Intro
Understand the difference between calf strain and tear, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options for muscle pulls, leg injuries, and lower limb pain, to promote recovery and prevent further damage.
The calf muscle, located at the back of the lower leg, plays a crucial role in mobility, balance, and overall lower limb function. Injuries to this muscle, such as strains and tears, are common, particularly among athletes and individuals who engage in physical activities that involve running, jumping, or quick changes of direction. Understanding the difference between a calf strain and a tear is essential for proper diagnosis, treatment, and recovery. Both conditions can significantly impact an individual's ability to perform daily activities and participate in sports, making it vital to address them appropriately.
Calf strains and tears are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences in terms of their severity, symptoms, and treatment approaches. A strain refers to the overstretching or partial tearing of the muscle fibers, whereas a tear implies a more severe injury where the muscle fibers are completely ruptured. The distinction between these two conditions is critical because it guides the management and rehabilitation process, ultimately affecting the outcome and the time it takes for the individual to return to their normal activities.
The importance of distinguishing between calf strains and tears cannot be overstated. Proper diagnosis is key to implementing an effective treatment plan. Misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis can lead to prolonged recovery times, increased risk of further injury, and, in some cases, the development of chronic conditions that may require more invasive treatments. Moreover, understanding the differences between these conditions empowers individuals to seek appropriate medical attention and adhere to rehabilitation protocols that are tailored to their specific needs, thereby optimizing their recovery and minimizing the risk of complications.
Understanding Calf Strains
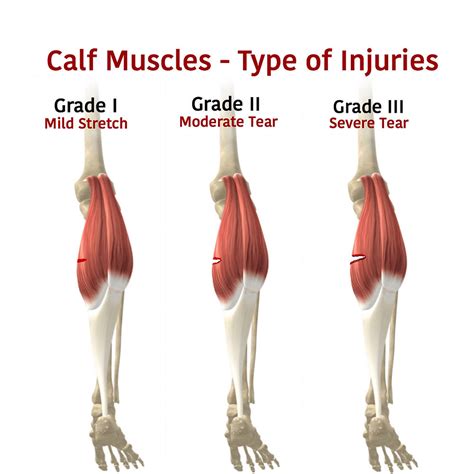
Calf strains are among the most common injuries affecting the lower leg. They occur when the calf muscles are stretched beyond their limit, leading to minor tears in the muscle fibers. This type of injury is prevalent in sports that involve sprinting, jumping, and sudden stops, as these actions can put significant stress on the calf muscles. The severity of a calf strain can vary, ranging from mild (grade 1), where the muscle is slightly stretched, to severe (grade 3), where the muscle is completely torn.
Symptoms of a calf strain may include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty walking. The pain is usually localized to the back of the lower leg and can be exacerbated by activities that stretch or contract the calf muscles. Treatment for calf strains typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with physical therapy to promote healing, maintain flexibility, and strengthen the affected muscle. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
Causes and Risk Factors of Calf Strains
The causes of calf strains can be multifactorial, including overuse, poor training techniques, inadequate warm-up, and muscle imbalances. Individuals who suddenly increase their physical activity level or change their exercise routine are at a higher risk of developing calf strains. Additionally, factors such as poor footwear, running on uneven surfaces, and previous injuries to the lower leg can also contribute to the risk of sustaining a calf strain.Understanding Calf Tears

A calf tear, on the other hand, is a more severe condition where there is a complete rupture of the muscle fibers. This type of injury can result from a sudden, forceful contraction of the calf muscles or from a direct blow to the muscle. Calf tears are less common than strains but can have a significant impact on an individual's mobility and quality of life.
The symptoms of a calf tear are more pronounced than those of a strain and may include a sudden, severe pain in the calf, significant swelling, bruising, and an inability to stand on tiptoes or walk without pain. Diagnosis often involves a combination of physical examination and imaging studies, such as ultrasound or MRI, to confirm the extent of the injury.
Treatment for a calf tear depends on the severity of the injury. Mild tears may be managed conservatively with rest, physical therapy, and bracing, while more severe tears may require surgical intervention to repair the damaged muscle. Rehabilitation after a calf tear is critical to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the affected muscle, and it typically involves a gradual progression of exercises and activities tailored to the individual's healing process.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from both calf strains and tears requires a comprehensive approach that includes rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to activity. The rehabilitation process is designed to promote healing, prevent further injury, and restore full function to the affected muscle. This may involve a series of exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and proprioception (awareness of the position and movement of the body), as well as modifications to training and activity levels to reduce the risk of re-injury.Prevention Strategies

Preventing calf strains and tears involves a combination of proper training techniques, warm-up routines, and equipment. Individuals can reduce their risk by incorporating exercises that strengthen the calf muscles, improving flexibility through stretching, and gradually increasing their activity level to avoid sudden spikes in physical demand. Additionally, wearing appropriate footwear and using orthotics when necessary can help reduce the stress on the calf muscles during activities.
Nutrition and Recovery
Nutrition plays a crucial role in the recovery from calf strains and tears. A diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals is essential for muscle repair and healing. Adequate hydration and the consumption of foods that reduce inflammation, such as those high in omega-3 fatty acids, can also support the recovery process. Furthermore, avoiding nutritional deficiencies, particularly in vitamin D and calcium, which are crucial for muscle function, can help prevent future injuries.Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, while both calf strains and tears are significant injuries, understanding their differences is key to effective management and rehabilitation. By recognizing the symptoms, causes, and appropriate treatments for these conditions, individuals can take proactive steps towards recovery and prevention. Future research directions may include the development of more effective rehabilitation protocols, the exploration of nutritional interventions to enhance recovery, and the investigation of innovative technologies to prevent and diagnose calf injuries more accurately.
As individuals become more aware of the importance of proper diagnosis and treatment, the demand for specialized care and preventive strategies is likely to increase. This underscores the need for continued education and awareness about calf strains and tears, not only among athletes and sports enthusiasts but also within the broader community. By fostering a deeper understanding of these conditions, we can work towards reducing their incidence and promoting healthier, more active lifestyles for all.
Final Thoughts

In final thoughts, the distinction between calf strains and tears is not merely semantic; it has profound implications for how these injuries are managed and treated. Whether you are an athlete seeking to optimize your performance, an individual looking to maintain an active lifestyle, or simply someone interested in understanding more about muscle injuries, recognizing the differences between these conditions is a crucial step towards achieving your goals. By embracing this knowledge and applying it in a practical, real-world context, we can all contribute to a culture of health, wellness, and resilience.
Call to Action

We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about calf strains and tears in the comments below. Your input is invaluable in fostering a community that values knowledge, support, and mutual encouragement. Whether you have personal experience with these injuries, are seeking advice on prevention, or simply wish to learn more, your participation is welcome. Let us work together to create a comprehensive resource that benefits everyone, from the casual reader to the dedicated athlete.
What is the main difference between a calf strain and a tear?
+A calf strain involves the overstretching or partial tearing of the muscle fibers, whereas a calf tear refers to a complete rupture of the muscle fibers.
How can I prevent calf strains and tears?
+Prevention strategies include proper training techniques, warm-up routines, wearing appropriate footwear, and gradually increasing activity levels to avoid sudden spikes in physical demand.
What is the typical recovery time for a calf strain versus a tear?
+The recovery time for a calf strain can range from a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on the severity. For a calf tear, the recovery time can be significantly longer, often requiring several months of rehabilitation and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
