Intro
Discover the C Reactive Protein meaning, a crucial biomarker for inflammation, and learn how CRP tests diagnose conditions like arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and infection, using related terms like blood work, medical diagnosis, and health screening.
The C reactive protein, commonly referred to as CRP, is a protein that is produced by the liver in response to inflammation in the body. This protein is an acute-phase reactant, meaning its levels increase in response to inflammation, infection, and tissue damage. The C reactive protein test is a blood test that measures the level of CRP in the blood, which can help doctors diagnose and monitor various conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular disease.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system to injury or infection. When the body detects the presence of foreign substances, such as bacteria or viruses, it releases chemical signals that trigger an inflammatory response. This response involves the activation of immune cells, the release of chemical mediators, and the production of proteins like CRP. The C reactive protein plays a key role in the inflammatory response by binding to phosphocholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells and some bacteria, helping to clear them from the body.
The importance of CRP lies in its ability to serve as a biomarker for inflammation and infection. Elevated levels of CRP in the blood can indicate the presence of inflammation, which can be caused by a variety of conditions, including bacterial and viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease. By measuring CRP levels, doctors can diagnose and monitor these conditions, as well as assess the effectiveness of treatment.
C Reactive Protein Test
The C reactive protein test is a simple blood test that measures the level of CRP in the blood. The test is usually performed on a blood sample taken from a vein in the arm, and the results are typically available within a few hours. The test can be used to diagnose and monitor a variety of conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular disease. There are two types of CRP tests: a standard test that measures high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) and a high-sensitivity test that can detect even slightly elevated levels of CRP.
Interpreting CRP Test Results
The results of the CRP test are measured in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The normal range for CRP is typically less than 10 mg/L, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test used. Elevated CRP levels can indicate the presence of inflammation or infection, while very high levels can indicate a severe infection or a life-threatening condition such as sepsis.Causes of Elevated CRP
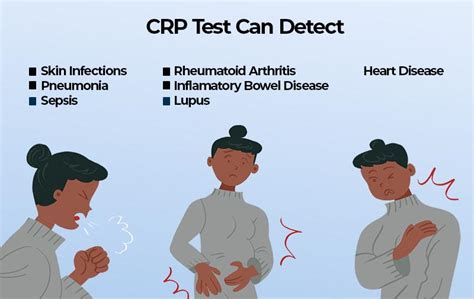
There are many potential causes of elevated CRP levels, including:
- Infections, such as pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis
- Inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Crohn's disease
- Cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease
- Cancer, including lymphoma, leukemia, and lung cancer
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Kidney disease, including nephrotic syndrome and kidney failure
- Autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and type 1 diabetes
Risk Factors for Elevated CRP
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of elevated CRP levels, including: * Age: CRP levels tend to increase with age * Obesity: Excess weight can lead to chronic inflammation and elevated CRP levels * Smoking: Smoking can cause inflammation and increase CRP levels * Family history: A family history of cardiovascular disease or other inflammatory conditions can increase the risk of elevated CRP levels * Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to chronic inflammation and elevated CRP levelsTreatment and Management
The treatment and management of elevated CRP levels depend on the underlying cause of the inflammation. In some cases, treatment may involve medications such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or immunosuppressants. In other cases, lifestyle changes such as weight loss, exercise, and stress reduction may be recommended. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment and to monitor CRP levels over time.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce CRP
There are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce CRP levels, including: * Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise * Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains * Getting regular exercise, such as walking or jogging, to reduce inflammation and improve overall health * Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke * Managing stress through techniques such as meditation or deep breathing * Getting enough sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per nightComplications and Prognosis
If left untreated, elevated CRP levels can lead to a range of complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and increased risk of infection. In some cases, elevated CRP levels can also indicate a poor prognosis for certain conditions, such as cancer or sepsis. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to manage CRP levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Monitoring CRP Levels
Regular monitoring of CRP levels can help healthcare providers track the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as needed. This can involve regular blood tests, as well as lifestyle changes and other interventions to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.Prevention

There are several steps that can be taken to prevent elevated CRP levels, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise
- Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Getting regular exercise, such as walking or jogging, to reduce inflammation and improve overall health
- Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke
- Managing stress through techniques such as meditation or deep breathing
- Getting enough sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per night
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection and treatment of elevated CRP levels can help reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to monitor CRP levels and make lifestyle changes as needed to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.What is the normal range for CRP levels?
+The normal range for CRP levels is typically less than 10 mg/L, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test used.
What are the potential causes of elevated CRP levels?
+Elevated CRP levels can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
How can I reduce my CRP levels?
+There are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce CRP levels, including maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
In conclusion, the C reactive protein is an important biomarker for inflammation and infection, and elevated levels can indicate a range of conditions, from infections to cardiovascular disease. By understanding the causes and risk factors for elevated CRP levels, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and improve their overall health. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with CRP levels in the comments below, and to share this article with anyone who may be interested in learning more about this important topic.
