Intro
Measure inflammation with C Reactive Protein Quant Test, detecting CRP levels to diagnose chronic conditions, cardiovascular risk, and infections, using precise laboratory testing and analysis for accurate results.
The C Reactive Protein Quant Test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood. CRP is a protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation, infection, or injury. Elevated CRP levels can indicate a range of health issues, from minor infections to chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and cancer. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the C Reactive Protein Quant Test, its working mechanisms, and the significance of CRP levels in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions.
The C Reactive Protein Quant Test is a highly sensitive and specific test that can detect even minor increases in CRP levels. This makes it an invaluable tool for early disease detection, allowing healthcare professionals to initiate timely interventions and prevent the progression of diseases. Moreover, the test is relatively simple and non-invasive, requiring only a blood sample from the patient. The results are typically available within a few hours, enabling prompt decision-making and treatment planning.
The importance of the C Reactive Protein Quant Test lies in its ability to provide valuable insights into the body's inflammatory response. Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for various diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. By monitoring CRP levels, healthcare professionals can identify individuals at high risk of developing these conditions and implement preventive measures. Additionally, the test can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments and adjust them as needed to achieve optimal outcomes.
C Reactive Protein Quant Test Working Mechanism
The C Reactive Protein Quant Test works by detecting the presence and concentration of CRP in the blood. The test uses a specialized assay that binds to CRP, allowing the measurement of its levels. The results are typically reported in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The test can be performed using various methods, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunoturbidimetry, and nephelometry.
Types of C Reactive Protein Quant Tests
There are two main types of C Reactive Protein Quant Tests: high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) and standard CRP tests. The hs-CRP test is more sensitive and can detect lower levels of CRP, making it suitable for assessing cardiovascular risk and monitoring chronic inflammation. The standard CRP test, on the other hand, is more commonly used to diagnose and monitor acute infections and inflammatory conditions.Interpretation of C Reactive Protein Quant Test Results
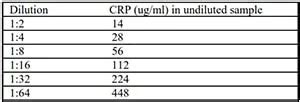
The interpretation of C Reactive Protein Quant Test results depends on the individual's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory findings. Generally, CRP levels are categorized into three ranges:
- Low risk: Less than 1 mg/L
- Average risk: 1-3 mg/L
- High risk: Greater than 3 mg/L
Elevated CRP levels can indicate a range of health issues, including:
- Infections, such as pneumonia or sepsis
- Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Cardiovascular disease, such as atherosclerosis or heart failure
- Cancer, such as lymphoma or lung cancer
Clinical Applications of C Reactive Protein Quant Test
The C Reactive Protein Quant Test has various clinical applications, including: * Diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus * Assessing cardiovascular risk and monitoring the effectiveness of treatments * Diagnosing and monitoring infections, such as pneumonia and sepsis * Monitoring the response to treatment in patients with cancerC Reactive Protein Quant Test and Cardiovascular Disease

The C Reactive Protein Quant Test is a valuable tool for assessing cardiovascular risk. Elevated CRP levels have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes. The test can be used to identify individuals at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease and to monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
Risk Factors for Elevated C Reactive Protein Levels
Several risk factors can contribute to elevated CRP levels, including: * Smoking * Obesity * Physical inactivity * High blood pressure * High cholesterol * DiabetesC Reactive Protein Quant Test and Cancer
The C Reactive Protein Quant Test can be used to diagnose and monitor cancer. Elevated CRP levels have been linked to various types of cancer, including lymphoma, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. The test can be used to assess the severity of cancer and to monitor the response to treatment.
Limitations of C Reactive Protein Quant Test
While the C Reactive Protein Quant Test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations. The test is not specific to any particular disease or condition, and elevated CRP levels can be caused by a range of factors, including infections, inflammatory conditions, and chronic diseases. Additionally, the test may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease.C Reactive Protein Quant Test and Inflammatory Conditions
The C Reactive Protein Quant Test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Elevated CRP levels can indicate the presence of inflammation, and the test can be used to assess the severity of the condition and to monitor the response to treatment.
Treatment Options for Elevated C Reactive Protein Levels
Treatment options for elevated CRP levels depend on the underlying cause of the elevation. For example: * Infections: Antibiotics or antiviral medications * Inflammatory conditions: Anti-inflammatory medications, such as corticosteroids or biologics * Cardiovascular disease: Statins, beta blockers, or other cardiovascular medications * Cancer: Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgeryWhat is the normal range for C Reactive Protein Quant Test results?
+The normal range for C Reactive Protein Quant Test results is typically less than 1 mg/L. However, the normal range may vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's medical history.
What are the risks of elevated C Reactive Protein levels?
+Elevated C Reactive Protein levels have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, as well as various types of cancer.
How often should I get a C Reactive Protein Quant Test?
+The frequency of C Reactive Protein Quant Tests depends on the individual's medical history and risk factors. Typically, the test is performed as part of a routine health checkup or to monitor the response to treatment.
In conclusion, the C Reactive Protein Quant Test is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide valuable insights into the body's inflammatory response. By understanding the working mechanisms, clinical applications, and limitations of the test, healthcare professionals can use it to diagnose and monitor various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and inflammatory conditions. If you have any questions or concerns about the C Reactive Protein Quant Test, we encourage you to consult with your healthcare provider or leave a comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of inflammation testing and the role of CRP in maintaining overall health.
