Intro
Discover 5 ways to manage blood sugar levels with accurate testing, including glucose monitoring, insulin tracking, and diabetes management techniques for optimal health and wellness.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps in managing the condition, preventing complications, and improving the quality of life. Over the years, various methods have been developed to test blood sugar levels, each with its unique advantages and purposes. In this article, we will delve into the different ways blood sugar can be tested, exploring their mechanisms, benefits, and practical applications.
The importance of blood sugar testing cannot be overstated. It provides valuable insights into how the body regulates glucose, helping individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. With the advancements in medical technology, testing blood sugar has become more accessible, accurate, and less invasive. Whether it's through traditional finger-prick tests or more innovative methods, the goal remains the same: to ensure that blood sugar levels are within a healthy range, thereby reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Understanding the different methods of blood sugar testing is essential for effective diabetes management. Each method serves a specific purpose, ranging from daily monitoring to periodic assessments of glucose control. By familiarizing oneself with these testing methods, individuals can better navigate their diabetes care plan, make necessary adjustments, and lead healthier lives. The diversity in testing methods also caters to different needs and preferences, ensuring that there's an option for everyone.
Introduction to Blood Sugar Testing

Blood sugar testing is a critical component of diabetes care. It involves measuring the amount of glucose in the blood to assess how well diabetes is being managed. The primary goal is to keep blood sugar levels as close to the target range as possible to prevent both short-term complications, such as hypoglycemia, and long-term complications, including heart disease and kidney damage.
Benefits of Regular Testing
Regular blood sugar testing offers several benefits: - **Improved glycemic control:** By monitoring blood glucose levels, individuals can identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to their diet, exercise, or medication. - **Reduced risk of complications:** Keeping blood sugar levels within the target range helps prevent diabetes-related complications. - **Enhanced quality of life:** Effective management of blood sugar levels can improve overall health and well-being, enabling individuals to lead active and fulfilling lives.Finger-Prick Test

The finger-prick test, also known as a blood glucose test, is the most common method of monitoring blood sugar levels. It involves pricking the fingertip with a small needle (lancet) to collect a drop of blood, which is then placed on a test strip and inserted into a glucose meter. The meter provides a reading of the current blood glucose level.
How It Works
The process is straightforward: 1. **Prepare the glucose meter:** Ensure the meter is ready for use and has a test strip inserted. 2. **Prick the finger:** Use a lancet to prick the side of the fingertip to collect a blood sample. 3. **Apply blood to the test strip:** Place the drop of blood onto the test strip. 4. **Read the result:** The glucose meter will display the blood glucose level after a few seconds.Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)

Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems track glucose levels throughout the day and night. A small sensor is inserted under the skin, usually on the abdomen or arm, and measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor sends data to a receiver or a smartphone app, providing real-time glucose levels and trends.
Benefits of CGM
CGM offers several advantages: - **Comprehensive data:** Provides a detailed picture of glucose levels over time. - **Reduced finger sticks:** Minimizes the need for frequent finger-prick tests. - **Alerts and alarms:** Can be set to alert the user of high or low glucose levels.Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)

The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) is used to assess the body's ability to regulate blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink. It's commonly used for diagnosing prediabetes and diabetes.
How It Works
The test involves: 1. **Fasting:** The individual fasts overnight. 2. **Glucose consumption:** A sugary drink is consumed. 3. **Blood glucose measurement:** Blood glucose levels are measured at intervals (usually 1 and 2 hours) after consuming the drink.Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Test
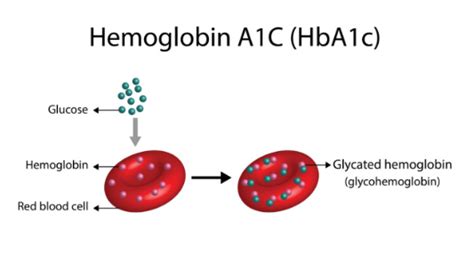
The Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) test provides an average of blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months. It measures the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Interpretation
HbA1c levels are interpreted as follows: - **Below 5.7%:** Normal - **5.7% to 6.4%:** Prediabetes - **6.5% or higher:** DiabetesFlash Glucose Monitoring
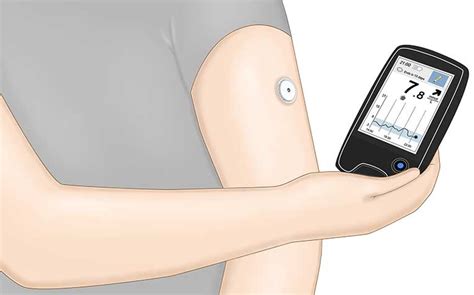
Flash glucose monitoring systems, like FreeStyle Libre, involve a small sensor applied to the back of the upper arm. The sensor measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid and stores data for up to 14 days. Users can scan the sensor with a reader or a smartphone app to get current glucose levels, trends, and historical data.
Advantages
Flash glucose monitoring offers: - **Convenience:** Eliminates the need for finger-prick tests. - **Comprehensive insights:** Provides detailed glucose data for better management.In conclusion, the methods of blood sugar testing are diverse, catering to different needs and preferences. Each method, from traditional finger-prick tests to more advanced technologies like CGM and flash glucose monitoring, plays a vital role in diabetes management. By understanding and utilizing these testing methods effectively, individuals can achieve better glycemic control, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance their overall quality of life.
What is the importance of regular blood sugar testing?
+Regular blood sugar testing is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. It helps in identifying patterns, making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan, and preventing diabetes-related complications.
How often should I test my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of testing depends on the type of diabetes, the treatment plan, and the individual's health status. Generally, people with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes may need to test their blood sugar levels several times a day.
What are the benefits of using a Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) system?
+CGM systems offer comprehensive data on glucose levels, reduce the need for frequent finger-prick tests, and can be set to alert the user of high or low glucose levels, thereby enhancing diabetes management and reducing the risk of complications.
To further engage with the topic of blood sugar testing and its implications for diabetes management, we invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, or explore additional resources. Understanding the nuances of blood sugar testing is a step towards better health outcomes for individuals with diabetes. By embracing the available testing methods and technologies, we can work towards a future where diabetes is managed more effectively, and its impact on lives is minimized.
