Intro
Discover the 5 causes of blood in cough, including respiratory infections, bronchitis, and lung cancer, and learn about symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for hemoptysis, a condition characterized by coughing up blood or rust-colored mucus.
Coughing is a natural reflex that helps to clear the airways of irritants, but when it's accompanied by blood, it can be a cause for concern. Blood in cough, also known as hemoptysis, can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, ranging from mild to life-threatening. In this article, we'll delve into the possible causes of blood in cough, exploring the potential reasons behind this distressing symptom.
The presence of blood in cough can be alarming, and it's essential to seek medical attention if you experience it. The causes of blood in cough can be broadly categorized into two groups: infectious and non-infectious. Infectious causes include respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and tuberculosis, while non-infectious causes encompass a range of conditions, including lung cancer, pulmonary embolism, and bronchiectasis.
Understanding the underlying causes of blood in cough is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. In the following sections, we'll examine the five primary causes of blood in cough, discussing their symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By exploring these causes, we hope to provide insight into the potential reasons behind this symptom and encourage readers to seek medical attention if they experience blood in their cough.
Respiratory Tract Infections

Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of respiratory tract infections can vary depending on the specific condition. For example, pneumonia may cause high fever, chills, and cough, while bronchitis may lead to a persistent cough and mucus production. Diagnosis of respiratory tract infections typically involves a physical examination, chest X-ray, and laboratory tests to identify the underlying cause.Treatment Options
Treatment for respiratory tract infections depends on the underlying cause. Antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial infections, while antiviral medications may be used to treat viral infections. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide oxygen therapy and supportive care.Lung Cancer
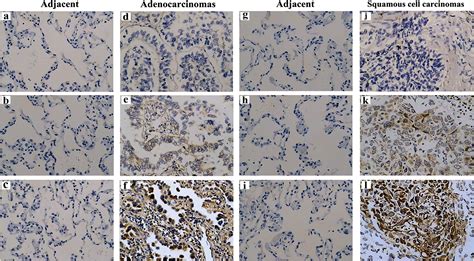
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of lung cancer can be non-specific, making it challenging to diagnose in the early stages. A persistent cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing are common symptoms, but they can also be caused by other conditions. Diagnosis of lung cancer typically involves a combination of imaging tests and biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer.Treatment Options
Treatment for lung cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy may be used to treat lung cancer, either alone or in combination. In some cases, targeted therapy or immunotherapy may be used to treat specific types of lung cancer.Pulmonary Embolism
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of pulmonary embolism can be severe and sudden, making it essential to seek medical attention immediately. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of imaging tests, including CT scan and ventilation-perfusion scan, to confirm the presence of a blood clot.Treatment Options
Treatment for pulmonary embolism typically involves anticoagulant medications to prevent further clotting and promote dissolution of the existing clot. In severe cases, thrombolytic therapy may be used to dissolve the clot quickly.Bronchiectasis

Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of bronchiectasis can be similar to those of other respiratory conditions, making diagnosis challenging. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of imaging tests, including CT scan and bronchoscopy, to confirm the presence of damaged airways.Treatment Options
Treatment for bronchiectasis typically involves a combination of medications, including antibiotics and bronchodilators, to manage symptoms and prevent complications. In some cases, pulmonary rehabilitation may be recommended to improve lung function and overall health.Tuberculosis
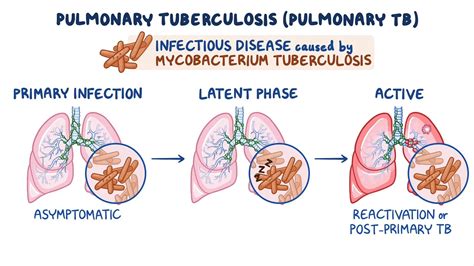
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of tuberculosis can be non-specific, making it challenging to diagnose in the early stages. A persistent cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing are common symptoms, but they can also be caused by other conditions. Diagnosis of tuberculosis typically involves a combination of imaging tests and laboratory tests to confirm the presence of the bacteria.Treatment Options
Treatment for tuberculosis typically involves a combination of antibiotics to kill the bacteria. The treatment regimen may last for several months, and it's essential to complete the full course of treatment to prevent resistance and ensure effective cure.In summary, blood in cough can be caused by various underlying conditions, ranging from mild to life-threatening. Understanding the potential causes of this symptom is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. By exploring the five primary causes of blood in cough, including respiratory tract infections, lung cancer, pulmonary embolism, bronchiectasis, and tuberculosis, we hope to provide insight into the potential reasons behind this symptom and encourage readers to seek medical attention if they experience blood in their cough.
What are the common causes of blood in cough?
+The common causes of blood in cough include respiratory tract infections, lung cancer, pulmonary embolism, bronchiectasis, and tuberculosis.
How is blood in cough diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of blood in cough typically involves a combination of imaging tests, including chest X-ray and CT scan, and laboratory tests to confirm the underlying cause.
What are the treatment options for blood in cough?
+Treatment options for blood in cough depend on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
If you've experienced blood in your cough, it's essential to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause. By understanding the potential causes of this symptom, you can take the first step towards effective diagnosis and treatment. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be experiencing similar symptoms and to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing underlying conditions and preventing complications. Take control of your health today and seek medical attention if you experience blood in your cough.
