Intro
Discover 5 ways to maintain normal blood glucose levels, managing diabetes through healthy diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes, ensuring stable blood sugar control and overall wellness.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood glucose levels are within the normal range, the body functions optimally, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke is reduced. In this article, we will explore the importance of normal blood glucose levels, the factors that affect them, and provide tips on how to maintain them.
Normal blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) after eating and less than 100 mg/dL when fasting. However, these levels can vary depending on factors such as age, physical activity level, and overall health. For example, people with diabetes may have higher blood glucose levels due to their body's inability to produce or effectively use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
The consequences of abnormal blood glucose levels can be severe. High blood glucose levels, also known as hyperglycemia, can cause damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs like the kidneys and eyes. On the other hand, low blood glucose levels, or hypoglycemia, can lead to confusion, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness. Therefore, it is essential to maintain normal blood glucose levels to prevent these complications and ensure optimal health.
Understanding Blood Glucose Regulation
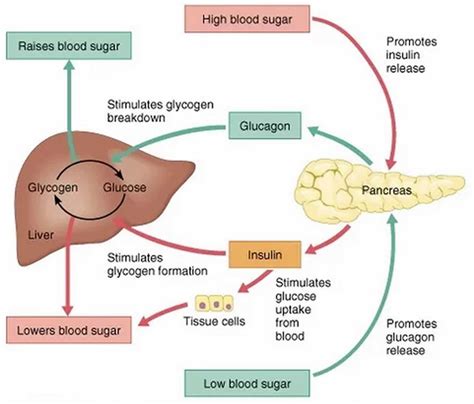
The body regulates blood glucose levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and other organs. The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon, two hormones that play a crucial role in maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Insulin lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells, while glucagon raises blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of glucose stored in the liver.
Factors such as diet, physical activity, and stress can affect blood glucose regulation. For example, consuming high-carbohydrate foods can cause a spike in blood glucose levels, while regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels. Stress can also affect blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise blood glucose levels.
Benefits of Normal Blood Glucose Levels

Maintaining normal blood glucose levels has numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke
- Improved energy levels and mental clarity
- Enhanced physical performance and endurance
- Better digestion and reduced symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Healthier skin, hair, and nails
To maintain normal blood glucose levels, it is essential to adopt a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques. A healthy diet should include a variety of whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Healthy Eating Tips
- Eat regular meals to maintain stable blood glucose levels
- Choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Include lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and legumes
- Healthy fats like avocado, nuts, and seeds can also help regulate blood glucose levels
- Limit sugary drinks and foods high in added sugars
Physical Activity and Blood Glucose Regulation

Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood glucose levels, and enhance overall health. Aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, and cycling are excellent for improving cardiovascular health and reducing blood glucose levels.
Resistance training, on the other hand, can help build muscle mass and improve insulin sensitivity. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is also effective for improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood glucose levels.
Physical Activity Tips
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week
- Include resistance training exercises at least two times per week
- Incorporate HIIT workouts for improved insulin sensitivity and weight management
- Start slowly and gradually increase exercise intensity and duration
Stress Management and Blood Glucose Regulation

Chronic stress can affect blood glucose regulation by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can raise blood glucose levels and worsen insulin resistance. Effective stress management techniques can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on blood glucose regulation.
Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve insulin sensitivity. Getting enough sleep is also essential for maintaining normal blood glucose levels, as sleep deprivation can worsen insulin resistance and increase blood glucose levels.
Stress Management Tips
- Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises
- Get enough sleep (7-9 hours per night) to help regulate blood glucose levels
- Engage in relaxing activities like reading, listening to music, or taking a warm bath
- Take regular breaks and prioritize self-care activities
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Regular blood glucose monitoring can help identify patterns and trends, allowing for adjustments to diet, physical activity, and stress management techniques.
There are several ways to monitor blood glucose levels, including:
- Fasting blood glucose tests
- Postprandial blood glucose tests (after eating)
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices
- Urine tests for ketones (a sign of high blood glucose levels)
Monitoring Tips
- Work with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule
- Use a blood glucose meter or CGM device to track blood glucose levels
- Keep a food and activity diary to identify patterns and trends
- Adjust diet, physical activity, and stress management techniques based on monitoring results
What are normal blood glucose levels?
+Normal blood glucose levels are typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL after eating and less than 100 mg/dL when fasting.
How can I maintain normal blood glucose levels?
+Maintaining normal blood glucose levels requires a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques.
What are the consequences of abnormal blood glucose levels?
+Abnormal blood glucose levels can cause damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs like the kidneys and eyes, and increase the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on individual factors, such as age, physical activity level, and overall health. Work with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule.
What are the benefits of maintaining normal blood glucose levels?
+Maintaining normal blood glucose levels can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve energy levels and mental clarity, enhance physical performance and endurance, and promote overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, maintaining normal blood glucose levels is essential for overall health and well-being. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques, individuals can reduce their risk of chronic diseases and promote optimal health. Regular blood glucose monitoring can help identify patterns and trends, allowing for adjustments to diet, physical activity, and stress management techniques. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on maintaining normal blood glucose levels in the comments below.
