Intro
Diagnose bladder infections with a urine sample test, analyzing symptoms, causes, and treatment options, including UTI diagnosis and lab results.
The importance of diagnosing and treating bladder infections promptly cannot be overstated. These infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing symptoms such as burning during urination, frequent urination, and abdominal pain. One of the key tools in diagnosing bladder infections is the urine sample test, which helps healthcare providers identify the presence of bacteria and determine the best course of treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of bladder infections, exploring the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis methods, with a focus on the urine sample test.
Bladder infections are a common health issue, affecting millions of people worldwide. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor hygiene, sexual activity, and underlying medical conditions. Women are more likely to develop bladder infections due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to enter the bladder more easily. If left untreated, bladder infections can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage and sepsis. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
The symptoms of bladder infections can vary in severity and may include cloudy or strong-smelling urine, pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, and abdominal pain or discomfort. In some cases, individuals may experience fever, chills, or nausea. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. A urine sample test is typically the first step in diagnosing a bladder infection, as it helps healthcare providers identify the presence of bacteria and determine the best course of treatment.
Understanding Bladder Infections
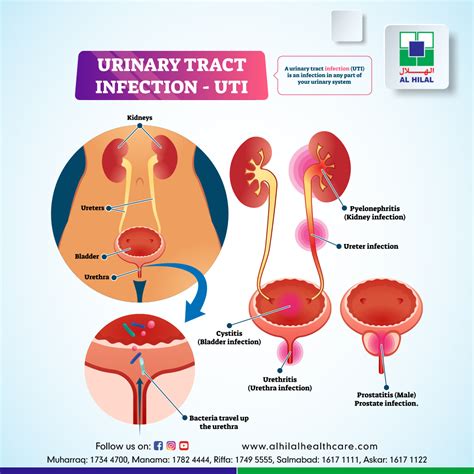
Bladder infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing inflammation and irritation. The most common type of bacteria responsible for bladder infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is normally found in the intestines. However, other bacteria, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus saprophyticus, can also cause bladder infections. Understanding the causes and risk factors of bladder infections is essential in preventing and treating these infections.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes and risk factors of bladder infections are diverse and complex. Some of the most common causes include: * Poor hygiene: Not wiping properly after using the bathroom or not washing hands before touching the genital area can increase the risk of bladder infections. * Sexual activity: Sex can push bacteria into the urethra, leading to bladder infections. * Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney stones, and spinal cord injuries, can increase the risk of bladder infections. * Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to bladder infections.Diagnosing Bladder Infections
Diagnosing bladder infections typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The most common laboratory test used to diagnose bladder infections is the urine sample test, also known as urinalysis. This test involves collecting a urine sample and analyzing it for the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities.
Urine Sample Test
The urine sample test is a crucial diagnostic tool in identifying bladder infections. The test involves collecting a midstream urine sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory test can detect the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities in the urine, such as: * Leukocyte esterase: A substance produced by white blood cells in response to infection. * Nitrites: A substance produced by bacteria that can indicate the presence of an infection. * Blood: The presence of blood in the urine can indicate a bladder infection or other underlying medical condition.Treatment and Prevention

Treating bladder infections typically involves a course of antibiotics, which can help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe pain medication or other treatments to help manage symptoms. Preventing bladder infections involves practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding certain behaviors that can increase the risk of infection.
Prevention Tips
Some tips to help prevent bladder infections include: * Practicing good hygiene: Wipe properly after using the bathroom and wash hands before touching the genital area. * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. * Avoiding certain behaviors: Avoiding sexual activity or using condoms can help reduce the risk of bladder infections. * Managing underlying medical conditions: Keeping underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, under control can help reduce the risk of bladder infections.Complications and Long-Term Effects
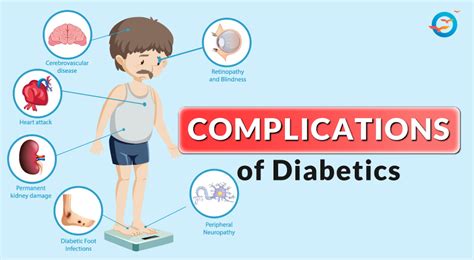
If left untreated, bladder infections can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage and sepsis. Repeated bladder infections can also increase the risk of long-term effects, such as scarring and narrowing of the urinary tract. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Long-Term Effects
Some long-term effects of bladder infections include: * Scarring and narrowing of the urinary tract: Repeated bladder infections can cause scarring and narrowing of the urinary tract, leading to difficulty urinating or increased risk of future infections. * Kidney damage: Untreated bladder infections can lead to kidney damage or failure. * Sepsis: In rare cases, bladder infections can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body's response to an infection becomes uncontrolled.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, bladder infections are a common health issue that can be diagnosed and treated with the help of a urine sample test. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis methods is essential in preventing and treating these infections. If you are experiencing symptoms of a bladder infection, it is crucial to seek medical attention to prevent complications and long-term effects. By practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding certain behaviors, you can reduce the risk of bladder infections and maintain a healthy urinary tract.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with bladder infections in the comments section below. Have you or someone you know been diagnosed with a bladder infection? What steps did you take to prevent and treat the infection? Your feedback and insights can help others understand and manage bladder infections more effectively.
What are the symptoms of a bladder infection?
+The symptoms of a bladder infection can include burning during urination, frequent urination, abdominal pain or discomfort, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and fever or chills.
How is a bladder infection diagnosed?
+A bladder infection is typically diagnosed with a urine sample test, also known as urinalysis, which can detect the presence of bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities in the urine.
What are the complications of untreated bladder infections?
+Untreated bladder infections can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage and sepsis, and increase the risk of long-term effects, such as scarring and narrowing of the urinary tract.
