugel, and cholent. These dishes are often served at Jewish holidays and celebrations, and are a delicious reflection of the group's cultural heritage.
As we conclude our exploration of the Ashkenazi Jewish meaning, we hope that you have gained a deeper understanding and appreciation of this fascinating topic. From the group's rich history and cultural heritage to its significant contributions to society, the Ashkenazi Jewish community is a vibrant and diverse group that continues to thrive and evolve in the modern era. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about this topic, and to continue exploring the many wonders of Ashkenazi Jewish culture and identity. Whether you are Ashkenazi Jewish yourself or simply interested in learning more, we hope that this article has provided a valuable resource and starting point for your journey of discovery.
