Intro
Discover the 5 ways to achieve a normal range in health metrics, including blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels, through lifestyle changes and natural remedies, promoting overall wellness and disease prevention.
Normal range is a term used in various fields, including medicine, statistics, and quality control. It refers to the typical or expected range of values for a particular measurement or parameter. Understanding what is considered within the normal range is crucial for identifying abnormalities, making informed decisions, and taking appropriate actions. In this article, we will delve into the concept of normal range, its importance, and how it applies to different areas.
The concept of normal range is essential because it provides a benchmark against which individual values can be compared. This comparison allows for the detection of outliers or values that fall outside the expected range, which can be indicative of a problem or an opportunity for improvement. For instance, in medical diagnostics, blood test results are compared against a normal range to determine if a patient's values are within a healthy range or if they indicate a potential health issue.
Normal ranges can vary significantly depending on the context and the specific parameter being measured. For example, the normal range for blood pressure is different from the normal range for blood glucose levels. Moreover, what is considered normal can change over time due to advancements in medical science, changes in population demographics, or shifts in environmental factors. Therefore, it is crucial to stay updated with the latest guidelines and reference ranges.
Understanding Normal Range in Medicine
In medicine, the normal range is critical for diagnosing and managing diseases. Laboratory tests, such as complete blood counts, electrolyte panels, and liver function tests, are compared against established normal ranges to assess a patient's health status. For instance, the normal range for hemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen) in adult men is approximately 13.5 to 17.5 grams per deciliter (g/dL), while in adult women, it is about 12 to 16 g/dL. Values outside these ranges can indicate conditions such as anemia or polycythemia.
The establishment of normal ranges in medicine involves studying large populations to determine the average values and the range of values that are considered healthy. These ranges can be influenced by factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, and the laboratory methods used for testing. Therefore, healthcare providers must consider these factors when interpreting laboratory results.
Factors Influencing Normal Range in Medicine

Several factors can influence what is considered a normal range in medicine. Age is a significant factor, as many physiological parameters change as we age. For example, the normal range for bone density is higher in young adults than in older adults, due to the natural loss of bone mass with aging. Sex is another factor, as men and women can have different normal ranges for certain parameters due to hormonal and physiological differences.
Ethnicity can also influence normal ranges, as genetic variations among different ethnic groups can affect how the body processes certain substances. For instance, individuals of African descent may have a different normal range for certain blood parameters compared to individuals of European descent. Lastly, the methods used for laboratory testing can impact the normal ranges, as different techniques and instruments can produce slightly different results.
Normal Range in Statistics

In statistics, the normal range often refers to the range of values that are within one standard deviation of the mean in a normal distribution. This range typically encompasses about 68% of the data points. Understanding the normal range in statistical terms is essential for data analysis, as it helps in identifying outliers and understanding the distribution of the data.
The normal range in statistics is crucial for hypothesis testing and confidence intervals. For example, in quality control, manufacturers might use statistical process control to ensure that the dimensions of manufactured parts fall within a specified normal range, indicating that the manufacturing process is under control.
Calculating Normal Range in Statistics

Calculating the normal range in statistics involves determining the mean and standard deviation of the dataset. The mean provides the central tendency of the data, while the standard deviation measures the variability or dispersion of the data points. Once these parameters are known, the normal range can be estimated by adding and subtracting one standard deviation from the mean for a basic understanding, though more precise calculations may involve using z-scores or t-distributions, especially when dealing with smaller sample sizes.
Importance of Normal Range in Quality Control
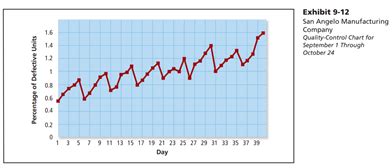
In quality control, understanding the normal range is vital for ensuring that products meet the required specifications and standards. By establishing a normal range for product dimensions, performance metrics, or other critical parameters, manufacturers can quickly identify any deviations that might indicate a problem in the production process.
The normal range in quality control helps in setting tolerance limits for products. For instance, in the manufacturing of auto parts, the normal range for the diameter of a specific component might be set between 9.95 and 10.05 mm. Parts with diameters outside this range would be considered defective and would not pass quality control.
Setting Normal Range in Quality Control

Setting the normal range in quality control involves a thorough analysis of the production process, including the capabilities of the machinery, the variability of the raw materials, and the specifications required by the customer or regulatory standards. Statistical methods, such as control charts, are often used to monitor the production process and ensure that it remains within the established normal range.
Applications of Normal Range
The concept of normal range has wide-ranging applications across various fields. In finance, normal ranges are used to assess the volatility of stocks or the creditworthiness of individuals. In environmental science, normal ranges are established for parameters such as air quality, water purity, and soil contamination to monitor and protect ecosystems.
In education, understanding the normal range can help in assessing student performance and identifying areas where additional support may be needed. By establishing a normal range for test scores or learning outcomes, educators can better understand how individual students or groups of students are performing relative to their peers.
Future of Normal Range

The future of normal range will likely involve more sophisticated and dynamic definitions, especially with the advent of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to establish more precise and personalized normal ranges, taking into account a myriad of factors that might influence an individual's or a system's performance.
Moreover, the integration of real-time data and feedback loops will allow for the continuous updating of normal ranges, reflecting changes in populations, environments, or technologies. This dynamic approach will enable more effective monitoring, decision-making, and intervention across various sectors.
What is the significance of normal range in medical diagnostics?
+The normal range in medical diagnostics is crucial for identifying abnormalities and making informed decisions about patient care. It provides a benchmark against which individual test results can be compared to determine if they fall within a healthy range or indicate a potential health issue.
How is the normal range established in statistics?
+The normal range in statistics is typically established by determining the mean and standard deviation of a dataset. The range of values within one standard deviation of the mean is often considered the normal range, encompassing about 68% of the data points.
What role does normal range play in quality control?
+In quality control, the normal range is vital for ensuring that products meet the required specifications and standards. It helps in setting tolerance limits and identifying any deviations that might indicate a problem in the production process.
In conclusion, the concept of normal range is multifaceted and plays a critical role in various fields, including medicine, statistics, and quality control. Understanding and applying the concept of normal range can lead to better decision-making, improved outcomes, and enhanced performance. As technology advances and data becomes more readily available, the definition and application of normal range will continue to evolve, offering new opportunities for growth and improvement. We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of normal range in different contexts and how it impacts your field of interest. Your insights can contribute to a deeper understanding and more effective application of this concept.
