Intro
Discover key Azithromycin facts, including its antibacterial uses, dosage, and side effects, to understand this antibiotics role in treating infections, respiratory issues, and more, with insights into its mechanism, benefits, and potential interactions.
Antibiotics have revolutionized the way we treat bacterial infections, and one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics is Azithromycin. This medication has been widely used for decades to treat a variety of infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. However, despite its widespread use, there are many facts about Azithromycin that are not well-known to the general public. In this article, we will delve into the world of Azithromycin and explore some of the most interesting and important facts about this medication.
Azithromycin is a type of macrolide antibiotic, which works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. It is commonly prescribed for both adults and children, and is available in a variety of forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquid suspensions. One of the main advantages of Azithromycin is its long half-life, which means that it can be taken once a day, making it a convenient option for people with busy schedules. Additionally, Azithromycin has been shown to be effective against a wide range of bacteria, including those that are resistant to other types of antibiotics.
The importance of Azithromycin cannot be overstated, as it has been instrumental in saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions of people around the world. However, like all medications, Azithromycin is not without its risks and side effects. It is essential to take Azithromycin exactly as prescribed by a doctor, and to be aware of the potential risks and benefits associated with its use. In the following sections, we will explore some of the most interesting and important facts about Azithromycin, including its history, mechanism of action, and potential side effects.
Azithromycin History and Development
The development of Azithromycin was a major breakthrough in the field of antibiotic research, as it provided a new and effective treatment option for a wide range of bacterial infections. Since its introduction, Azithromycin has been widely used to treat infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis, as well as skin infections and sexually transmitted diseases. Today, Azithromycin is one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics in the world, and its use has been instrumental in saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions of people.
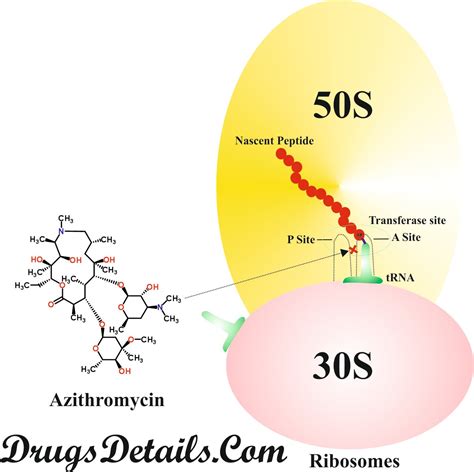
Azithromycin Mechanism of Action
One of the key advantages of Azithromycin is its ability to concentrate in high levels in the tissues, which allows it to effectively target and eliminate bacteria. Additionally, Azithromycin has a long half-life, which means that it can be taken once a day, making it a convenient option for people with busy schedules. The medication is also available in a variety of forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquid suspensions, which makes it easy to administer to both adults and children.
Azithromycin Benefits and Uses

Azithromycin is also effective against a wide range of bacteria, including those that are resistant to other types of antibiotics. This makes it a valuable treatment option for people who have developed antibiotic-resistant infections. Additionally, Azithromycin has been shown to be safe and effective in both adults and children, making it a popular choice for families and healthcare providers.
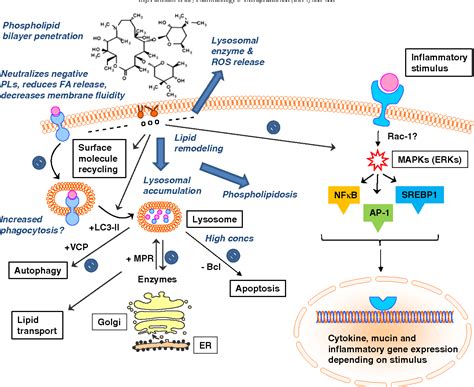
Azithromycin Side Effects and Risks

In rare cases, Azithromycin can also cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Allergic reactions and anaphylaxis
- Liver damage and elevated liver enzymes
- Kidney damage and acute kidney injury
- Cardiac arrhythmias and QT prolongation
It is essential to take Azithromycin exactly as prescribed by a doctor, and to be aware of the potential risks and benefits associated with its use. People who are allergic to Azithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics should not take the medication, and those with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, should use caution when taking Azithromycin.
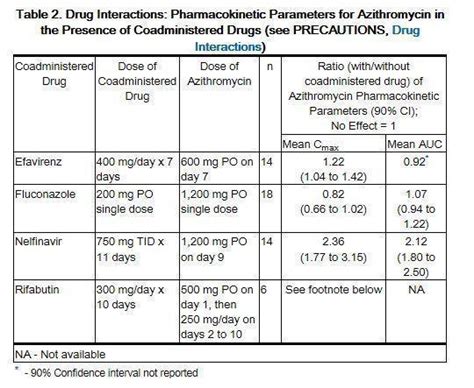
Azithromycin Interactions and Contraindications
People who are taking Azithromycin should avoid consuming grapefruit and grapefruit juice, as it can increase the levels of the medication in the blood and increase the risk of side effects. Additionally, people who are allergic to Azithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics should not take the medication, and those with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, should use caution when taking Azithromycin.
Azithromycin Dosage and Administration
Azithromycin can be taken with or without food, but it is recommended to take it with food to reduce the risk of stomach upset. The medication should be taken exactly as prescribed by a doctor, and the full course of treatment should be completed to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Azithromycin Resistance and Future Directions

Some of the future directions for Azithromycin include the development of new formulations and delivery systems, such as extended-release tablets and injectable forms. Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of Azithromycin in combination with other medications to enhance its effectiveness and reduce the risk of resistance.
What is Azithromycin used for?
+Azithromycin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases.
How does Azithromycin work?
+Azithromycin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, which is essential for the treatment of bacterial infections.
What are the common side effects of Azithromycin?
+The common side effects of Azithromycin include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain, headache and dizziness, fatigue and weakness, and rash and itching.
Can I take Azithromycin with other medications?
+Azithromycin can interact with other medications and substances, so it is essential to consult with a doctor before taking it with other medications.
How can I reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance when taking Azithromycin?
+To reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance, it is essential to take Azithromycin exactly as prescribed by a doctor, complete the full course of treatment, and avoid sharing the medication with others.
In conclusion, Azithromycin is a powerful and effective antibiotic that has been instrumental in saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions of people around the world. By understanding the benefits, risks, and uses of Azithromycin, people can make informed decisions about their health and well-being. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Azithromycin in the comments section below, and to consult with a doctor before taking any medication.
