Intro
Discover the risks of high blood chloride levels, including hypertension, kidney damage, and electrolyte imbalance, and learn 5 ways to manage and reduce chloride levels naturally, promoting overall health and wellbeing.
High blood chloride levels, also known as hyperchloremia, can have significant effects on the body. Chloride is an essential electrolyte that helps maintain fluid balance and is a key component of digestive fluids. However, when chloride levels become elevated, it can lead to a range of health issues. In this article, we will explore the importance of monitoring blood chloride levels and the potential consequences of high blood chloride levels.
The human body regulates electrolyte levels, including chloride, to maintain proper bodily functions. Chloride helps regulate fluid balance and blood pressure, and it is also necessary for the production of digestive fluids. However, when chloride levels become too high, it can disrupt these processes and lead to a range of health problems. High blood chloride levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including dehydration, kidney disease, and certain medications.
It is essential to monitor blood chloride levels to prevent and manage hyperchloremia. Regular blood tests can help identify elevated chloride levels, and healthcare professionals can provide guidance on how to manage and treat high blood chloride levels. In addition to medical treatment, there are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce blood chloride levels. These include staying hydrated, following a balanced diet, and managing stress. By understanding the causes and consequences of high blood chloride levels, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy electrolyte levels and prevent related health issues.
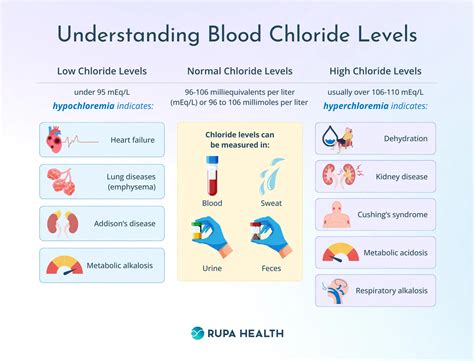
Understanding High Blood Chloride Levels
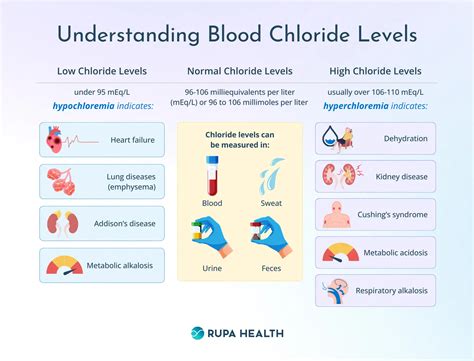
Causes of High Blood Chloride Levels
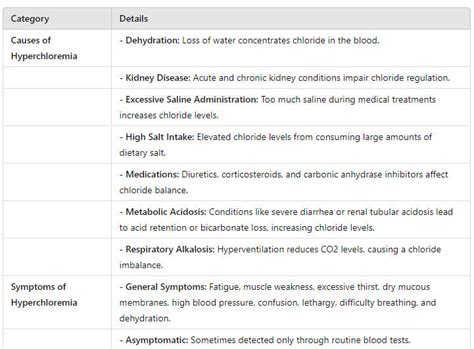
High blood chloride levels can be caused by: * Dehydration * Kidney disease * Certain medications, such as diuretics * Metabolic disorders, such as diabetic ketoacidosis * Respiratory acidosis, a condition characterized by excessive levels of acid in the bloodEffects of High Blood Chloride Levels
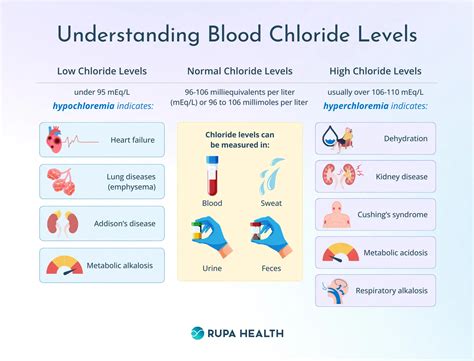
Symptoms of High Blood Chloride Levels
The symptoms of high blood chloride levels can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include: * Fatigue * Muscle weakness * Digestive issues, such as diarrhea or constipation * Fluid imbalance, leading to swelling or bloating * Changes in blood pressure * Respiratory problems, such as shortness of breath or wheezingTreatment and Management of High Blood Chloride Levels
Lifestyle Changes to Manage High Blood Chloride Levels
In addition to medical treatment, there are several lifestyle changes that can help manage high blood chloride levels. These include: * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water to prevent dehydration and fluid imbalance. * Following a balanced diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to help regulate electrolyte levels. * Managing stress: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga, to help manage stress and prevent electrolyte imbalances.Complications of Untreated High Blood Chloride Levels
Prevention of High Blood Chloride Levels
Prevention of high blood chloride levels involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions. This can include: * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water to prevent dehydration and fluid imbalance. * Following a balanced diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to help regulate electrolyte levels. * Managing stress: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga, to help manage stress and prevent electrolyte imbalances. * Regular health check-ups: Regular blood tests and health check-ups to monitor chloride levels and manage underlying conditions.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with high blood chloride levels in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Share this article with friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of monitoring blood chloride levels.
What are the symptoms of high blood chloride levels?
+The symptoms of high blood chloride levels can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, digestive issues, fluid imbalance, changes in blood pressure, and respiratory problems.
How can I manage high blood chloride levels?
+Management of high blood chloride levels depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Medical treatment may include fluid replacement, medications, and dietary changes. Lifestyle changes, such as staying hydrated, following a balanced diet, and managing stress, can also help manage high blood chloride levels.
What are the complications of untreated high blood chloride levels?
+Untreated high blood chloride levels can lead to a range of complications, including kidney damage, respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and muscle weakness. It is essential to monitor blood chloride levels and manage underlying conditions to prevent and treat hyperchloremia.
