Intro
Lisinopril, an ACE inhibitor, effectively lowers high blood pressure, reducing heart risk and stroke, while managing hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and kidney protection.
Lisinopril is a popular medication used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. It belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which work by relaxing blood vessels and reducing the amount of blood the heart has to pump. This can help to lower blood pressure and increase the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart. High blood pressure is a common condition that can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease, if left untreated. Lisinopril is often prescribed to help manage high blood pressure and reduce the risk of these complications.
The importance of managing high blood pressure cannot be overstated. According to the American Heart Association, high blood pressure affects nearly 80 million adults in the United States, and it is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Untreated high blood pressure can cause damage to the blood vessels, heart, and kidneys, leading to serious health problems. Lisinopril is an effective medication for managing high blood pressure, and it has been shown to reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. In addition to its use in treating high blood pressure, lisinopril is also used to treat heart failure, a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
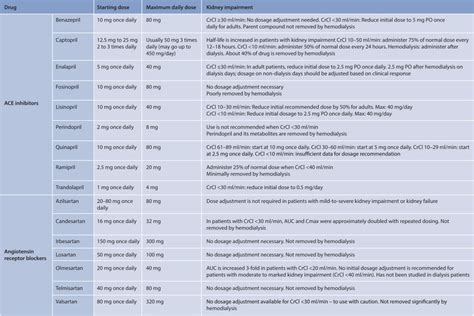
Lisinopril works by blocking the action of a natural chemical in the body called angiotensin II, which causes blood vessels to constrict and blood pressure to rise. By blocking the action of angiotensin II, lisinopril helps to relax blood vessels and reduce blood pressure. This can help to improve blood flow to the heart and reduce the amount of blood the heart has to pump. Lisinopril is usually taken once a day, and it can be taken with or without food. It is available in several different strengths, including 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, and 40 mg. The usual starting dose of lisinopril is 10 mg per day, but this can be adjusted based on the individual's response to the medication.
How Lisinopril Works
Benefits of Lisinopril
The benefits of lisinopril include: * Lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease * Improving blood flow to the heart and reducing the amount of blood the heart has to pump * Reducing the amount of fluid in the body and increasing the amount of potassium * Improving symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue * Reducing the risk of death from cardiovascular diseaseSide Effects of Lisinopril

Precautions and Warnings
Lisinopril can cause a number of precautions and warnings, including: * Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Lisinopril should not be taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding, as it can cause harm to the developing fetus or baby. * Kidney disease: Lisinopril can worsen kidney disease, so it should be used with caution in people with kidney problems. * Liver disease: Lisinopril can worsen liver disease, so it should be used with caution in people with liver problems. * Allergic reactions: Lisinopril can cause allergic reactions, such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.Interactions with Other Medications

Overdose and Missed Dose
If an overdose of lisinopril is suspected, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Symptoms of an overdose can include: * Dizziness * Lightheadedness * Fainting * Low blood pressure * Increased heart rate If a dose of lisinopril is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, the missed dose should be skipped and the regular dosing schedule should be continued.Dosage and Administration
Storage and Disposal
Lisinopril should be stored at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. It should be kept out of reach of children and pets. If lisinopril is no longer needed or has expired, it should be disposed of properly. It should not be flushed down the toilet or thrown away in the trash.Conclusion and Future Directions

What is lisinopril used for?
+Lisinopril is used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. It works by blocking the action of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor, and reducing the amount of blood the heart has to pump.
What are the benefits of lisinopril?
+The benefits of lisinopril include lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. It can also improve symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
What are the side effects of lisinopril?
+The most common side effects of lisinopril include cough, dizziness, headache, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and increased potassium levels.
Can lisinopril be taken with other medications?
+Lisinopril can interact with a number of other medications, including diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and lithium. It is essential to consult a doctor before taking any other medications with lisinopril.
How should lisinopril be stored and disposed of?
+Lisinopril should be stored at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. It should be kept out of reach of children and pets. If lisinopril is no longer needed or has expired, it should be disposed of properly. It should not be flushed down the toilet or thrown away in the trash.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of lisinopril, its uses, benefits, and side effects. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of managing high blood pressure and heart failure. Take action today and consult with your doctor about whether lisinopril is right for you.
