Intro
Discover 5 ways to prevent blood clots, reducing risk of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and stroke through lifestyle changes, exercise, and medical interventions, promoting cardiovascular health and overall wellbeing.
Preventing blood clots is a crucial aspect of maintaining overall health, as these clots can lead to serious conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, and even stroke. Blood clots form when the blood's clotting mechanism is activated, either due to injury, certain medical conditions, or prolonged periods of immobility. Understanding the risks and taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing blood clots. This article delves into the importance of blood clot prevention, its benefits, and provides actionable advice on how to incorporate preventive measures into daily life.
The formation of blood clots is a natural process that occurs to prevent excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. However, when clots form unnecessarily or in inappropriate locations, they can pose a significant threat to health. Conditions such as DVT, where a clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs, can be particularly dangerous if the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Given the potential severity of these conditions, adopting lifestyle habits and medical interventions aimed at preventing blood clots is essential for individuals at risk.
Preventing blood clots not only saves lives but also improves the quality of life for those who would otherwise suffer from the debilitating effects of clot-related diseases. By understanding the factors that contribute to blood clot formation, individuals can make informed decisions about their health. Factors such as age, family history, obesity, and prolonged immobility during long flights or bed rest increase the risk of developing blood clots. Awareness of these risk factors is the first step towards taking preventive measures.
Understanding Blood Clots
Understanding how blood clots form and the conditions that predispose individuals to their development is crucial for effective prevention. Blood clots can form due to three main factors: blood flow changes, injury to the blood vessel wall, and alterations in the constitution of blood, making it more prone to clotting. Each of these factors can be influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle elements. For instance, smoking and high blood pressure can damage blood vessel walls, while certain medications and dehydration can affect blood composition.
Risk Factors for Blood Clots
Several risk factors increase an individual's likelihood of developing blood clots. These include but are not limited to: - Age: The risk increases with age, especially after 40. - Family History: A history of blood clots in the family. - Obesity: Being overweight or obese. - Prolonged Bed Rest: Extended periods of immobility due to illness, surgery, or injury. - Long-Distance Travel: Sitting for long periods, such as during long flights or car rides. - Pregnancy: The risk is higher during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth. - Smoking: Damages the lining of blood vessels, making clots more likely. - High Blood Pressure: Can damage blood vessels.Preventive Measures

Preventing blood clots involves a combination of lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medical interventions. For individuals at high risk, such as those undergoing surgery or with a history of clotting disorders, anticoagulant medications may be prescribed. However, for the general population, adopting healthy lifestyle habits is key.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Blood Clots
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in reducing the risk of blood clots. Key changes include: - **Regular Exercise:** Engaging in physical activity helps improve circulation and reduces the risk of obesity. - **Maintaining a Healthy Weight:** Reduces pressure on veins and minimizes the risk of obesity-related conditions. - **Avoiding Prolonged Immobility:** Regular movement, even during long trips, can help prevent clot formation. - **Quitting Smoking:** Reduces damage to blood vessels and decreases the risk of clotting. - **Staying Hydrated:** Helps maintain healthy blood flow and prevents dehydration, which can contribute to clot formation.Medical Interventions

For individuals at high risk of developing blood clots, medical interventions may be necessary. This can include the use of anticoagulant medications, which prevent the formation of blood clots, and in some cases, the use of compression stockings to improve blood flow in the legs.
Anticoagulant Medications
Anticoagulants are prescribed for individuals with a high risk of clot formation, such as those with atrial fibrillation, DVT, or pulmonary embolism. These medications work by preventing the formation of new clots and stopping existing clots from getting bigger. However, they require careful monitoring as they can increase the risk of bleeding.Nutritional Considerations

Diet plays a crucial role in the prevention of blood clots. Certain foods and nutrients can help reduce inflammation, improve blood vessel health, and prevent excessive clotting. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, and those high in antioxidants, like berries, can be beneficial. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining healthy blood flow.
Foods That Help Prevent Blood Clots
- **Omega-3 Rich Foods:** Fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. - **Vitamin E Rich Foods:** Nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils. - **Antioxidant-Rich Foods:** Berries, leafy greens, and other fruits and vegetables. - **Foods High in Fiber:** Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which can help lower cholesterol levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

Preventing blood clots requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, awareness of risk factors, and in some cases, medical intervention. By understanding the factors that contribute to blood clot formation and taking proactive steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk. It's essential for those at high risk to consult with healthcare professionals to discuss personalized preventive strategies.
If you found this information helpful and would like to learn more about maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing blood clots, consider sharing this article with friends and family who may benefit from it. Engaging in conversations about health and wellness can encourage others to take proactive steps towards preventing blood clots and other cardiovascular diseases. Feel free to comment below with any questions or personal stories related to blood clot prevention, and don't forget to subscribe for more health-related content.
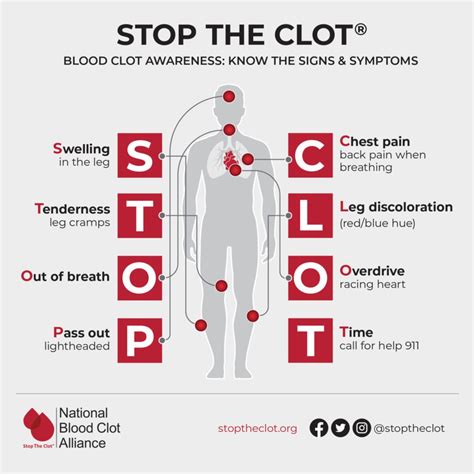
What are the symptoms of a blood clot?
+Symptoms can include pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area, typically the leg. In severe cases, such as pulmonary embolism, symptoms can include sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood.
How can I reduce my risk of blood clots during long flights?
+Stay hydrated, avoid tight clothing, and move regularly by walking up and down the aisle or doing seat stretches. Wearing compression stockings can also help improve blood flow.
Are there any natural remedies for preventing blood clots?
+While there are no proven natural remedies to replace medical treatment, certain foods and supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin E, and turmeric may help reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular health. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
