Intro
Discover 5 BDD symptoms, including obsessive behaviors, body dysmorphic disorder signs, and compulsive habits, to understand this mental health condition and its effects on self-esteem, anxiety, and daily life.
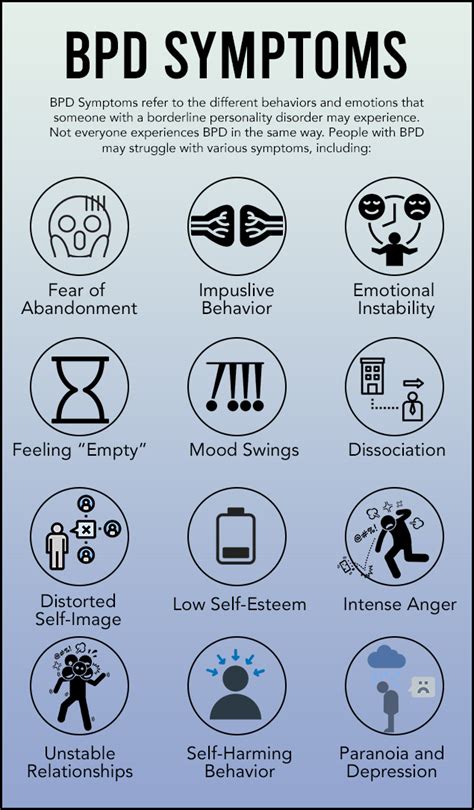
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a complex mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the key aspects of BPD is the presence of borderline personality disorder symptoms, which can have a significant impact on an individual's daily life. In this article, we will delve into the world of BPD symptoms, exploring what they are, how they manifest, and what it means to live with this condition.
The importance of understanding BPD symptoms cannot be overstated. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of this condition, individuals can seek the help they need to manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. Furthermore, educating oneself about BPD symptoms can help to reduce stigma and promote empathy and understanding towards those who are struggling with this condition. Whether you are someone who is living with BPD, or you know someone who is, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the symptoms that are associated with this condition.
Living with BPD can be a challenging and isolating experience. The symptoms of this condition can affect every aspect of an individual's life, from their relationships and work to their daily routines and overall well-being. However, with the right treatment and support, it is possible to manage BPD symptoms and live a fulfilling and meaningful life. In the following sections, we will explore the different types of BPD symptoms, including emotional dysregulation, impulsivity, and interpersonal difficulties. We will also discuss the importance of seeking professional help and the various treatment options that are available for individuals with BPD.
Introduction to BPD Symptoms
Emotional Dysregulation
Emotional dysregulation is a hallmark symptom of BPD. Individuals with this condition often experience intense emotional episodes, which can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, relationships, or past traumas. These emotional episodes can manifest in different ways, including: * Mood swings: Individuals with BPD may experience rapid shifts in mood, moving from feelings of happiness and euphoria to intense anger, sadness, or anxiety. * Irritability: People with BPD may become easily irritated or frustrated, even in response to minor stressors or provocations. * Anxiety: BPD is often associated with anxiety, which can manifest as fear, worry, or apprehension.Impulsivity and Self-Destructive Behaviors
Interpersonal Difficulties
Interpersonal difficulties are a common symptom of BPD. Individuals with this condition may struggle with forming and maintaining healthy relationships, due to: * Intense attachment: People with BPD may become intensely attached to others, which can lead to clingy or dependent behaviors. * Abandonment fears: Individuals with BPD may experience intense fears of abandonment, which can lead to anxiety, anger, or desperation. * Conflict: BPD is often associated with conflict, which can manifest in relationships, workplaces, or social settings.Treatment Options for BPD
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that can be effective in managing BPD symptoms. CBT involves: * Identifying negative thought patterns: Individuals with BPD may learn to identify and challenge negative thought patterns, which can contribute to emotional dysregulation and impulsivity. * Developing coping skills: CBT can help individuals with BPD to develop healthy coping skills, such as problem-solving, self-soothing, or assertiveness.Living with BPD

Reducing Stigma
Reducing stigma is an essential aspect of promoting awareness and understanding of BPD. By educating oneself about BPD symptoms and treatment options, individuals can help to reduce stigma and promote empathy and understanding towards those who are struggling with this condition. Some ways to reduce stigma include: * Educating oneself: Educating oneself about BPD symptoms, treatment options, and recovery stories can help to reduce stigma and promote understanding. * Sharing personal experiences: Sharing personal experiences or stories of recovery can help to reduce stigma and promote hope and inspiration for others. * Supporting others: Supporting others who are struggling with BPD, such as friends, family, or loved ones, can help to reduce stigma and promote a sense of community and connection.Conclusion and Next Steps

What are the common symptoms of BPD?
+The common symptoms of BPD include emotional dysregulation, impulsivity, and interpersonal difficulties. These symptoms can manifest in different ways, including mood swings, irritability, anxiety, substance abuse, reckless spending, and self-destructive behaviors.
How is BPD diagnosed?
+BPD is typically diagnosed through a combination of clinical interviews, psychological assessments, and behavioral observations. A mental health professional will assess the individual's symptoms, behavior, and medical history to determine whether they meet the diagnostic criteria for BPD.
What are the treatment options for BPD?
+The treatment options for BPD include psychotherapy, medications, and lifestyle changes. Psychotherapy, such as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) or psychodynamic therapy, can help individuals with BPD to manage their symptoms and improve their relationships. Medications, such as antidepressants or mood stabilizers, may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of depression, anxiety, or mood instability.
Can BPD be cured?
+While BPD cannot be "cured" in the classical sense, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life with the right treatment and support. With therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes, individuals with BPD can learn to manage their symptoms and live a fulfilling and meaningful life.
How can I support someone with BPD?
+Supporting someone with BPD requires empathy, understanding, and patience. It is essential to educate oneself about BPD symptoms and treatment options, and to provide a supportive and non-judgmental environment. Encouraging the individual to seek professional help, connecting them with support groups, and practicing self-care can also be helpful.
