Intro
Identify broken wrist fracture symptoms, including pain, swelling, and limited mobility, and learn about treatment options for a speedy recovery from wrist injuries and fractures.
A broken wrist, also known as a wrist fracture, is a common injury that can occur due to various reasons such as falls, sports injuries, or accidents. The wrist is a complex joint that consists of multiple bones, and a fracture can occur in any of these bones. Understanding the symptoms of a broken wrist is crucial for prompt medical attention and proper treatment. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms of a broken wrist fracture, its causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention methods.
The importance of recognizing the symptoms of a broken wrist cannot be overstated. A delayed diagnosis or inadequate treatment can lead to complications such as nerve damage, arthritis, or chronic pain. Moreover, a broken wrist can significantly impact daily activities, making it essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms persist. The good news is that with proper treatment, most people can recover fully from a broken wrist and regain normal function.
A broken wrist can be caused by various factors, including falls, sports injuries, or accidents. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, can also increase the risk of a wrist fracture. In addition, certain activities such as gymnastics, football, or skiing can put individuals at a higher risk of sustaining a wrist injury. Recognizing the causes and risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures to avoid a broken wrist.
Types of Wrist Fractures
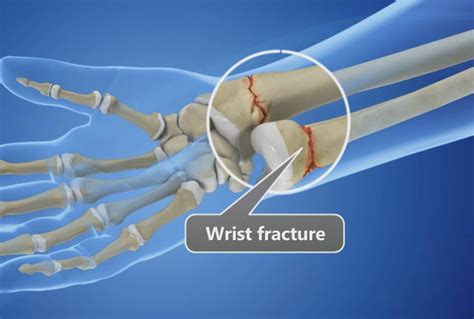
Causes of Wrist Fractures
The causes of wrist fractures can be broadly classified into two categories: traumatic and non-traumatic. Traumatic causes include falls, sports injuries, or accidents, while non-traumatic causes include osteoporosis, tumors, or infections. Understanding the underlying cause of a wrist fracture is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.Symptoms of a Broken Wrist

Diagnosis of Wrist Fractures
Diagnosing a wrist fracture typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans. The doctor may also perform a neurological examination to assess nerve function and check for any signs of nerve damage. In some cases, an MRI or bone scan may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions.Treatment Options for Wrist Fractures
Prevention of Wrist Fractures
Preventing wrist fractures requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, safety measures, and regular exercise. Individuals can reduce their risk of sustaining a wrist injury by wearing protective gear, maintaining strong bones through exercise and nutrition, and avoiding falls. Regular exercise can also help improve balance, flexibility, and overall mobility, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.Complications of Wrist Fractures
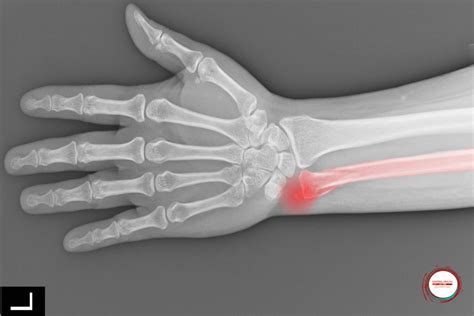
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery and rehabilitation from a wrist fracture can take several weeks to months, depending on the severity of the injury. A physical therapist can help individuals regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion through exercises and stretches. It is essential to follow a rehabilitation plan carefully to ensure proper healing and prevent complications.Conclusion and Next Steps

What are the common symptoms of a broken wrist?
+Pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility are common symptoms of a broken wrist. In some cases, individuals may experience numbness or tingling in the hand or fingers.
How is a wrist fracture diagnosed?
+A wrist fracture is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans.
What are the treatment options for a wrist fracture?
+Treatment options for a wrist fracture depend on the type and severity of the fracture and may include conservative treatment options such as immobilization, pain management, and physical therapy, or surgical intervention.
