Intro
Discover how C Peptide levels impact diabetes management, insulin function, and overall health, exploring the significance of C Peptide testing and its role in diagnosing and treating related conditions, including diabetic nephropathy and cardiovascular disease.
The importance of understanding C peptide levels cannot be overstated, particularly for individuals dealing with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. C peptide, a compound produced during the manufacture of insulin in the pancreas, serves as a vital marker for assessing the body's ability to produce insulin. Its level matters significantly in various aspects of health and disease management, making it a crucial point of discussion for healthcare providers and patients alike. The significance of C peptide levels extends beyond the realm of diabetes management, influencing overall health, treatment strategies, and the quality of life for those affected.
C peptide's role as an indicator of insulin production makes it an invaluable tool in the diagnosis and management of diabetes. By measuring C peptide levels, healthcare providers can differentiate between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, tailor treatment plans, and monitor the progression of the disease over time. Furthermore, understanding C peptide levels can help in the early detection of potential complications associated with diabetes, such as kidney damage or nerve damage, allowing for timely intervention. The implications of C peptide levels are multifaceted, touching on aspects of treatment efficacy, patient education, and the psychological impact of living with a chronic condition.
The relevance of C peptide levels in contemporary healthcare is underscored by ongoing research into its potential applications beyond diabetes management. Studies exploring the role of C peptide in vascular health, inflammation, and even neuroprotection suggest a broader significance of this molecule in human physiology. As our understanding of C peptide's functions expands, so does the potential for developing new therapeutic strategies that leverage its properties to improve outcomes for patients with a range of conditions. This evolving landscape of knowledge highlights the importance of staying informed about the latest developments and insights regarding C peptide levels.
Introduction to C Peptide
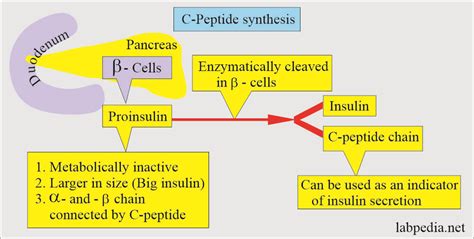
C peptide is a byproduct of insulin production, created when proinsulin, the precursor to insulin, is split into insulin and C peptide in the pancreas. Both insulin and C peptide are then released into the bloodstream in equal amounts. Since C peptide is not cleared by the liver like insulin, its levels can provide a more accurate picture of insulin production. This characteristic makes C peptide an essential marker in clinical settings for assessing beta-cell function and monitoring the effectiveness of treatments aimed at enhancing insulin secretion or sensitivity.
Diagnosis and Management of Diabetes
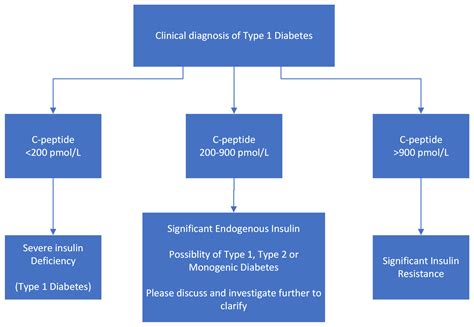
In the context of diabetes, measuring C peptide levels is critical for distinguishing between different forms of the disease. Type 1 diabetes, characterized by the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells, results in significantly reduced or undetectable C peptide levels. In contrast, type 2 diabetes, which often involves insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion, may present with variable C peptide levels, depending on the disease stage and the presence of beta-cell dysfunction. This distinction is vital for selecting the appropriate treatment strategy, as patients with type 1 diabetes require exogenous insulin therapy, whereas those with type 2 diabetes may initially be managed with lifestyle modifications or oral medications.
Role in Treatment Planning
The assessment of C peptide levels plays a pivotal role in tailoring treatment plans for individuals with diabetes. For instance, patients with residual beta-cell function, as indicated by detectable C peptide levels, may benefit from therapies aimed at preserving or enhancing this function, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists. Conversely, those with negligible C peptide levels may require more intensive insulin regimens. This personalized approach to diabetes management can lead to improved glycemic control, reduced risk of complications, and enhanced quality of life.C Peptide and Beyond Diabetes
The significance of C peptide extends beyond the management of diabetes, with implications for our understanding of metabolic health, cardiovascular disease, and even neurodegenerative conditions. Research has suggested that C peptide itself may have biological activities, including effects on vascular health and potential anti-inflammatory properties. These findings open up new avenues for exploring the therapeutic potential of C peptide or C peptide analogs in treating conditions characterized by endothelial dysfunction or chronic inflammation.
Potential Therapeutic Applications
The exploration of C peptide's therapeutic potential is an area of active research, with studies investigating its use in treating diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, and other complications associated with diabetes. Additionally, the role of C peptide in conditions not directly related to diabetes, such as certain cardiovascular diseases and possibly even neurodegenerative disorders, is being explored. As our understanding of C peptide's biological activities expands, so does the possibility of developing novel treatments that can improve outcomes for a broader range of patients.Monitoring and Maintenance

Regular monitoring of C peptide levels, along with other markers of glycemic control, is essential for the effective management of diabetes. This approach allows healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as needed, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate and effective care. Furthermore, ongoing education and support are critical for empowering patients to manage their condition proactively, making informed decisions about their health, and navigating the complexities of living with diabetes.
Importance of Patient Education
Patient education plays a vital role in diabetes management, with a focus on understanding C peptide levels being a key component. By grasping the significance of C peptide and how it relates to their condition, patients can better comprehend their treatment plans, recognize the importance of adherence to therapy, and adopt lifestyle modifications that support their overall health and well-being. This empowered approach to healthcare can lead to improved health outcomes, enhanced quality of life, and reduced healthcare costs over the long term.Future Directions

As research into C peptide and its applications continues to evolve, we can expect to see new developments in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diabetes and potentially other conditions. Advances in technology, including more sensitive and specific assays for measuring C peptide levels, will further enhance our ability to utilize this marker in clinical practice. Moreover, the exploration of C peptide's therapeutic potential may lead to innovative treatments that not only improve glycemic control but also address the underlying pathophysiology of related conditions.
Emerging Technologies and Therapies
Emerging technologies, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems and advanced insulin pump therapies, are transforming the landscape of diabetes management. These innovations, coupled with a deeper understanding of C peptide's role in health and disease, promise to revolutionize the way we approach diabetes care. Future therapies, potentially including C peptide-based treatments, may offer new hope for patients, providing more effective and personalized management strategies that can significantly improve health outcomes and quality of life.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, the significance of C peptide levels in managing diabetes and potentially other conditions cannot be overstated. As our understanding of this molecule and its roles in human health continues to grow, so does the potential for developing more effective, personalized treatment strategies. By staying informed about the latest research and advancements in C peptide-related science, individuals can better navigate their healthcare journey, making empowered decisions about their health and well-being.
We invite readers to share their thoughts, experiences, or questions regarding C peptide levels and their implications for health and disease management. Your engagement can help foster a community of individuals dedicated to advancing our understanding of this critical topic and improving outcomes for those affected by diabetes and related conditions. Share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and let's work together to promote awareness and education about the importance of C peptide levels in contemporary healthcare.
What is C peptide, and why is it important?
+C peptide is a molecule produced during insulin manufacture in the pancreas. It serves as a marker of insulin production and is crucial for diagnosing and managing diabetes, as well as understanding metabolic health and potential complications.
How do C peptide levels help in distinguishing between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
+C peptide levels can help differentiate between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is characterized by low or undetectable C peptide levels due to autoimmune destruction of beta cells, whereas type 2 diabetes may present with variable C peptide levels, reflecting the presence of residual beta-cell function.
What are the potential therapeutic applications of C peptide beyond diabetes management?
+Research suggests that C peptide may have biological activities with potential therapeutic implications, including effects on vascular health, anti-inflammatory properties, and possibly neuroprotection. These findings open up avenues for exploring C peptide's use in treating conditions like diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, and other complications associated with diabetes, as well as non-diabetes related conditions.
