Intro
Boost potassium intake with 7 rich foods, including bananas, spinach, and sweet potatoes, to support healthy blood pressure, muscle function, and bone health, while preventing deficiency and related diseases like hypokalemia.
Potassium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, including heart health, blood pressure, and muscle function. Despite its importance, many people do not consume enough potassium-rich foods in their diet. The recommended daily intake of potassium is 4,700 milligrams per day, but the average person consumes only about 2,600 milligrams per day. This deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart palpitations. In this article, we will explore the importance of potassium, its benefits, and provide a list of potassium-rich foods that you can incorporate into your diet.
The importance of potassium cannot be overstated. It helps to regulate fluid balance in the body, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Potassium also helps to counteract the effects of sodium, which can help to reduce blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, potassium is essential for maintaining healthy muscles and nerves, which can help to prevent muscle cramps, weakness, and fatigue. With so many benefits, it is essential to ensure that you are consuming enough potassium-rich foods in your diet.
A diet rich in potassium can have a significant impact on overall health and wellbeing. Potassium helps to reduce blood pressure, which can reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. It also helps to regulate blood sugar levels, which can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, potassium helps to maintain healthy bones, which can reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. With so many benefits, it is essential to incorporate potassium-rich foods into your diet.
Potassium Rich Foods

Benefits of Potassium

Potassium Deficiency

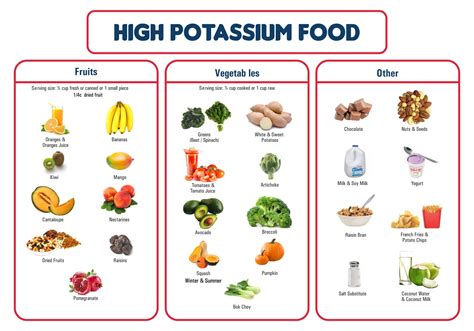
Foods High in Potassium
Potassium Supplements
Potassium and Blood Pressure
Potassium and Heart Health

Importance of Potassium for Athletes
Potassium is essential for athletes, as it helps to regulate fluid balance and maintain healthy muscles and nerves. Here are some ways that potassium can help athletes: * Reduces muscle cramps: Potassium helps to reduce muscle cramps and weakness. * Improves endurance: Potassium helps to improve endurance by regulating fluid balance and maintaining healthy muscles and nerves. * Reduces fatigue: Potassium helps to reduce fatigue by regulating fluid balance and maintaining healthy muscles and nerves.What are the symptoms of a potassium deficiency?
+A potassium deficiency can cause a range of symptoms, including muscle weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps, heart palpitations, and abnormal heart rhythms.
How can I increase my potassium intake?
+You can increase your potassium intake by eating a variety of potassium-rich foods, including leafy greens, fruits, fish, legumes, and nuts and seeds.
Can I take a potassium supplement?
+While potassium supplements are available, they are not necessary for most people. A balanced diet that includes a variety of potassium-rich foods can provide all the potassium you need. However, if you are experiencing symptoms of a potassium deficiency, your doctor may recommend a supplement.
In conclusion, potassium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions. A diet rich in potassium can have a significant impact on overall health and wellbeing, reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. By incorporating potassium-rich foods into your diet, you can help to maintain healthy blood pressure, reduce muscle cramps and weakness, and improve overall health. We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of potassium and how you incorporate potassium-rich foods into your diet. Please comment below and share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of potassium.
