Intro
Discover 5 ways to detect kidney disease early, including symptoms, tests, and risk factors, to prevent kidney failure and promote renal health through timely diagnosis and treatment.
Kidney disease is a serious health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where the kidneys are damaged and cannot function properly, leading to waste buildup in the body. Early detection of kidney disease is crucial to prevent further damage and improve treatment outcomes. In this article, we will discuss the importance of detecting kidney disease and provide five ways to detect it.
Kidney disease can be caused by various factors, including diabetes, high blood pressure, family history, and age. It can also be caused by certain medications, such as pain relievers and antibiotics. If left untreated, kidney disease can lead to serious complications, including kidney failure, heart disease, and stroke. Therefore, it is essential to detect kidney disease early to prevent these complications.
Detecting kidney disease can be challenging, as it often has no symptoms in the early stages. However, there are several ways to detect kidney disease, including blood tests, urine tests, imaging tests, and physical exams. In this article, we will discuss five ways to detect kidney disease and provide tips on how to prevent it.
Understanding Kidney Disease
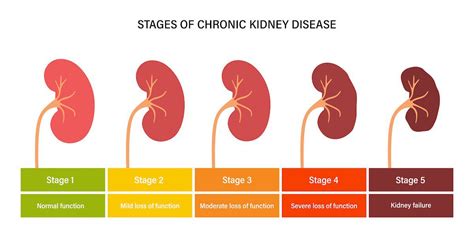
Causes and Risk Factors
Kidney disease can be caused by various factors, including diabetes, high blood pressure, family history, and age. People with diabetes are at higher risk of developing kidney disease, as high blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys. High blood pressure can also damage the kidneys, as it can cause the blood vessels in the kidneys to narrow and harden. Family history and age are also risk factors for kidney disease, as people with a family history of kidney disease are more likely to develop it, and the risk of kidney disease increases with age.5 Ways to Detect Kidney Disease
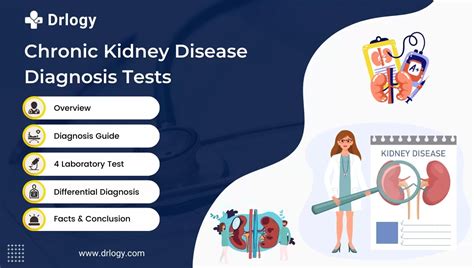
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can detect waste buildup in the blood, which can indicate kidney damage. The most common blood test used to detect kidney disease is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) test, which measures the level of waste in the blood.
- Urine Tests: Urine tests can detect protein and blood in the urine, which can indicate kidney damage. The most common urine test used to detect kidney disease is the protein-to-creatinine ratio test, which measures the level of protein in the urine.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound and CT scans, can detect kidney damage and disease. These tests can show the size and shape of the kidneys, as well as any blockages or damage to the kidneys.
- Physical Exams: Physical exams can detect signs of kidney disease, such as high blood pressure and swelling in the legs and feet. A physical exam can also detect any abnormalities in the kidneys, such as pain or tenderness.
- Medical History: A medical history can detect risk factors for kidney disease, such as diabetes and high blood pressure. A medical history can also detect any family history of kidney disease, which can increase the risk of developing the condition.
Tips for Prevention
There are several tips that can help prevent kidney disease, including: * Controlling blood sugar levels to prevent diabetes * Controlling blood pressure to prevent high blood pressure * Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce the risk of kidney disease * Avoiding certain medications, such as pain relievers and antibiotics, which can damage the kidneys * Getting regular check-ups to detect kidney disease earlyBenefits of Early Detection

Common Symptoms
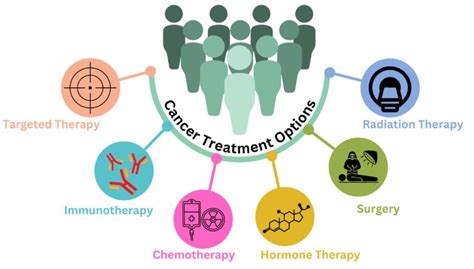
Kidney disease can cause several symptoms, including: * Fatigue and weakness * Swelling in the legs and feet * Pain in the back and sides * Blood in the urine * Protein in the urine * Frequent urination * Foamy urineTreatment Options
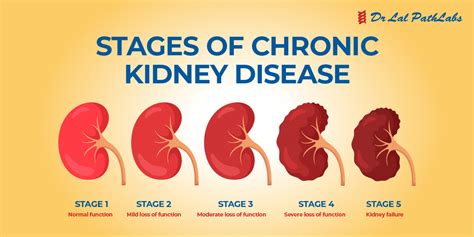
Complications of Kidney Disease
Kidney disease can cause several complications, including: * Kidney failure: Kidney failure is a condition where the kidneys are no longer able to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. * Heart disease: Kidney disease can increase the risk of heart disease, as it can cause high blood pressure and cholesterol levels. * Stroke: Kidney disease can increase the risk of stroke, as it can cause high blood pressure and cholesterol levels. * Anemia: Kidney disease can cause anemia, as it can reduce the production of red blood cells. * Bone disease: Kidney disease can cause bone disease, as it can reduce the production of vitamin D and calcium.Living with Kidney Disease
Coping with Kidney Disease
Coping with kidney disease can be emotionally challenging, but there are several ways to manage stress and anxiety. These include: * Seeking support: Seeking support from family and friends can help manage stress and anxiety. * Joining a support group: Joining a support group can provide a sense of community and help manage stress and anxiety. * Practicing relaxation techniques: Relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help manage stress and anxiety. * Seeking professional help: Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can help manage stress and anxiety.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with kidney disease in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with the most up-to-date and accurate information on kidney disease.
What are the symptoms of kidney disease?
+The symptoms of kidney disease include fatigue, swelling in the legs and feet, pain in the back and sides, blood in the urine, protein in the urine, frequent urination, and foamy urine.
How is kidney disease diagnosed?
+Kidney disease is diagnosed using blood tests, urine tests, imaging tests, physical exams, and medical history.
What are the treatment options for kidney disease?
+The treatment options for kidney disease include medications, lifestyle changes, dialysis, and kidney transplant.
Can kidney disease be prevented?
+Yes, kidney disease can be prevented by controlling blood sugar levels, controlling blood pressure, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding certain medications, and getting regular check-ups.
What is the prognosis for kidney disease?
+The prognosis for kidney disease depends on the stage of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. Early detection and treatment can improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
