Intro
Discover the significance of Blood Analysis Hct Levels, including hematocrit, red blood cell count, and hemoglobin tests, to diagnose anemia, blood disorders, and overall health conditions, understanding Hct levels and their impact on wellness.
The importance of blood analysis cannot be overstated, as it provides crucial information about an individual's health and wellbeing. One key component of blood analysis is the measurement of hematocrit (Hct) levels, which can reveal vital details about the body's ability to transport oxygen and fight off infections. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood analysis and explore the significance of Hct levels, including what they mean, how they are measured, and what the results can indicate about a person's health.
Blood analysis is a routine medical procedure that involves examining the various components of blood to diagnose and monitor a range of health conditions. From detecting anemia and blood clotting disorders to identifying signs of infection and inflammation, blood tests are an essential tool for healthcare professionals. Among the various parameters measured in a blood test, Hct levels play a critical role in assessing the body's overall health and identifying potential issues. By understanding what Hct levels represent and how they are interpreted, individuals can gain valuable insights into their health and take proactive steps to maintain their wellbeing.
The measurement of Hct levels is a straightforward process that involves analyzing a blood sample to determine the proportion of red blood cells (RBCs) present. This is typically done using a centrifuge, which separates the blood into its various components, allowing healthcare professionals to calculate the Hct level. The results are usually expressed as a percentage, with normal ranges varying depending on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. In the following sections, we will explore the intricacies of Hct levels, including their significance, measurement, and interpretation, as well as the potential implications of abnormal results.
What are Hct Levels?
Normal Hct Levels
Normal Hct levels vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. In general, the normal range for Hct levels is between 34.9% and 44.5% for adult women and between 40.7% and 50.3% for adult men. These ranges can vary slightly depending on the laboratory or medical institution, but they provide a general guideline for interpreting Hct results. It is essential to note that Hct levels can fluctuate due to various factors, such as dehydration, altitude, and certain medical conditions, so results should be evaluated in conjunction with other health parameters.How are Hct Levels Measured?
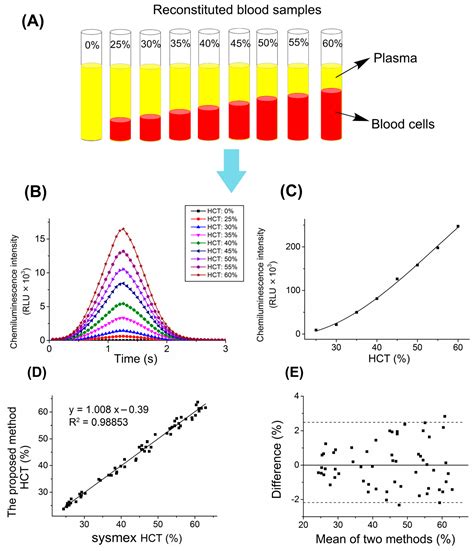
The resulting Hct value provides a snapshot of the body's RBC count and can be used to diagnose and monitor a range of health conditions.
Interpreting Hct Results
Interpreting Hct results requires a comprehensive understanding of the underlying health conditions and factors that can influence the measurement. In general, Hct levels can be categorized into three main ranges: * Normal: Hct levels within the normal range (34.9% to 44.5% for women and 40.7% to 50.3% for men) indicate a healthy RBC count and adequate oxygen transport. * Low: Hct levels below the normal range (e.g., 30% to 34.9% for women and 35% to 40.7% for men) may indicate anemia, blood loss, or other conditions that affect RBC production or destruction. * High: Hct levels above the normal range (e.g., 45% to 50% for women and 51% to 55% for men) may indicate dehydration, polycythemia vera, or other conditions that affect RBC production or viscosity.It is essential to note that Hct results should be evaluated in conjunction with other health parameters, such as hemoglobin levels, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), to gain a comprehensive understanding of the underlying health condition.
Abnormal Hct Levels: Causes and Implications

Abnormal Hct levels can also be associated with various health risks, including:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Pale skin
- Poor wound healing
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if abnormal Hct levels are detected, as prompt diagnosis and treatment can help mitigate potential health risks.
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management of abnormal Hct levels depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common treatments include: * Iron supplements or vitamin injections for anemia * Blood transfusions for severe blood loss * Fluid replacement for dehydration * Medications or surgery for polycythemia veraIn addition to medical treatment, lifestyle modifications can also help manage abnormal Hct levels, such as:
- Increasing iron intake through diet or supplements
- Staying hydrated through adequate fluid intake
- Avoiding excessive sweating or heat exposure
- Engaging in regular exercise to improve cardiovascular health
By understanding the causes and implications of abnormal Hct levels, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and maintain their overall health and wellbeing.
Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Hct levels and blood analysis in the comments section below. Your input can help others better understand the importance of this vital health parameter and encourage them to take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and wellbeing.
What is the normal range for Hct levels in adults?
+The normal range for Hct levels in adults is between 34.9% and 44.5% for women and between 40.7% and 50.3% for men.
What are the causes of low Hct levels?
+Low Hct levels can be caused by anemia, blood loss, or other conditions that affect RBC production or destruction.
How are Hct levels measured?
+Hct levels are measured by analyzing a blood sample using a centrifuge, which separates the blood into its various components.
What are the implications of abnormal Hct levels?
+Abnormal Hct levels can have significant implications for an individual's health and wellbeing, including fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and poor wound healing.
How can I manage abnormal Hct levels?
+Treatment and management of abnormal Hct levels depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but may include iron supplements, blood transfusions, fluid replacement, and lifestyle modifications.
