Intro
Discover 5 ways to measure body fat, including hydrostatic weighing, skinfold calipers, and bioelectrical impedance analysis, to track progress and achieve weight loss goals with accurate body composition analysis and fat percentage measurement.
Measuring body fat is a crucial aspect of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, as excessive body fat can increase the risk of various health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. Accurate measurement of body fat helps individuals monitor their progress, set realistic goals, and make informed decisions about their diet and exercise routine. With the numerous methods available, it's essential to understand the different techniques, their advantages, and limitations. In this article, we will delve into the world of body fat measurement, exploring the various methods, their applications, and the importance of accurate measurement.
The importance of measuring body fat cannot be overstated, as it provides valuable insights into an individual's overall health and fitness level. Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat, can lead to a range of health issues, including insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease. By monitoring body fat levels, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of developing these conditions, improve their overall well-being, and enhance their quality of life. Furthermore, measuring body fat helps individuals track their progress, stay motivated, and make adjustments to their lifestyle as needed.
Measuring body fat is not just about aesthetics; it's about maintaining optimal health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. With the rising obesity rates and increasing awareness of the importance of healthy living, the demand for accurate and reliable body fat measurement methods has never been higher. Whether you're a fitness enthusiast, an athlete, or simply someone looking to improve your overall health, understanding the different methods of measuring body fat is essential. In the following sections, we will explore the various techniques, their advantages, and limitations, providing you with a comprehensive guide to measuring body fat.
Introduction to Body Fat Measurement
Hydrostatic Weighing

Advantages and Limitations of Hydrostatic Weighing
The advantages of hydrostatic weighing include its high accuracy and reliability. However, the limitations of this method include the need for specialized equipment, the requirement for individuals to be comfortable in the water, and the potential for errors if the individual is not fully submerged. Additionally, hydrostatic weighing can be time-consuming and may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions.Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
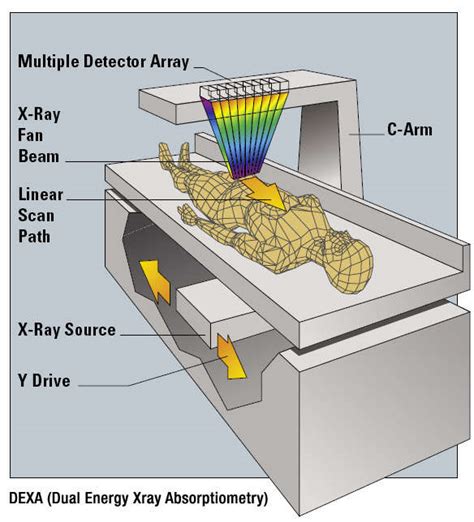
Advantages and Limitations of DXA
The advantages of DXA include its high accuracy, non-invasive nature, and ability to provide detailed information about body composition. However, the limitations of this method include the need for specialized equipment, the potential for radiation exposure, and the high cost of the procedure. Additionally, DXA may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as pacemakers or metal implants.Skifold Measurements

Advantages and Limitations of Skinfeld Measurements
The advantages of skinfold measurements include their relatively low cost, ease of use, and non-invasive nature. However, the limitations of this method include the potential for errors if the measurements are not taken correctly, the need for specialized training, and the limited accuracy of the results. Additionally, skinfold measurements may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as lymphedema or skin conditions.Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)

Advantages and Limitations of BIA
The advantages of BIA include its relatively low cost, ease of use, and non-invasive nature. However, the limitations of this method include the potential for errors if the measurements are not taken correctly, the need for specialized equipment, and the limited accuracy of the results. Additionally, BIA may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as pacemakers or metal implants.Air Displacement Plethysmography (ADP)

Advantages and Limitations of ADP
The advantages of ADP include its relatively high accuracy, non-invasive nature, and ease of use. However, the limitations of this method include the need for specialized equipment, the potential for errors if the measurements are not taken correctly, and the limited availability of the technique. Additionally, ADP may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as claustrophobia or respiratory problems.In conclusion, measuring body fat is a complex process that involves various techniques, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. By understanding the different methods of measuring body fat, individuals can make informed decisions about their lifestyle and take proactive steps to reduce their risk of chronic diseases. Whether you're a fitness enthusiast, an athlete, or simply someone looking to improve your overall health, accurate measurement of body fat is essential for achieving your goals and maintaining optimal health.
To stay up-to-date with the latest information on body fat measurement and to learn more about the different techniques, we invite you to comment below, share this article with your friends and family, or take specific actions to improve your overall health and well-being. Remember, accurate measurement of body fat is just the first step towards achieving your goals – it's what you do with the information that really matters.
What is the most accurate method of measuring body fat?
+Hydrostatic weighing is considered the most accurate method of measuring body fat, as it provides a direct measurement of body density.
What is the easiest method of measuring body fat?
+Skifold measurements are often considered the easiest method of measuring body fat, as they are relatively inexpensive and easy to perform.
What is the most common method of measuring body fat?
+Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) is one of the most common methods of measuring body fat, as it is relatively inexpensive and easy to use.
How often should I measure my body fat?
+The frequency of measuring body fat depends on your individual goals and needs. Generally, it's recommended to measure body fat every 4-6 weeks to track progress and make adjustments to your lifestyle as needed.
What are the risks associated with excessive body fat?
+Excessive body fat is associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases, including diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. Additionally, excessive body fat can lead to a range of other health problems, including joint pain, sleep apnea, and mental health issues.
