The average BMI index is a widely used metric to assess an individual's weight status and potential health risks associated with their weight. Understanding the average BMI index is essential, as it can help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle and health. In recent years, there has been a growing concern about the increasing prevalence of obesity and related health issues, making it crucial to understand the concept of BMI and its implications. The average BMI index is a vital tool for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals to promote healthy weight management and reduce the risk of weight-related health problems.
The importance of understanding the average BMI index cannot be overstated, as it has significant implications for public health. A high or low BMI can increase the risk of various health problems, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Moreover, a healthy BMI can improve overall well-being, increase energy levels, and enhance mental health. With the rising burden of obesity and related health issues, it is essential to educate individuals about the average BMI index and its significance in maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By understanding the average BMI index, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their weight, reduce health risks, and improve their overall quality of life.
The concept of BMI has been widely used for decades, and its significance in assessing weight status and health risks has been extensively researched. BMI is calculated by dividing an individual's weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. The resulting value is then categorized into different weight status categories, including underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese. Understanding these categories and the average BMI index is crucial in identifying potential health risks and taking preventive measures. Furthermore, the average BMI index can vary across different populations, ages, and ethnic groups, making it essential to consider these factors when interpreting BMI values.
Average Bmi Index Calculation
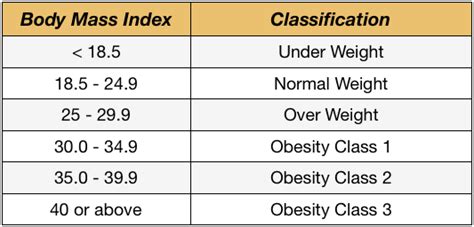
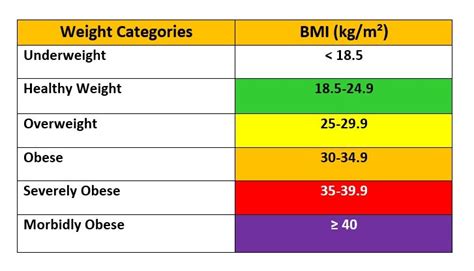
The calculation of the average BMI index involves a simple mathematical formula. To calculate BMI, individuals need to know their weight in kilograms and their height in meters. The formula for calculating BMI is: BMI = weight (in kg) / height (in meters) squared. For example, if an individual weighs 70 kg and is 1.75 meters tall, their BMI would be: BMI = 70 kg / (1.75 m)² = 22.9. This value can then be categorized into different weight status categories, including underweight (BMI < 18.5), normal weight (BMI = 18.5-24.9), overweight (BMI = 25-29.9), and obese (BMI ≥ 30).
Weight Status Categories
The average BMI index is categorized into different weight status categories, each with its own set of health implications. Understanding these categories is essential in identifying potential health risks and taking preventive measures. The weight status categories are:
* Underweight: BMI < 18.5
* Normal weight: BMI = 18.5-24.9
* Overweight: BMI = 25-29.9
* Obese: BMI ≥ 30
Each category has its own set of health risks, and understanding these risks is crucial in maintaining a healthy lifestyle. For example, individuals with a BMI in the underweight category may be at risk of osteoporosis, while those in the obese category may be at risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Health Risks Associated With Bmi
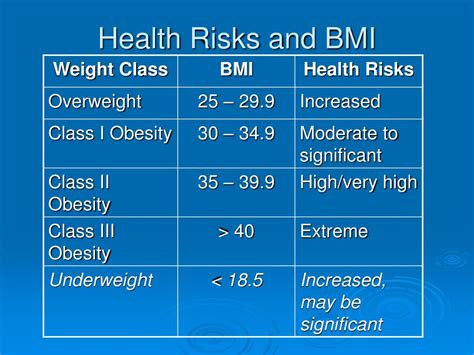
The average BMI index is associated with various health risks, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Understanding these risks is essential in taking preventive measures and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Some of the health risks associated with BMI include:
* Cardiovascular disease: High BMI values are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure.
* Diabetes: High BMI values are associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
* Certain types of cancer: High BMI values are associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, colon, and kidney cancer.
* Osteoarthritis: High BMI values are associated with an increased risk of osteoarthritis, particularly in the joints of the hips, knees, and spine.
* Mental health: High BMI values are associated with an increased risk of mental health problems, including depression and anxiety.
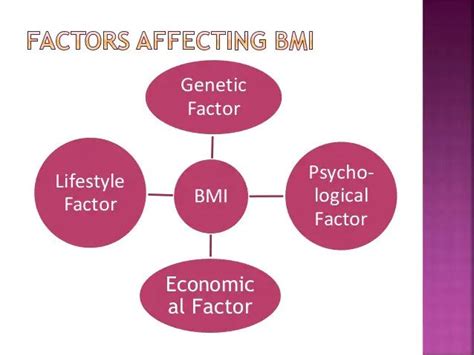
Factors Affecting Bmi
The average BMI index can be affected by various factors, including age, sex, ethnicity, and lifestyle. Understanding these factors is essential in interpreting BMI values and taking preventive measures. Some of the factors that can affect BMI include:
* Age: BMI values can change with age, with older adults tend to have higher BMI values than younger adults.
* Sex: BMI values can differ between men and women, with women tend to have higher BMI values than men.
* Ethnicity: BMI values can differ between different ethnic groups, with some ethnic groups tend to have higher BMI values than others.
* Lifestyle: Lifestyle factors, such as diet and physical activity, can affect BMI values.
Interpretation Of Bmi Values
The interpretation of BMI values is essential in understanding the average BMI index and its implications for health. BMI values can be interpreted in different ways, including:
* Underweight: BMI < 18.5
* Normal weight: BMI = 18.5-24.9
* Overweight: BMI = 25-29.9
* Obese: BMI ≥ 30
Understanding these categories is essential in identifying potential health risks and taking preventive measures.
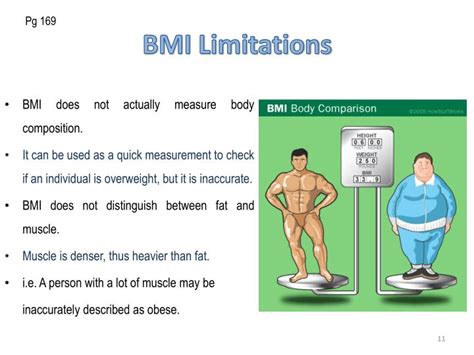
Limitations Of Bmi
The average BMI index has several limitations, including:
* Does not account for muscle mass: BMI does not distinguish between lean body mass and body fat, which can lead to misclassification of individuals with high muscle mass.
* Does not account for age and sex: BMI does not account for age and sex differences in body composition, which can lead to misclassification of older adults and women.
* Does not account for ethnicity: BMI does not account for ethnic differences in body composition, which can lead to misclassification of individuals from different ethnic groups.
Alternatives To Bmi
There are several alternatives to BMI, including:
* Waist circumference: Measures the distance around the natural waistline, which can be an indicator of central obesity.
* Waist-to-hip ratio: Measures the ratio of waist circumference to hip circumference, which can be an indicator of central obesity.
* Body fat percentage: Measures the percentage of body fat, which can be an indicator of overall health.
* Skinfold measurements: Measures the thickness of skinfolds at different points on the body, which can be an indicator of body fat percentage.
Conclusion And Recommendations
In conclusion, the average BMI index is a widely used metric to assess an individual's weight status and potential health risks associated with their weight. Understanding the average BMI index is essential in identifying potential health risks and taking preventive measures. However, the average BMI index has several limitations, and alternative measures, such as waist circumference and body fat percentage, can provide a more accurate assessment of health risks. Based on the findings of this article, the following recommendations can be made:
* Individuals should aim to maintain a healthy weight, with a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9.
* Individuals should engage in regular physical activity and follow a balanced diet to maintain a healthy weight.
* Individuals should consult with a healthcare professional to determine their individual health risks and develop a plan to manage their weight and reduce their risk of chronic diseases.
What is the average BMI index?
+
The average BMI index is a widely used metric to assess an individual's weight status and potential health risks associated with their weight. It is calculated by dividing an individual's weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared.
What are the weight status categories?
+
The weight status categories are: underweight (BMI < 18.5), normal weight (BMI = 18.5-24.9), overweight (BMI = 25-29.9), and obese (BMI ≥ 30).
What are the health risks associated with BMI?
+
The health risks associated with BMI include cardiovascular disease, diabetes, certain types of cancer, osteoarthritis, and mental health problems.
How can I maintain a healthy weight?
+
Individuals can maintain a healthy weight by engaging in regular physical activity, following a balanced diet, and consulting with a healthcare professional to determine their individual health risks and develop a plan to manage their weight and reduce their risk of chronic diseases.
What are the limitations of BMI?
+
The limitations of BMI include not accounting for muscle mass, age and sex, and ethnicity, which can lead to misclassification of individuals.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the average BMI index and its implications for health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with your friends and family to help promote healthy weight management and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. By working together, we can create a healthier and more informed community.