Intro
Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to diabetes, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, impacting glucose control and overall health, requiring management through diet, exercise, and medication to regulate blood glucose and prevent complications.
Elevated blood sugar levels can have a significant impact on an individual's overall health and wellbeing. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can lead to a range of complications, including damage to organs such as the kidneys, heart, and eyes. Furthermore, elevated blood sugar levels can increase the risk of developing conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and nerve damage. It is essential to understand the causes and effects of elevated blood sugar levels to take proactive steps towards managing and regulating them.
The importance of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood sugar levels are within a healthy range, the body can function optimally, and the risk of developing chronic diseases is significantly reduced. However, when blood sugar levels are elevated, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including increased thirst and hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left unmanaged, elevated blood sugar levels can have severe consequences, making it crucial to understand the underlying causes and take steps towards prevention and management.
Elevated blood sugar levels can be caused by a range of factors, including a poor diet, lack of physical activity, and certain medical conditions. For instance, consuming high amounts of sugary and processed foods can lead to a spike in blood sugar levels, while a sedentary lifestyle can reduce the body's ability to regulate blood sugar. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can also cause elevated blood sugar levels. Understanding the underlying causes of elevated blood sugar levels is crucial in developing effective management and prevention strategies.
Blood Sugar Regulation
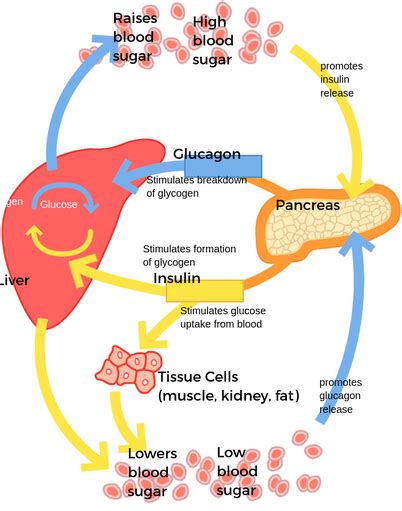
Insulin and Glucagon
The hormones insulin and glucagon play a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin is produced by the pancreas in response to elevated blood sugar levels, and it helps to lower blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. Glucagon, on the other hand, is produced by the pancreas in response to low blood sugar levels, and it helps to raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of glucose from stored energy sources. The balance between insulin and glucagon is crucial in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, and any disruption to this balance can lead to elevated blood sugar levels.Causes of Elevated Blood Sugar

Diet and Lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle play a significant role in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. A diet that is high in whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help to regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases. Additionally, getting enough sleep and managing stress levels can also help to regulate blood sugar levels.Effects of Elevated Blood Sugar
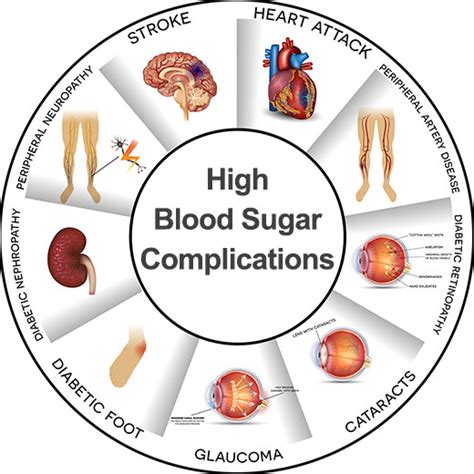
Complications of Elevated Blood Sugar
The complications of elevated blood sugar levels can be severe and long-lasting. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, leading to a range of cardiovascular problems, including heart disease and stroke. Elevated blood sugar levels can also damage the kidneys, leading to kidney disease and kidney failure. Additionally, high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to nerve damage and numbness in the hands and feet.Managing Elevated Blood Sugar

Medical Interventions
Medical interventions, such as medication and insulin therapy, may be necessary to manage elevated blood sugar levels. Medications, such as metformin, can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver. Insulin therapy may also be necessary to help regulate blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with type 1 diabetes. Additionally, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels can help to identify any changes or trends, allowing for prompt interventions and adjustments to treatment plans.Prevention of Elevated Blood Sugar

Risk Factors for Elevated Blood Sugar
There are several risk factors for elevated blood sugar levels, including a family history of diabetes, obesity, and certain medical conditions. A family history of diabetes can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, while obesity can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and acromegaly, can also increase the risk of developing elevated blood sugar levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on managing elevated blood sugar levels. What strategies have you found to be effective in regulating your blood sugar levels? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? Your input and feedback are invaluable in helping us to better understand the complexities of elevated blood sugar levels and develop effective management and prevention strategies.
What are the symptoms of elevated blood sugar levels?
+The symptoms of elevated blood sugar levels include increased thirst and hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left unmanaged, elevated blood sugar levels can lead to a range of complications, including damage to organs such as the kidneys, heart, and eyes.
How can I prevent elevated blood sugar levels?
+Preventing elevated blood sugar levels requires a proactive approach that includes a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. A diet that is low in sugary and processed foods and high in whole, unprocessed foods can help to regulate blood sugar levels.
What are the risk factors for elevated blood sugar levels?
+There are several risk factors for elevated blood sugar levels, including a family history of diabetes, obesity, and certain medical conditions. A family history of diabetes can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, while obesity can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
How can I manage elevated blood sugar levels?
+Managing elevated blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes diet, lifestyle, and medical interventions. A healthy diet that is low in sugary and processed foods and high in whole, unprocessed foods can help to regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases.
What are the complications of elevated blood sugar levels?
+The complications of elevated blood sugar levels can be severe and long-lasting. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, leading to a range of cardiovascular problems, including heart disease and stroke. Elevated blood sugar levels can also damage the kidneys, leading to kidney disease and kidney failure.
