Intro
Learn about Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion Treatment, a procedure restoring heart rhythm, using electrical cardioversion, medication, and ablation to manage AFib symptoms, preventing stroke and heart failure.
Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat, also known as arrhythmia, that can increase the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications. It occurs when the upper chambers of the heart, or atria, beat too quickly and irregularly, preventing the heart from pumping blood effectively. One of the treatment options for atrial fibrillation is cardioversion, a procedure that aims to restore a normal heart rhythm. In this article, we will delve into the world of atrial fibrillation cardioversion treatment, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to the topic.
Atrial fibrillation affects millions of people worldwide, and its prevalence is expected to increase as the population ages. The condition can be caused by various factors, including high blood pressure, heart valve problems, and certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders. Symptoms of atrial fibrillation may include palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain. If left untreated, atrial fibrillation can lead to serious complications, making it essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
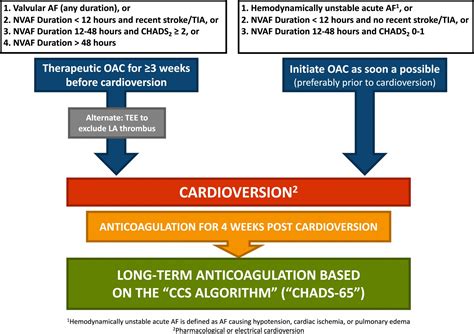
The primary goal of treating atrial fibrillation is to restore a normal heart rhythm and prevent complications. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition, underlying causes, and individual patient needs. Medications, such as blood thinners and anti-arrhythmics, are often used to control symptoms and prevent stroke. However, in some cases, cardioversion may be recommended to restore a normal heart rhythm. Cardioversion is a non-surgical procedure that uses electrical shocks or medication to convert an abnormal heart rhythm back to a normal one.
Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion Treatment Overview
Benefits of Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion Treatment
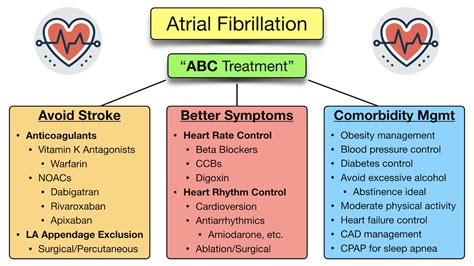
The benefits of cardioversion for atrial fibrillation are numerous. The procedure can help restore a normal heart rhythm, reducing the risk of stroke and heart failure. Cardioversion can also improve symptoms, such as palpitations and shortness of breath, and enhance overall quality of life. Additionally, cardioversion can reduce the need for long-term medication use, which can have significant benefits for patients with certain medical conditions.How Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion Treatment Works
Steps Involved in Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion Treatment
The steps involved in cardioversion for atrial fibrillation are as follows: * Preparation: The patient is prepared for the procedure, which may include fasting, removing jewelry, and changing into a hospital gown. * Sedation: The patient is given sedation to help them relax during the procedure. * Cardioversion: The cardioversion procedure is performed, either using electrical shocks or medication. * Monitoring: The patient is monitored for several hours to ensure that their heart rhythm has returned to normal.Risks and Complications of Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion Treatment
Precautions and Contraindications for Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion Treatment
There are several precautions and contraindications to consider before undergoing cardioversion for atrial fibrillation. These include: * Pregnancy: Cardioversion is generally avoided during pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester. * Breastfeeding: Cardioversion is generally avoided during breastfeeding, as the medication used during the procedure can pass into breast milk. * Certain medical conditions: Cardioversion may be contraindicated in patients with certain medical conditions, such as severe heart disease or lung disease.Alternative Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation

Long-Term Management of Atrial Fibrillation
Long-term management of atrial fibrillation involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular monitoring. Lifestyle modifications may include: * Quitting smoking * Reducing alcohol consumption * Engaging in regular exercise * Eating a healthy, balanced diet * Managing stressMedications may include:
- Anti-arrhythmic medications
- Anticoagulant medications
- Beta blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
Regular monitoring may include:
- ECGs
- Holter monitors
- Event monitors
- Blood tests
What are the benefits of cardioversion for atrial fibrillation?
+The benefits of cardioversion for atrial fibrillation include restoring a normal heart rhythm, reducing the risk of stroke and heart failure, and improving symptoms.
What are the risks and complications of cardioversion for atrial fibrillation?
+The risks and complications of cardioversion for atrial fibrillation include stroke, heart attack, arrhythmias, and bleeding.
What are the alternative treatment options for atrial fibrillation?
+Alternative treatment options for atrial fibrillation include medications, catheter ablation, and surgical ablation.
How can I manage atrial fibrillation in the long term?
+Long-term management of atrial fibrillation involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular monitoring.
What are the precautions and contraindications for cardioversion for atrial fibrillation?
+The precautions and contraindications for cardioversion for atrial fibrillation include pregnancy, breastfeeding, and certain medical conditions.
In conclusion, atrial fibrillation cardioversion treatment is a highly effective option for restoring a normal heart rhythm and reducing the risk of stroke and heart failure. While it is not without risks and complications, the benefits of cardioversion far outweigh the risks for many patients. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to cardioversion, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with atrial fibrillation cardioversion treatment in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
