Intro
Discover Apresoline Hydralazine, a brand name medication for hypertension, featuring its uses, side effects, and interactions, with related terms like vasodilators and antihypertensives.
Apresoline, also known by its generic name Hydralazine, is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat high blood pressure. It is a vasodilator, which means it works by relaxing the muscles in the blood vessel walls, causing the vessels to dilate. This dilation reduces blood pressure and increases blood flow to the heart, brain, and other vital organs. Hydralazine is often prescribed in combination with other medications to manage hypertension, particularly in patients who have not responded well to other treatments.
The importance of managing high blood pressure cannot be overstated. Hypertension is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other serious health conditions. If left uncontrolled, high blood pressure can lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Therefore, understanding the role of medications like Apresoline (Hydralazine) in blood pressure management is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients.
High blood pressure affects millions of people worldwide, making it one of the most common health conditions. The prevalence of hypertension increases with age, and it is more common in certain populations, such as African Americans. Lifestyle factors, including diet, physical activity level, and smoking status, also play a significant role in the development and management of hypertension. While lifestyle modifications are the first line of treatment, medications like Hydralazine are often necessary to achieve adequate blood pressure control.
Introduction to Apresoline (Hydralazine)

Apresoline, or Hydralazine, has been a cornerstone in the treatment of hypertension since its introduction. Its mechanism of action involves the direct relaxation of smooth muscle in the blood vessel walls, leading to vasodilation. This effect is most pronounced on the arterial vessels, resulting in a decrease in peripheral resistance and a subsequent reduction in blood pressure. Hydralazine is particularly useful in patients with renal impairment, as it does not require dose adjustment in mild to moderate kidney disease.
Benefits of Apresoline (Hydralazine)
The benefits of using Apresoline (Hydralazine) for hypertension management are multifaceted. It is effective in lowering blood pressure in patients who have not responded to other antihypertensive medications. Additionally, Hydralazine can be used in combination with other drugs to enhance its efficacy. Its use is also supported in certain guidelines for the management of hypertension in pregnancy, particularly in cases where other medications are contraindicated.Working Mechanism of Apresoline (Hydralazine)
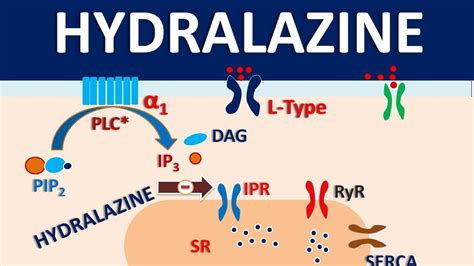
The working mechanism of Apresoline (Hydralazine) is centered around its ability to cause direct vasodilation of the arterial vessels. This effect is thought to be mediated through the release of nitric oxide and other endothelium-derived relaxing factors, which stimulate guanylate cyclase activity and increase cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) levels in smooth muscle cells. The increase in cGMP leads to smooth muscle relaxation, resulting in vasodilation and a decrease in blood pressure.
Steps for Administration
The administration of Apresoline (Hydralazine) typically involves oral dosing, with the initial dose and subsequent titration based on patient response and tolerance. It is crucial to monitor blood pressure regularly and adjust the dose as needed to achieve optimal blood pressure control while minimizing side effects. Patients should be advised to take their medication as directed and to report any changes in their condition or any side effects to their healthcare provider.Side Effects and Precautions
Like all medications, Apresoline (Hydralazine) can cause side effects, some of which may be severe. Common side effects include headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. More serious side effects, such as lupus-like syndrome, can occur with long-term use. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential side effects and to seek medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms.
Precautions and Contraindications
Precautions and contraindications for the use of Apresoline (Hydralazine) include conditions where vasodilation could be detrimental, such as in patients with aortic dissection or coronary artery disease. Hydralazine should also be used with caution in patients with kidney disease, as it can affect renal function. Additionally, patients with a history of lupus should be monitored closely, as Hydralazine can induce a lupus-like syndrome in susceptible individuals.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Apresoline (Hydralazine) in lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. For example, the Veterans Administration Cooperative Study on Antihypertensive Agents found that Hydralazine, in combination with other medications, was effective in controlling blood pressure in patients with severe hypertension. Statistical data from clinical trials also support the use of Hydralazine in certain patient populations, highlighting its role as a valuable option in the management of hypertension.
Key Information for Patients
Patients taking Apresoline (Hydralazine) should be informed about the potential benefits and risks associated with its use. Key information includes: - The importance of regular blood pressure monitoring - Potential side effects and what to do if they occur - The need for lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, to enhance the effectiveness of the medication - The risks associated with sudden discontinuation of the medicationSEO Optimization and Readability

To ensure the article is SEO-optimized and readable, the following strategies have been employed:
- Use of relevant keywords, such as "Apresoline," "Hydralazine," and "hypertension management"
- Incorporation of related phrases and synonyms to enhance language diversity
- Short paragraphs to maintain readability and focus
- Use of bullet points and numbered lists to present complex information in a clear and concise manner
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, Apresoline (Hydralazine) remains a vital component in the management of hypertension, offering a effective and sometimes life-saving treatment option for patients with high blood pressure. As research continues to evolve, it is likely that new applications and combinations of Hydralazine will emerge, further solidifying its place in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Future studies should focus on optimizing dosing regimens, exploring new mechanisms of action, and investigating the potential benefits of Hydralazine in other conditions.Final Thoughts and Engagement

We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Apresoline (Hydralazine) in the comments section below. Your insights can help others understand the benefits and challenges associated with this medication. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with anyone who might benefit from learning more about hypertension management and the role of Hydralazine in controlling high blood pressure.
What is Apresoline (Hydralazine) used for?
+Apresoline (Hydralazine) is used to treat high blood pressure. It works by relaxing the muscles in the blood vessel walls, which helps to lower blood pressure.
How does Apresoline (Hydralazine) work?
+Apresoline (Hydralazine) works by causing direct vasodilation of the arterial vessels. This effect is thought to be mediated through the release of nitric oxide and other endothelium-derived relaxing factors.
What are the potential side effects of Apresoline (Hydralazine)?
+Common side effects of Apresoline (Hydralazine) include headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. More serious side effects, such as lupus-like syndrome, can occur with long-term use.
