Intro
Discover 5 key uses of Augmentin, a potent antibiotic, for treating bacterial infections, pneumonia, skin infections, and more, with its amoxicillin and clavulanic acid combination, fighting antibiotic resistance and promoting recovery.
The importance of antibiotics in modern medicine cannot be overstated. These medications have revolutionized the treatment of bacterial infections, saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions of people around the world. Among the many antibiotics available, Augmentin stands out for its effectiveness against a wide range of bacterial infections. Understanding the uses and benefits of Augmentin is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it can help ensure that this powerful medication is used appropriately and safely.
Augmentin, a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that has been widely used for decades. Its unique formulation allows it to overcome certain types of bacterial resistance, making it a valuable tool in the fight against infections. The combination of amoxicillin, a penicillin-like antibiotic, and clavulanic acid, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, extends the spectrum of activity of the antibiotic, allowing it to target a broader range of bacteria, including those that might be resistant to amoxicillin alone.
The versatility of Augmentin is one of its most significant advantages. It can be used to treat a variety of infections, from mild to severe, and is available in different formulations, including tablets, chewable tablets, and a liquid suspension, making it suitable for patients of all ages. This flexibility, combined with its efficacy, has made Augmentin a popular choice among healthcare providers for treating bacterial infections. However, like all antibiotics, it must be used judiciously to minimize the risk of side effects and the development of antibiotic resistance.
Introduction to Augmentin

Augmentin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. The amoxicillin component interferes with the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, while clavulanic acid blocks the action of beta-lactamase enzymes that some bacteria produce to inactivate amoxicillin. This dual mechanism of action makes Augmentin effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Benefits of Augmentin
The benefits of Augmentin are numerous. It is effective against many common bacterial infections, including those of the respiratory tract, skin, and urinary tract. Its broad-spectrum activity means that it can be used empirically before the specific bacteria causing an infection are identified. Additionally, Augmentin is generally well-tolerated, with common side effects being mild and temporary.Common Uses of Augmentin
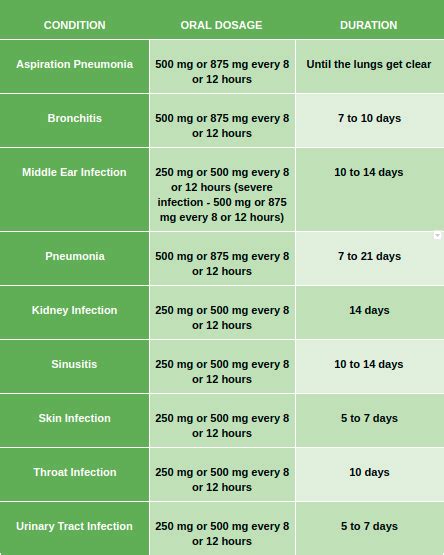
Augmentin is commonly used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including:
- Pneumonia: Augmentin can be used to treat community-acquired pneumonia, which is pneumonia acquired outside of hospitals or other healthcare facilities.
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: These include infections like cellulitis, impetigo, and infected wounds.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Augmentin is effective against many of the bacteria that cause UTIs, including E. coli.
- Sinusitis: Augmentin can be used to treat bacterial sinusitis, which is an infection of the sinuses.
Administration and Dosage
The dosage and administration of Augmentin depend on the type and severity of the infection being treated, as well as the patient's age, weight, and renal function. It is crucial to follow the prescribing instructions carefully to ensure the infection is fully treated and to minimize the risk of side effects.Side Effects and Precautions

While Augmentin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash. In rare cases, more serious side effects can occur, such as allergic reactions or liver dysfunction. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential side effects and to report any concerns to their healthcare provider.
Interactions with Other Medications
Augmentin can interact with other medications, including blood thinners, methotrexate, and probenecid. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking before starting Augmentin.Resistance and Stewardship

The rise of antibiotic resistance is a global health concern. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics, including Augmentin, contribute to the development of resistance. Therefore, it is crucial to use Augmentin and other antibiotics judiciously, following principles of antibiotic stewardship to preserve their effectiveness for future generations.
Future Directions
Research into new antibiotics and strategies to combat resistance is ongoing. The development of new beta-lactamase inhibitors and other agents that can overcome resistance mechanisms is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of antibiotics like Augmentin.Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, Augmentin is a valuable antibiotic that plays a critical role in treating bacterial infections. Its effectiveness, combined with its relatively favorable side effect profile, makes it a popular choice among healthcare providers. However, it is essential to use Augmentin responsibly, adhering to principles of antibiotic stewardship to ensure its continued efficacy.
To make the most of Augmentin and other antibiotics, patients should:
- Always follow the prescribing instructions carefully.
- Complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
- Not share antibiotics or use leftover prescriptions.
- Inform their healthcare provider about any allergies or previous reactions to antibiotics.
By working together, we can preserve the effectiveness of Augmentin and other antibiotics, ensuring they remain a vital tool in the fight against bacterial infections for years to come.
What is Augmentin used for?
+Augmentin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including pneumonia, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and sinusitis.
How does Augmentin work?
+Augmentin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. It does this through a dual mechanism of action, with amoxicillin interfering with the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall and clavulanic acid blocking the action of beta-lactamase enzymes.
What are the common side effects of Augmentin?
+Common side effects of Augmentin include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash. In rare cases, more serious side effects can occur, such as allergic reactions or liver dysfunction.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about Augmentin and its uses in the comments below. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most accurate and helpful information possible. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this knowledge. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of antibiotics and their role in maintaining our health and well-being.
