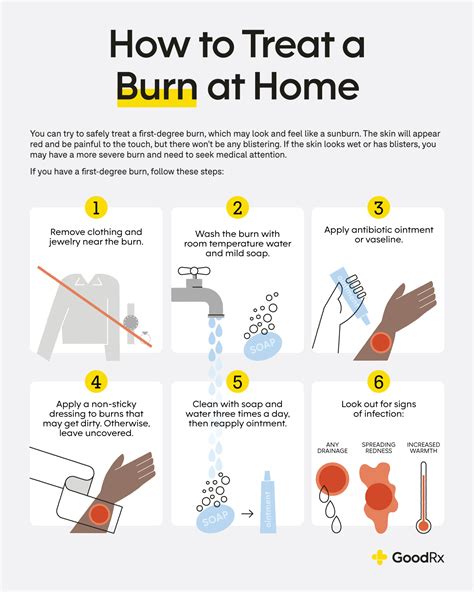
Intro
Learn burn wound care essentials, including treatment, dressing, and management, to promote healing and prevent infection, with tips on wound cleaning, debridement, and topical creams.
Burn wounds can be devastating, causing significant pain, discomfort, and potentially long-term damage to the skin and underlying tissues. Proper burn wound care is essential to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. In this article, we will delve into the world of burn wound care, exploring the importance of proper treatment, the different types of burns, and the various methods of care.
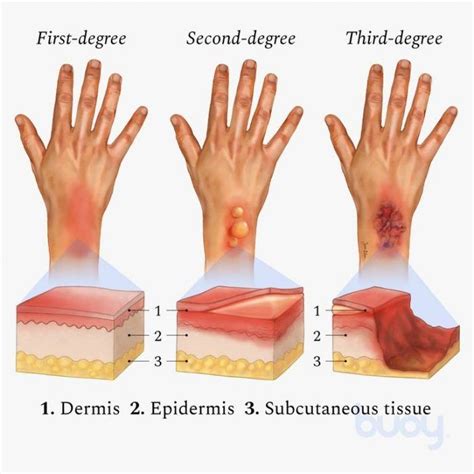
Burns can occur due to various reasons, including fires, scalds, electrical accidents, and chemical exposures. The severity of a burn depends on its depth, size, and location. Burn wounds can be categorized into four main types: first-degree, second-degree, third-degree, and fourth-degree. First-degree burns affect only the outermost layer of the skin, causing redness, swelling, and pain. Second-degree burns extend into the dermis, leading to blisters, redness, and swelling. Third-degree burns destroy both the epidermis and dermis, causing charred skin, and can be life-threatening. Fourth-degree burns are the most severe, extending into the muscle, tendon, or bone.
Understanding the different types of burns is crucial in providing effective care. Burn wound care involves a range of treatments, from simple wound dressing to complex surgical interventions. The primary goal of burn wound care is to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. This can be achieved through a combination of wound cleaning, dressing, and topical treatments. In addition, burn patients may require pain management, nutritional support, and psychological counseling to cope with the trauma and stress associated with their injuries.
Introduction to Burn Wound Care
Assessment and Diagnosis
The first step in burn wound care is assessment and diagnosis. This involves evaluating the patient's overall condition, including the size, depth, and location of the burn. The care team will also assess the patient's vital signs, including temperature, pulse, and blood pressure. The diagnosis of a burn wound is typically based on the patient's medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The care team may use various tools, including the Rule of Nines, to estimate the size of the burn.Types of Burn Wounds
Treatment Options
The treatment of burn wounds depends on the type and severity of the burn. First-degree burns can be treated with simple wound care, including cleaning, dressing, and topical treatments. Second-degree burns may require more complex treatments, including debridement, grafting, and surgical interventions. Third-degree burns typically require hospitalization and intensive care, including fluid resuscitation, pain management, and surgical interventions. Fourth-degree burns require immediate medical attention and may involve amputation or other complex surgical procedures.Wound Cleaning and Dressing
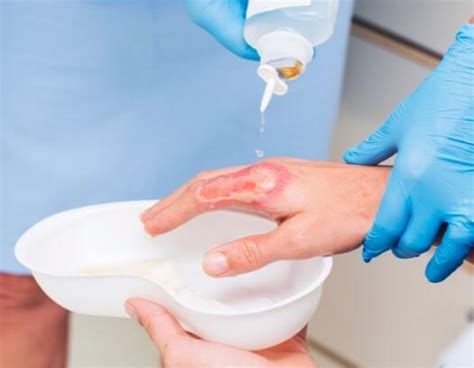
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are an essential component of burn wound care. These treatments can help promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. Common topical treatments for burn wounds include antibiotics, antiseptics, and growth factors. Antibiotics can help prevent infection, while antiseptics can help reduce the risk of infection. Growth factors can help promote healing by stimulating cell growth and tissue repair.Pain Management

Nutritional Support
Nutritional support is essential for burn patients, as they require a high-calorie diet to support healing and recovery. Burn patients may require nutritional supplements, including protein, vitamins, and minerals, to support tissue repair and healing. A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support the patient's overall health and well-being.Psychological Support

Rehabilitation and Reconstruction
Rehabilitation and reconstruction are essential components of burn wound care. The goal of rehabilitation is to help the patient regain their strength, mobility, and independence. This can be achieved through a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Reconstruction involves surgical interventions to repair or replace damaged tissues, promoting a functional and aesthetically pleasing outcome.Complications and Challenges
Future Directions
The future of burn wound care is exciting and promising. Advances in technology, including stem cell therapy, tissue engineering, and nanotechnology, are being explored to improve burn wound care. These advances have the potential to promote faster healing, reduce scarring, and improve functional outcomes.What are the most common causes of burn wounds?
+The most common causes of burn wounds include fires, scalds, electrical accidents, and chemical exposures.
How can I prevent burn wounds?
+Preventing burn wounds involves taking precautions, including being careful with fire, electricity, and chemicals, and following safety guidelines in the home and workplace.
What are the different types of burn wounds?
+There are four main types of burn wounds: first-degree, second-degree, third-degree, and fourth-degree, each with its unique characteristics and treatment requirements.
In conclusion, burn wound care is a complex and multidisciplinary field that requires a deep understanding of the underlying physiology and pathology of burn injuries. Effective burn wound care involves a team of healthcare professionals working together to assess the patient's condition, develop a treatment plan, and provide ongoing support and monitoring. By understanding the different types of burn wounds, treatment options, and complications, healthcare professionals can provide high-quality care that promotes healing, prevents infection, and minimizes scarring. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on burn wound care, and we hope that this article has provided you with valuable insights and information on this critical topic.
