Intro
Discover key facts about CRP, including its role in inflammation, heart disease, and cancer risk. Learn about C-reactive protein, its causes, and effects on overall health, and understand the importance of CRP levels and testing.
The importance of C-Reactive Protein (CRP) has been a topic of discussion in the medical community for several years. CRP is a protein that is produced by the liver in response to inflammation, and it has been linked to various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Understanding CRP and its role in the body is essential for maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases. In this article, we will explore five facts about CRP that you should know.
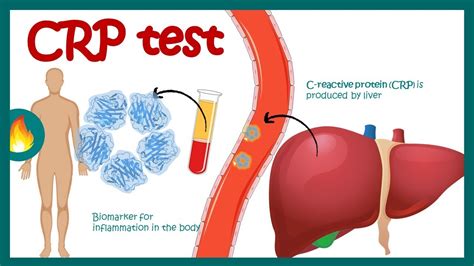
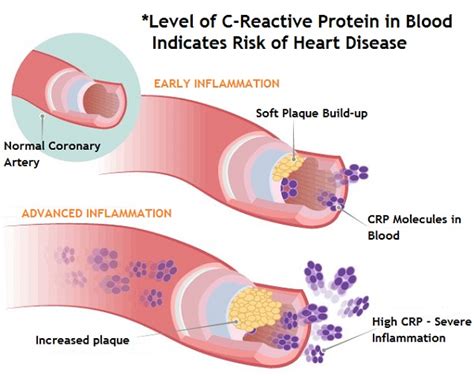
CRP is a widely used marker of inflammation in the body. It is produced by the liver in response to the presence of inflammatory cytokines, which are signaling molecules that promote inflammation. When CRP levels are elevated, it indicates that there is inflammation present in the body, which can be a sign of an underlying health condition. For example, high CRP levels have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
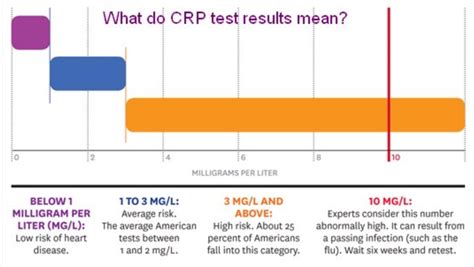
The measurement of CRP levels is a simple and non-invasive process. A blood test can be used to measure CRP levels, and the results can provide valuable information about the level of inflammation in the body. There are two types of CRP tests: high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) and standard CRP. The hs-CRP test is more sensitive and can detect smaller changes in CRP levels, making it a more accurate indicator of inflammation.
What is CRP and How is it Measured?
Factors that Affect CRP Levels
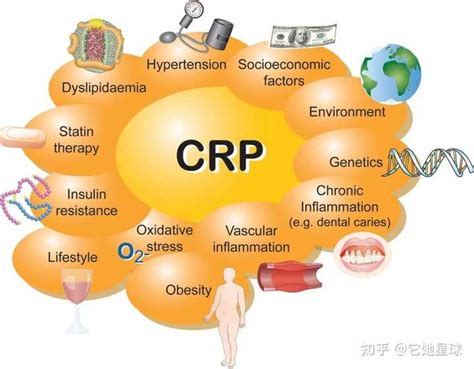
Several factors can affect CRP levels, including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), and lifestyle. For example, CRP levels tend to increase with age, and women tend to have higher CRP levels than men. Additionally, individuals with a high BMI or those who smoke or have a family history of cardiovascular disease may have higher CRP levels. Understanding these factors is essential for interpreting CRP test results and making informed decisions about health.The Role of CRP in Inflammation
Benefits of Reducing CRP Levels
Reducing CRP levels can have several benefits for overall health. For example, lowering CRP levels can help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of cancer. Additionally, reducing CRP levels can help to alleviate symptoms of chronic diseases, such as arthritis and lupus. There are several ways to reduce CRP levels, including lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, and medications, such as statins and anti-inflammatory agents.CRP and Cardiovascular Disease
Statins and CRP Reduction
Statins are a class of medications that are commonly used to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. They also have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce CRP levels. Several studies have shown that statins can reduce CRP levels by 30-50%, which can help to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, statins can help to reduce the risk of other chronic diseases, such as diabetes and cancer.CRP and Diabetes
Lifestyle Modifications for CRP Reduction
There are several lifestyle modifications that can help to reduce CRP levels. For example, a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to reduce inflammation and lower CRP levels. Regular exercise, such as walking or jogging, can also help to reduce CRP levels and improve overall health. Additionally, stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help to reduce CRP levels and improve mental health.CRP and Cancer
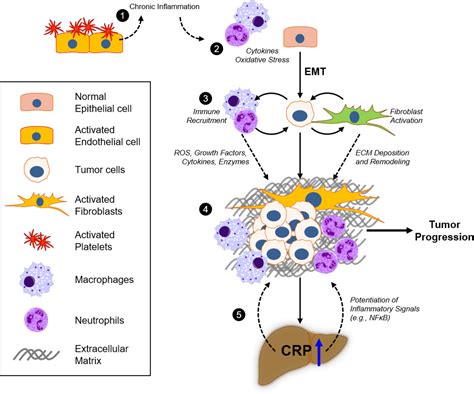
Benefits of CRP Testing
CRP testing can provide valuable information about the level of inflammation in the body. It can help to identify individuals who are at high risk of developing chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Additionally, CRP testing can help to monitor the effectiveness of treatments and lifestyle modifications. For example, a decrease in CRP levels can indicate that a treatment or lifestyle modification is effective in reducing inflammation and improving overall health.Conclusion and Future Directions
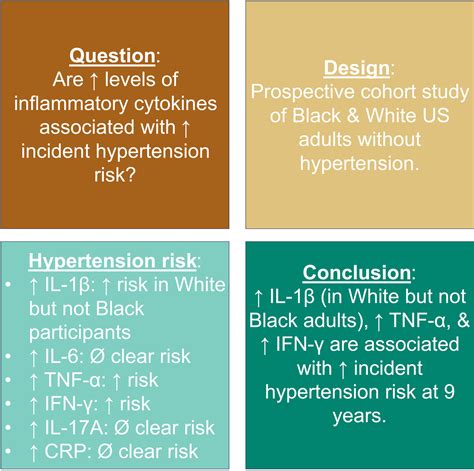
Final Thoughts
In final thoughts, CRP is an important marker of inflammation that can provide valuable information about the level of inflammation in the body. Understanding CRP and its role in inflammation is essential for maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases. By reducing CRP levels, individuals can lower their risk of developing chronic diseases and improve their overall health. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with CRP testing and reduction in the comments below.What is CRP and how is it measured?
+CRP is a protein that is produced by the liver in response to inflammation. It is measured in milligrams per liter (mg/L) of blood using a simple and non-invasive blood test.
What are the benefits of reducing CRP levels?
+Reducing CRP levels can help to lower the risk of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. It can also help to alleviate symptoms of chronic diseases and improve overall health.
How can I reduce my CRP levels?
+There are several ways to reduce CRP levels, including lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, and medications, such as statins and anti-inflammatory agents. Additionally, stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help to reduce CRP levels and improve mental health.
What is the normal range for CRP levels?
+The normal range for CRP is typically less than 3 mg/L, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test used.
Can CRP testing help to identify individuals who are at high risk of developing chronic diseases?
+Yes, CRP testing can help to identify individuals who are at high risk of developing chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Elevated CRP levels can indicate the presence of inflammation, which is a key factor in the development of these diseases.
