Intro
Discover the 5 B12 normal values and understand vitamin B12 levels, including deficiency symptoms, normal ranges, and optimal levels for healthy individuals, covering blood tests, lab results, and medical guidelines.
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in the production of red blood cells, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to various health problems, including anemia, fatigue, and neurological disorders. Therefore, it is essential to understand the normal values of vitamin B12 in the body and how they are measured.
The normal range for vitamin B12 levels in the blood is typically between 200 and 900 picograms per milliliter (pg/mL). However, the ideal range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's overall health. It is also important to note that vitamin B12 levels can fluctuate throughout the day, and a single measurement may not accurately reflect an individual's overall vitamin B12 status.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a common problem, particularly among older adults, vegetarians, and individuals with certain medical conditions. The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can be mild at first, but if left untreated, they can progress to more severe health problems. Some common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, vitamin B12 deficiency can cause neurological problems, such as numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, balance problems, and cognitive impairment.
Vitamin B12 Normal Ranges
The normal range for vitamin B12 levels can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and overall health. In general, the following ranges are considered normal:
- Newborns: 150-640 pg/mL
- Infants: 100-550 pg/mL
- Children: 200-900 pg/mL
- Adults: 200-900 pg/mL
- Pregnant women: 130-650 pg/mL
- Breastfeeding women: 100-500 pg/mL
It is essential to note that these ranges are general guidelines and may vary depending on the specific laboratory and the individual's health status.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
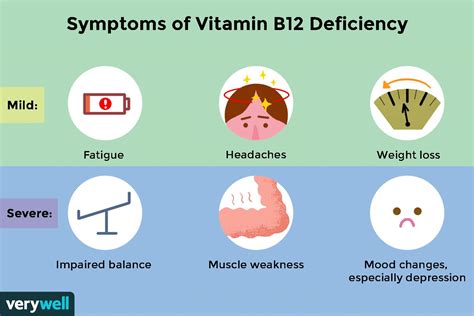
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a common problem that can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Poor diet: Vegetarians and vegans are at a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency because they do not consume animal products, which are rich in vitamin B12.
- Malabsorption: Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and gastric bypass surgery, can impair the absorption of vitamin B12 from food.
- Increased demand: Pregnant and breastfeeding women have a higher demand for vitamin B12, which can lead to deficiency if not met.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and metformin, can interfere with vitamin B12 absorption.
Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can be mild at first, but if left untreated, they can progress to more severe health problems. Some common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet
- Balance problems
- Cognitive impairment
Vitamin B12 Testing

Vitamin B12 levels can be measured using a blood test. The test measures the amount of vitamin B12 in the blood and can help diagnose deficiency or toxicity. There are two types of vitamin B12 tests:
- Serum vitamin B12 test: This test measures the amount of vitamin B12 in the blood serum.
- Urine methylmalonic acid (MMA) test: This test measures the amount of MMA in the urine, which is a byproduct of vitamin B12 metabolism.
The serum vitamin B12 test is the most commonly used test to diagnose vitamin B12 deficiency. However, it may not always accurately reflect the body's vitamin B12 status. The urine MMA test can provide a more accurate diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency, particularly in individuals with borderline vitamin B12 levels.
Vitamin B12 Food Sources

Vitamin B12 is found naturally in animal products, such as:
- Meat: Beef, pork, lamb, and veal
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey, and duck
- Fish and seafood: Salmon, tuna, and shrimp
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Eggs
Plant-based sources of vitamin B12 include:
- Fortified plant-based milk
- Fortified cereals
- Nutritional yeast
- Seaweed
It is essential to note that plant-based sources of vitamin B12 are not always reliable, and individuals who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet may need to take supplements to meet their daily needs.
Vitamin B12 Supplements

Vitamin B12 supplements are available in various forms, including:
- Oral supplements: Tablets, capsules, and lozenges
- Injectable supplements: Vitamin B12 injections
- Nasal supplements: Vitamin B12 nasal sprays
Vitamin B12 supplements can help treat deficiency and prevent health problems. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements, as they can interact with medications and have side effects.
Vitamin B12 Benefits

Vitamin B12 has several benefits, including:
- Producing red blood cells: Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Maintaining nerve function: Vitamin B12 is necessary for the maintenance of healthy nerves and the transmission of nerve impulses.
- Supporting DNA synthesis: Vitamin B12 is involved in the synthesis of DNA, which is essential for cell growth and development.
- Reducing homocysteine levels: Vitamin B12 helps reduce homocysteine levels in the blood, which can help prevent cardiovascular disease.
Overall, vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining overall health. Understanding the normal values of vitamin B12 and how they are measured can help diagnose deficiency and prevent health problems.
What are the normal values of vitamin B12?
+The normal range for vitamin B12 levels in the blood is typically between 200 and 900 pg/mL. However, the ideal range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's overall health.
What are the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
+Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can be mild at first, but if left untreated, they can progress to more severe health problems. Some common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and shortness of breath.
How is vitamin B12 deficiency diagnosed?
+Vitamin B12 deficiency is typically diagnosed using a blood test that measures the amount of vitamin B12 in the blood. The test can help diagnose deficiency or toxicity and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
What are the benefits of vitamin B12?
+Vitamin B12 has several benefits, including producing red blood cells, maintaining nerve function, supporting DNA synthesis, and reducing homocysteine levels. Overall, vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining overall health.
Can vitamin B12 deficiency be prevented?
+Yes, vitamin B12 deficiency can be prevented by consuming a balanced diet that includes animal products, such as meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products. Individuals who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet may need to take supplements to meet their daily needs.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of vitamin B12 normal values and their importance in maintaining overall health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Additionally, if you are experiencing any symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember, maintaining adequate vitamin B12 levels is crucial for preventing health problems and ensuring overall well-being.
