Intro
Discover B12 as Cyanocobalamin benefits, boosting energy, brain function, and nerve health with this essential vitamin, also aiding in red blood cell formation and anemia prevention.
The importance of vitamins and supplements in our daily lives cannot be overstated. One such crucial vitamin is B12, also known as cyanocobalamin, which plays a significant role in various bodily functions. From the production of red blood cells to the maintenance of the nervous system, B12 is essential for overall health and well-being. Despite its importance, many individuals suffer from B12 deficiency, which can lead to a range of health problems. In this article, we will delve into the benefits of B12 as cyanocobalamin, exploring its functions, benefits, and the ways in which it can be incorporated into our daily lives.
B12 deficiency is a common issue, particularly among certain groups such as vegetarians, vegans, and older adults. This deficiency can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, and neurological problems. However, by understanding the benefits of B12 as cyanocobalamin, individuals can take steps to prevent deficiency and maintain optimal health. Whether through dietary changes, supplements, or other means, incorporating B12 into our daily routine can have a significant impact on our overall well-being.
The benefits of B12 as cyanocobalamin are numerous and well-documented. From reducing the risk of heart disease to improving cognitive function, this vitamin plays a critical role in maintaining our health. In addition to its physical benefits, B12 also has a significant impact on our mental health, with research suggesting that it can help to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. As we explore the benefits of B12 as cyanocobalamin, it becomes clear that this vitamin is an essential component of a healthy lifestyle.
B12 as Cyanocobalamin: What is it?
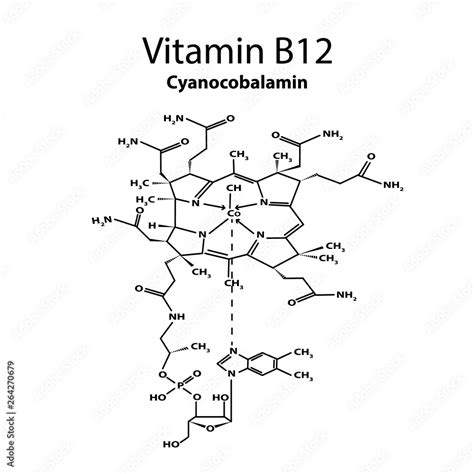
Functions of B12 as Cyanocobalamin
The functions of B12 as cyanocobalamin are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key functions of this vitamin include: * The production of red blood cells: B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. * The maintenance of the nervous system: B12 plays a critical role in the maintenance of the nervous system, including the production of myelin, the fatty substance that surrounds nerve fibers. * The synthesis of DNA: B12 is involved in the synthesis of DNA, the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and function of all living organisms.Benefits of B12 as Cyanocobalamin

Food Sources of B12 as Cyanocobalamin
B12 as cyanocobalamin can be found in a variety of food sources, including: * Meat: Meat is a rich source of B12, particularly organ meats such as liver and kidney. * Fish: Fish is also a rich source of B12, particularly fatty fish such as salmon and tuna. * Dairy products: Dairy products, such as milk and cheese, are good sources of B12. * Eggs: Eggs are a good source of B12, particularly the yolks.B12 as Cyanocobalamin Deficiency
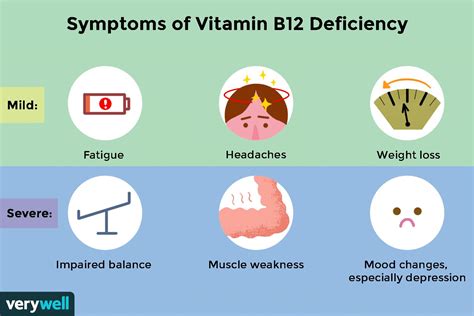
Treatment of B12 as Cyanocobalamin Deficiency
The treatment of B12 deficiency typically involves supplements or injections of B12. In some cases, dietary changes may also be necessary to ensure that the individual is getting enough B12 through their diet. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms of B12 deficiency are experienced, as early treatment can help to prevent long-term damage.B12 as Cyanocobalamin Supplements

Precautions and Interactions of B12 as Cyanocobalamin Supplements
When taking B12 supplements, it is essential to be aware of the potential precautions and interactions. Some of the key precautions and interactions include: * Interactions with medications: B12 supplements can interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners and certain antibiotics. * Allergic reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to B12 supplements, particularly if they have a sensitivity to cobalt. * Overdose: Taking too much B12 can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.What is B12 as cyanocobalamin?
+B12, also known as cyanocobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a critical role in various bodily functions, including the production of red blood cells, the maintenance of the nervous system, and the synthesis of DNA.
What are the benefits of B12 as cyanocobalamin?
+The benefits of B12 as cyanocobalamin include reducing the risk of heart disease, improving cognitive function, and reducing the risk of neurological disorders.
What are the symptoms of B12 deficiency?
+The symptoms of B12 deficiency can vary, but may include fatigue, weakness, and neurological problems, such as numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hands and feet.
In conclusion, B12 as cyanocobalamin is a crucial vitamin that plays a significant role in various bodily functions. From reducing the risk of heart disease to improving cognitive function, the benefits of B12 are numerous and well-documented. By understanding the benefits and functions of B12, individuals can take steps to prevent deficiency and maintain optimal health. Whether through dietary changes, supplements, or other means, incorporating B12 into our daily routine can have a significant impact on our overall well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with B12 as cyanocobalamin in the comments below, and to explore other articles on our website for more information on this essential vitamin.
