Intro
Improve overall health with 5 basal body tips, enhancing metabolism, balancing hormones, and boosting energy through thermoregulation, temperature regulation, and core body heat management techniques.
The basal body is a crucial component of the cell division process, playing a central role in the formation of cilia, flagella, and centrioles. Understanding the basal body is essential for gaining insights into various cellular processes, including cell signaling, cell division, and the development of certain diseases. In this article, we will delve into the world of basal bodies, exploring their structure, function, and importance in cellular biology.
The basal body is a complex organelle found in eukaryotic cells, responsible for the formation of cilia and flagella. These structures are vital for cell motility, signaling, and the transport of molecules across the cell surface. The basal body is composed of a cylindrical structure made up of nine triplet microtubules, which are arranged in a specific pattern to form the axoneme. This unique structure allows the basal body to perform its functions, including the regulation of cell division, cell signaling, and the development of certain tissues.
The study of basal bodies has become increasingly important in recent years, as researchers have begun to understand the role of these organelles in various diseases, including cancer, respiratory disorders, and neurological conditions. By understanding the structure and function of basal bodies, scientists can gain valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of these diseases, ultimately leading to the development of new treatments and therapies. In this article, we will explore the world of basal bodies, providing an in-depth look at their structure, function, and importance in cellular biology.
Introduction to Basal Bodies
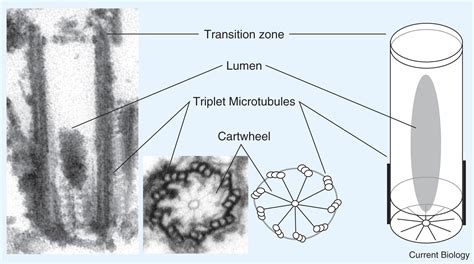
Structure of Basal Bodies
The basal body is composed of several key components, including the triplet microtubules, the axoneme, and the basal plate. The triplet microtubules are arranged in a specific pattern, with each triplet consisting of three microtubules: A, B, and C. The axoneme is the central structure of the basal body, composed of the nine triplet microtubules. The basal plate is a flat, disc-like structure that forms the base of the basal body, attaching it to the cell membrane.Function of Basal Bodies
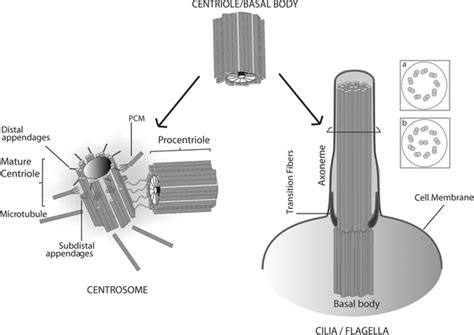
Importance of Basal Bodies in Cellular Biology
The basal body is essential for the proper functioning of eukaryotic cells, playing a crucial role in various cellular processes. The basal body is involved in the regulation of cell division, ensuring that the cell divides correctly and that the genetic material is evenly distributed between the daughter cells. The basal body is also responsible for the formation of cilia and flagella, which are essential for cell motility, signaling, and the transport of molecules across the cell surface.Basal Body and Disease
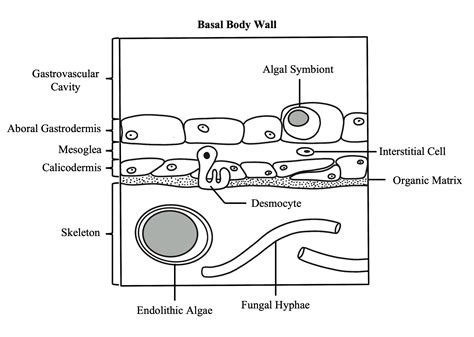
Treatment and Therapy
The study of basal bodies has led to the development of new treatments and therapies for various diseases. Researchers have identified several key components of the basal body that are involved in the regulation of cell division and the formation of cilia and flagella. By targeting these components, scientists can develop new treatments and therapies for diseases such as cancer, respiratory disorders, and neurological conditions.Basal Body and Cell Signaling
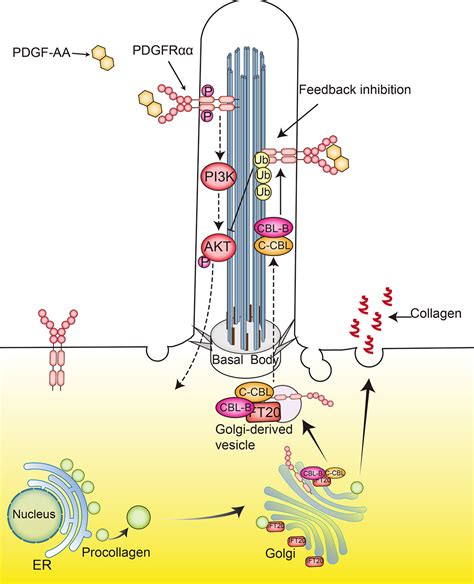
Basal Body and Cell Motility
The basal body is essential for cell motility, regulating the formation of cilia and flagella. The basal body is involved in the formation of the axoneme, which is the central structure of the cilium or flagellum. The axoneme is composed of nine triplet microtubules, which are arranged in a specific pattern to form the axoneme. The basal body is also responsible for the regulation of cell division, ensuring that the cell divides correctly and that the genetic material is evenly distributed between the daughter cells.Basal Body and Development
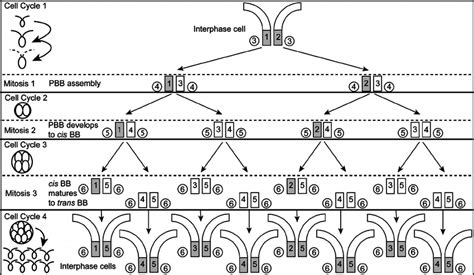
Basal Body and Tissue Formation
The basal body is essential for the formation of certain tissues, including the respiratory and nervous systems. The basal body is involved in the formation of cilia and flagella, which are essential for the proper functioning of these systems. The basal body is also responsible for the regulation of cell division, ensuring that the cell divides correctly and that the genetic material is evenly distributed between the daughter cells.Basal Body and Research

Future Directions
The study of basal bodies is a rapidly evolving field, with new discoveries and advancements being made regularly. Future research directions include the development of new treatments and therapies for diseases related to basal body dysfunction, as well as the exploration of the role of basal bodies in various cellular processes. The study of basal bodies has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of cellular biology and disease, ultimately leading to the development of new treatments and therapies for a range of diseases.What is the basal body?
+The basal body is a small, cylindrical organelle found in eukaryotic cells, typically located at the base of cilia and flagella.
What is the function of the basal body?
+The basal body plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including cell division, cell signaling, and the development of certain tissues.
What diseases are related to basal body dysfunction?
+The basal body has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, respiratory disorders, and neurological conditions.
In conclusion, the basal body is a complex and fascinating organelle that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes. By understanding the structure and function of basal bodies, scientists can gain valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of various diseases, ultimately leading to the development of new treatments and therapies. We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the basal body and its importance in cellular biology. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and colleagues, and join the conversation on social media using the hashtag #basalbody. Together, we can advance our understanding of cellular biology and improve human health.
