Intro
Discover 5 ways to reduce low CO2 emissions, promoting sustainable living, eco-friendly practices, and a healthier environment through carbon footprint reduction and climate change mitigation strategies.
The importance of reducing carbon dioxide emissions cannot be overstated. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, it has become increasingly clear that lowering CO2 levels is crucial for the health of our planet. From individuals to governments, everyone has a role to play in this endeavor. By adopting simple yet effective strategies, we can significantly decrease our carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. In this article, we will delve into the world of low CO2 emissions, exploring the benefits, mechanisms, and practical steps that can be taken to achieve this goal.
As we navigate the complexities of climate change, it is essential to understand the impact of CO2 emissions on our environment. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes are among the primary sources of CO2 emissions, which contribute to global warming and its associated consequences, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems. By reducing our reliance on these sources and transitioning to cleaner, more sustainable alternatives, we can mitigate these effects and create a better future for generations to come.
The journey to a low CO2 world is not only a moral imperative but also an economic and social one. As technologies and innovations in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable practices continue to advance, the cost of transitioning to a low-carbon economy decreases, making it more accessible and viable for countries and individuals alike. Furthermore, the benefits of a low CO2 lifestyle extend beyond environmental protection, offering improvements in public health, economic growth, and social equity. With the right mindset and strategies, we can make significant strides in reducing our carbon footprint and embracing a more sustainable way of living.
Understanding CO2 Emissions

Sources of CO2 Emissions
The primary sources of CO2 emissions can be categorized into several sectors: - Energy: This includes the generation of electricity, heat, and power from fossil fuels. - Transportation: The burning of fossil fuels for vehicles, airplanes, and other forms of transportation. - Industry: The production of goods and services, including manufacturing and construction. - Agriculture: Practices such as deforestation and the use of synthetic fertilizers contribute to CO2 emissions. - Waste: The decomposition of waste in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas, but also contributes to CO2 emissions through the energy used in waste management.Benefits of Low CO2 Emissions

Strategies for Reduction
Implementing effective strategies to reduce CO2 emissions requires a comprehensive approach, involving governments, businesses, and individuals. Key strategies include: - **Transition to Renewable Energy**: Investing in solar, wind, and hydroelectric power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. - **Energy Efficiency**: Improving the efficiency of buildings, appliances, and vehicles to reduce energy consumption. - **Sustainable Land Use**: Practicing reforestation, sustainable agriculture, and reducing deforestation to sequester carbon dioxide. - **Carbon Capture and Storage**: Developing technologies to capture CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial processes and storing them underground.Technologies for a Low CO2 Future

Challenges and Opportunities
While there are numerous benefits and technologies available for reducing CO2 emissions, there are also challenges to overcome, including: - **Economic Barriers**: The high upfront costs of transitioning to low-carbon technologies and infrastructure. - **Technological Limitations**: The efficiency, scalability, and reliability of some low-carbon technologies are still evolving. - **Policy and Regulation**: The need for supportive policies and regulations to incentivize the adoption of low-carbon technologies and practices.Individual Actions for a Low CO2 Lifestyle

Community and Collective Action
While individual actions are crucial, collective action and community engagement can amplify the impact of low CO2 initiatives. This includes: - **Advocacy and Awareness**: Raising awareness about climate change and the importance of reducing CO2 emissions. - **Community Projects**: Participating in or initiating local projects focused on sustainability, such as community gardens or renewable energy cooperatives. - **Supporting Low-Carbon Policies**: Encouraging and supporting policymakers in implementing low-carbon policies and regulations.Global Cooperation for a Low CO2 Future
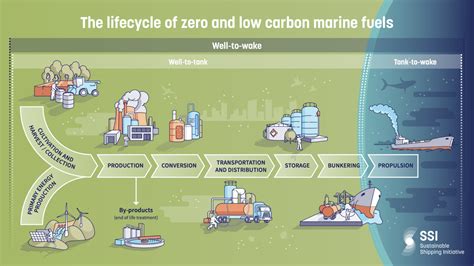
International Agreements and Initiatives
Some notable international agreements and initiatives focused on reducing CO2 emissions include: - **The Paris Agreement**: A global agreement to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. - **The Kyoto Protocol**: An international treaty that aimed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, especially CO2, based on country-specific targets. - **The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)**: While not exclusively focused on CO2 reduction, SDG 13 (Climate Action) emphasizes the need for urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.Conclusion and Next Steps

As we move forward, it is essential to stay informed, get involved, and support initiatives that promote low CO2 lifestyles and technologies. Whether through personal choices, community engagement, or professional endeavors, every action counts in the global effort to reduce CO2 emissions and protect our planet for future generations.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and ideas on how to achieve a low CO2 future. Your comments, questions, and stories can inspire others and contribute to a broader discussion on the importance of reducing carbon dioxide emissions. Together, we can make a difference and create a more sustainable world for all.
What are the main sources of CO2 emissions?
+The main sources of CO2 emissions include the energy sector (especially from the combustion of fossil fuels for electricity and heat), transportation, industry, agriculture, and waste management.
How can individuals contribute to reducing CO2 emissions?
+Individuals can contribute by making energy-efficient choices at home, using sustainable transportation, adopting a plant-based diet, reducing waste, and supporting policies and technologies that promote low-carbon living.
What role do governments and international agreements play in reducing CO2 emissions?
+Governments and international agreements are crucial for setting targets, implementing policies, and coordinating global efforts to reduce CO2 emissions. They provide the framework and incentives for transitioning to a low-carbon economy and can facilitate the sharing of technologies and best practices.
How can businesses and industries reduce their CO2 footprint?
+Businesses and industries can reduce their CO2 footprint by investing in renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, adopting sustainable practices in their operations and supply chains, and developing products and services that support low-carbon lifestyles.
What are some of the benefits of reducing CO2 emissions?
+The benefits include mitigating climate change, improving public health by reducing air pollution, stimulating economic growth through the development of low-carbon technologies and industries, and enhancing energy security by reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
